Subsections of tech docs
MCP4kR2
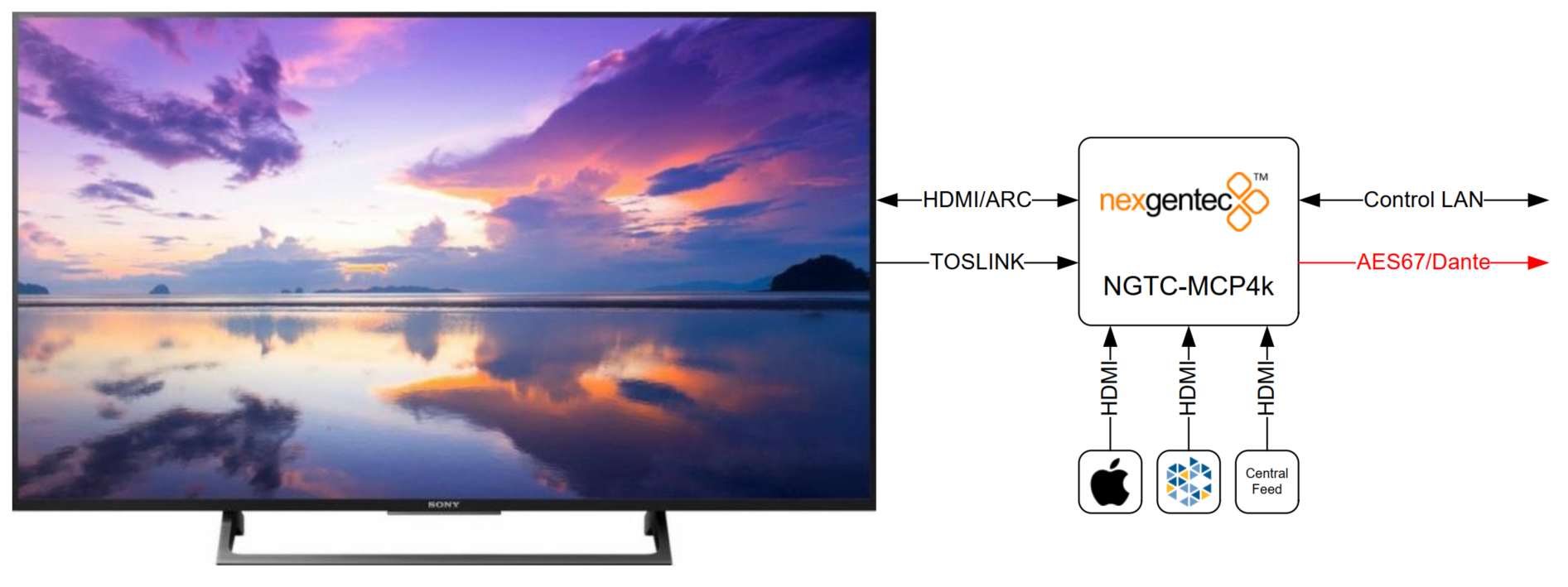
The NGTC-MCP4kR2 is an AES67 enabled multichannel audio processor for the nexgentec™ audio distribution solution.
Common Features
- Decoding of all common digital audio formats, up to 8 channels
- Outputs decoded channels on AES67 for audio processing by the NGTC digital signal processor or any AES67 enabled device.
- Can be controller by any 3rd party control systems via the Control API.
- Powered by a POE on the AES67 port.
- Web UI on the AES67 interface for AES67 related settings
- Control network port featuring the configuration web UI as well as the Control API.
Hardware Revision B (MCP4kR2B) addition Features
- Ability to receive of a 2 channel AES audio stream that can be upmixed with ProLogic or DTS Neo.
Subsections of MCP4kR2
Application Note
Hardware
The NGTC-MCP4kR2 is an AES67 enabled multichannel audio processor for the Genesis TechnologiesTM audio distribution solution. It is capable of decoding all common digital audio formats, delivering up to 8 AES67 channels of audio for processing by the NGTC digital signal processors. It can be easily interfaced with 3rd party control systems via the control network port. The small form factor makes it very flexible in its application.
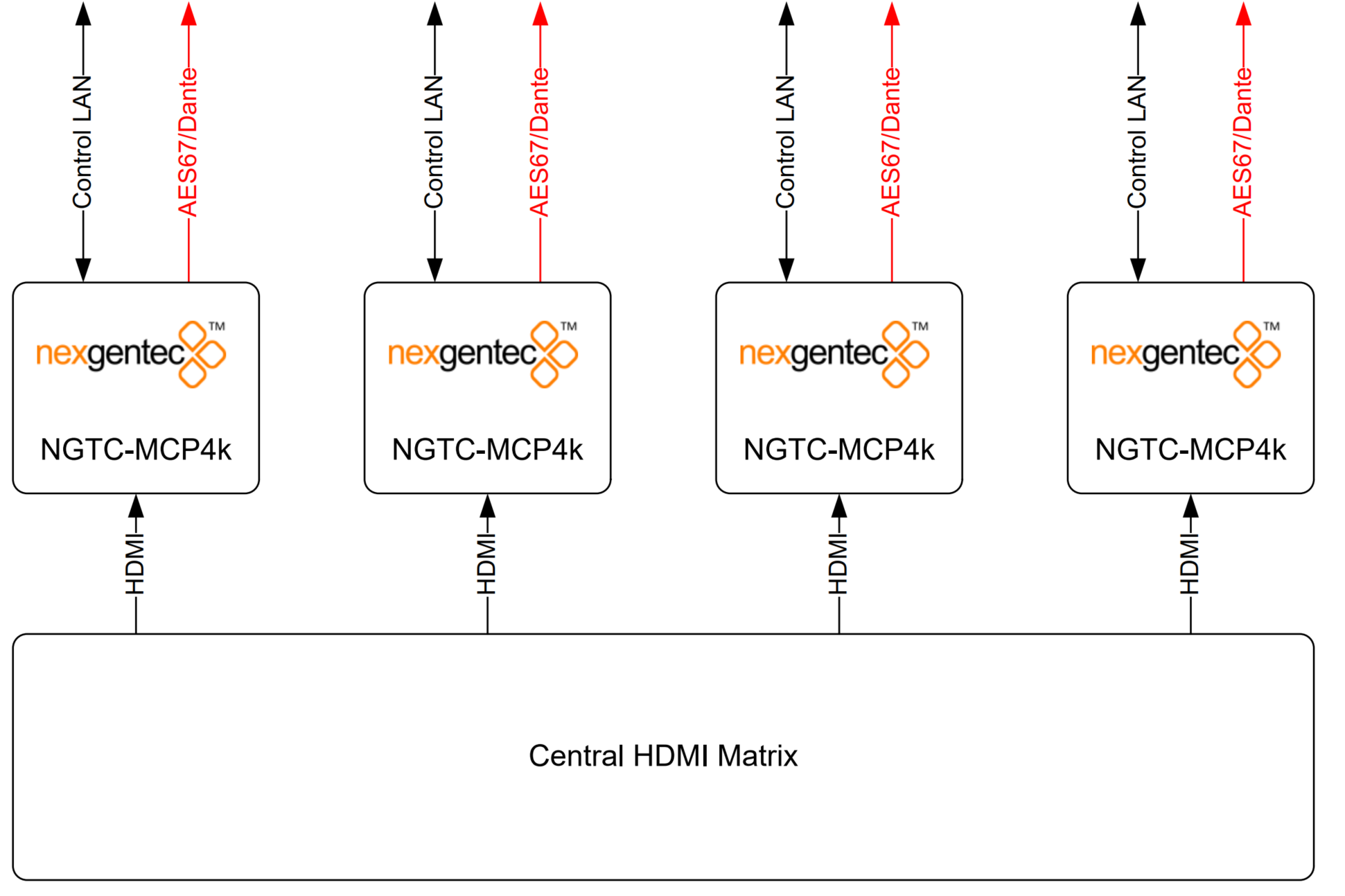
Application 1 – In Room, Zone assigned
The MCP4kR2 audio processor will be placed in the zone. It will accept local sources, central feed and the audio return from the TV (ARC,TOSLINK). The unit will decode, post process and sent out 8 discrete channels via AES67 to the audio network. The bass management, time alignment and channel mapping will be done in the DSP’s for maximum flexibility and performance. To have in the master zone a full 7.1 system while the master bath and dressing may run 2.0 or 1.0 no more an issue. The NGTC DSP super modules by nexgentecTM enable efficient design and deployment of NGTC AVOIP systems, featuring the highest levels of functionality and performance.
Application 2 – In Rack, Zone assigned
The MCP4kR2 audio processor will be placed in the rack and does accept the feed from the central matrix. Each zone has its own MCP. The unit will decode, post process and sent out 8 discrete channels via AES67 to the audio network. The bass management, time alignment and channel mapping will be done in the DSP’s for maximum flexibility and performance. To have in the master zone a full 7.1 system while the master bath and dressing may run 2.0 or 1.0 no more an issue. The NGTC DSP super modules by nexgentecTM enable efficient design and deployment of NGTC AVOIP systems, featuring the highest levels of functionality and performance.
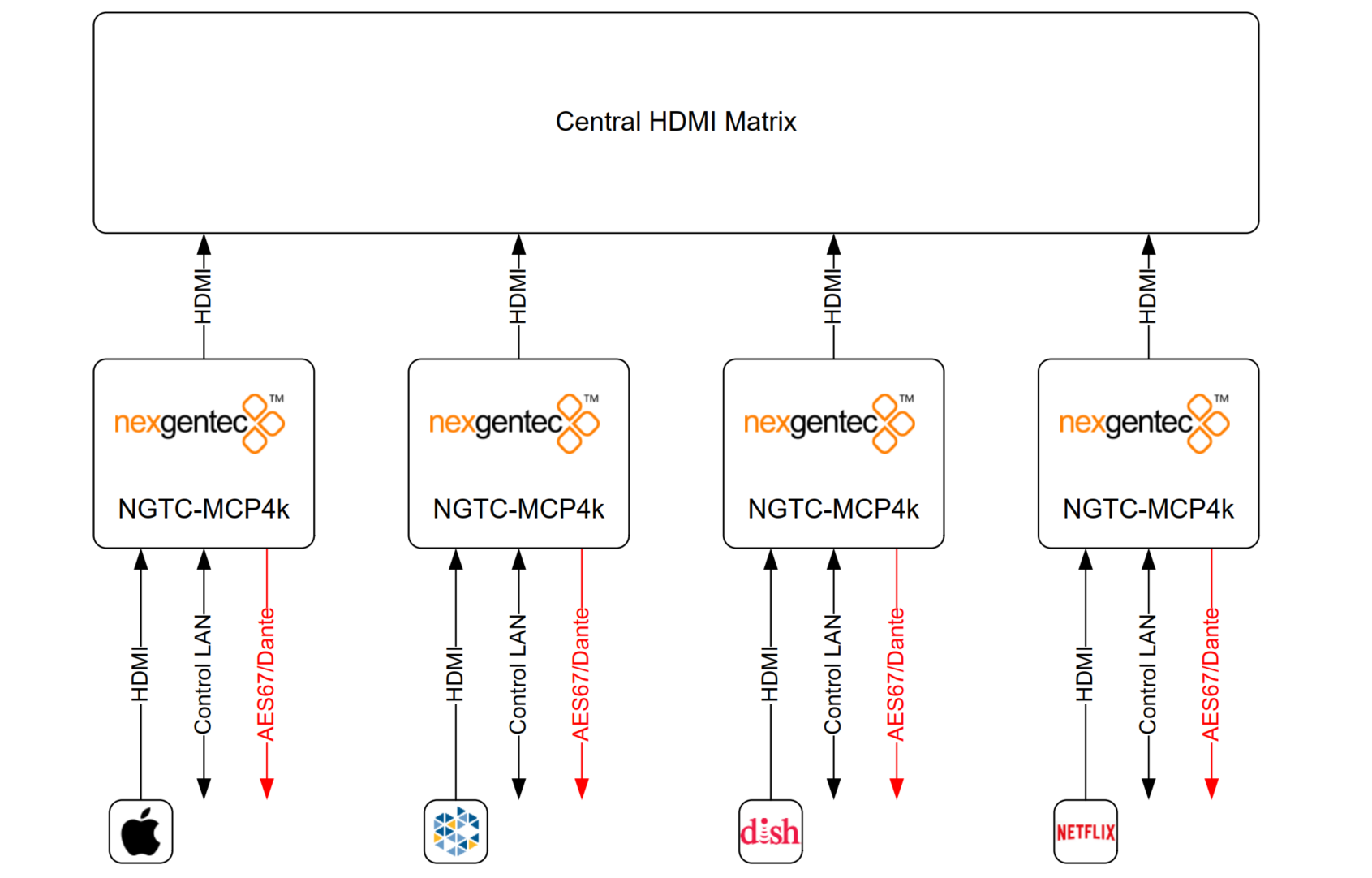
Application 3 – In Rack, Source assigned
The MCP4kR2 audio processor will be placed in the rack, connected to each source and the output of the processor will run into the central matrix. Audio and Video will be separated from the beginning. The MCP4k will decode, post process and sent out 8 discrete channels via AES67 to the audio network. The bass management, time alignment and channel mapping will be done in the DSP’s for maximum flexibility and performance. To have in the master zone a full 7.1 system while the master bath and dressing may run 2.0 or 1.0 no more an issue. The NGTC DSP super modules by nexgentecTM enable efficient design and deployment of NGTC AVOIP systems, featuring the highest levels of functionality and performance.
Installation
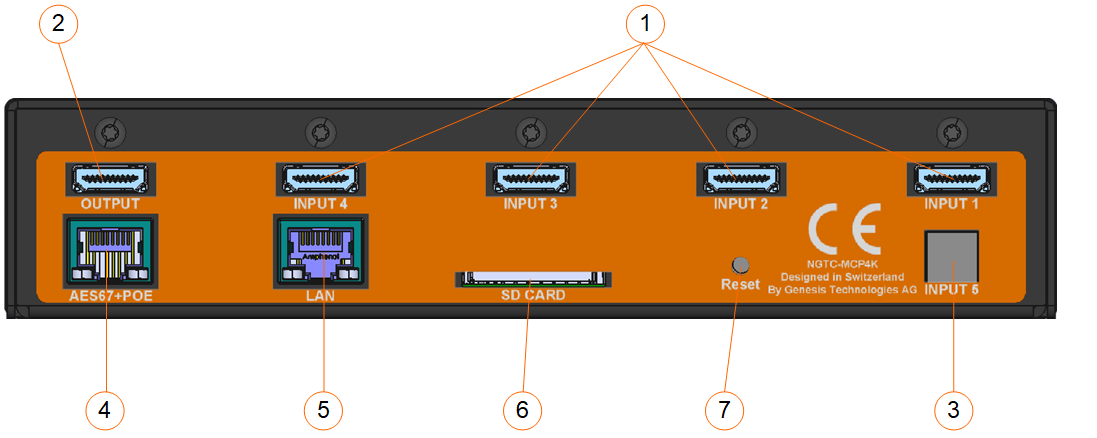
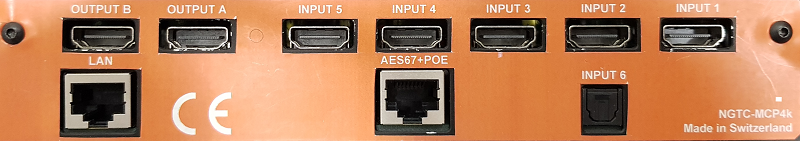
1.) HDMI inputs
2.) HDMI output
3.) Toslink digital input
4.) AES67 network interface (POE) – please use UTP cabling
5.) Control network interface – please use UTP cabling
6.) Service interface, not for use
7.) Reset button
All connections to the NGTC-MCP4kR2 should be made before power is applied
• Attach any multimedia sources that will be used, to the inputs
• Attach the LAN network port to the control network switch, using an UTP CAT-5 cable
• Attach the AES67 network port to the AES67/Dante POE network switch, using an UTP CAT-5 cable.
To reset the control network address (IP) long press (5s) the reset button on the back
Configuration
Setup interoperability between MCP4kR2 and Dante devices
AES67 interoperability settings are required for every Dante device that should receive a AES67 stream
To enable your Dante devices to receive an AES67 stream, AES67 interoperability must be enabled. This is done by using Audinate’s Dante Controller, which can be obtained from the Audinate website or any other manufacturer specific software tool.
In Dante controller all your Dante devices that are connected to the network will show up automatically.
- Start the Dante Controller Software and wait for it to be synchronized with the network
- Select the “device info” tab in the software
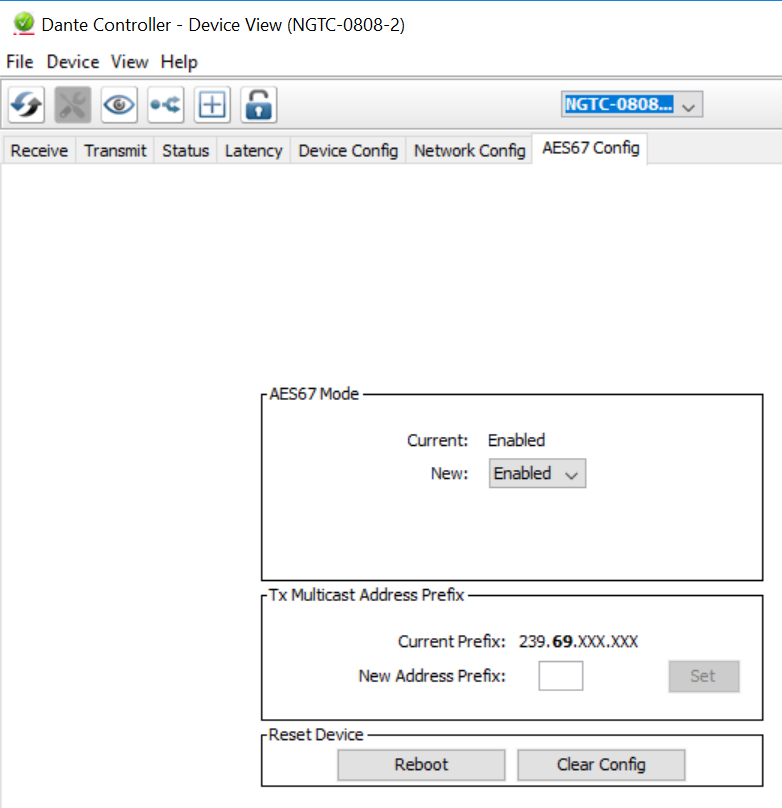
- Double click on the DSP you would like to configure for AES67, a new window will open
- Select the “AES67 config” tab
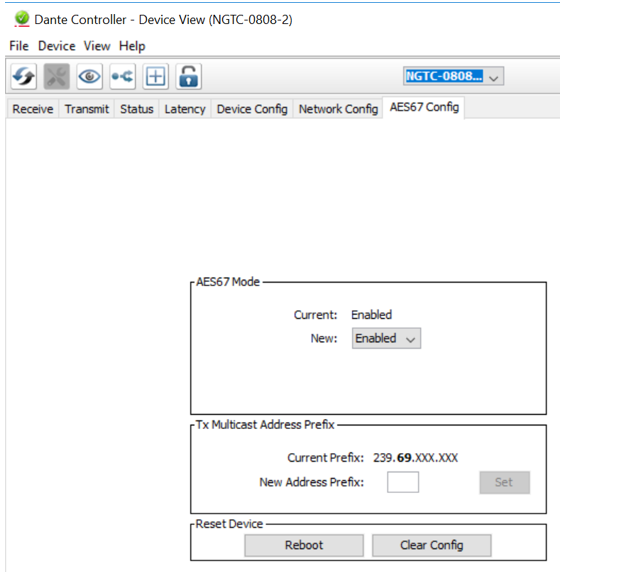
- Enable AES67 mode and make a note of the Tx multicast prefix. You will need this number later, even if you are not using the DSP as a transmitter. This must be the same for all DSP’s that are ready for AES67.
- Reboot the Dante device
- This needs to be done with every Dante device that will receive an AES67 stream
Subsections of Configuration
Control Network Setup
Control Network Address Setup
The setup of the control network of the MCP4kR2 will be done via it’s Web UI. It is self-explaining
By default the interface is set to DHCP
It is visible on the front display of the unit
Please make sure your computer network address is in the same network range to access the setup pages
Refer to the MAC address if multiple MCP’s are in the network to identify the right unit. The MAC address is also printed on each units top cover
To reset the control network address (IP) long press (5s) the reset button on the back
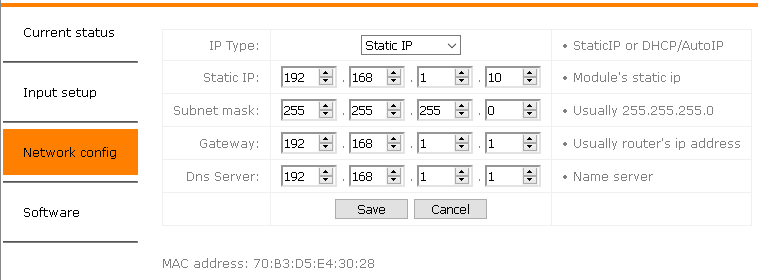
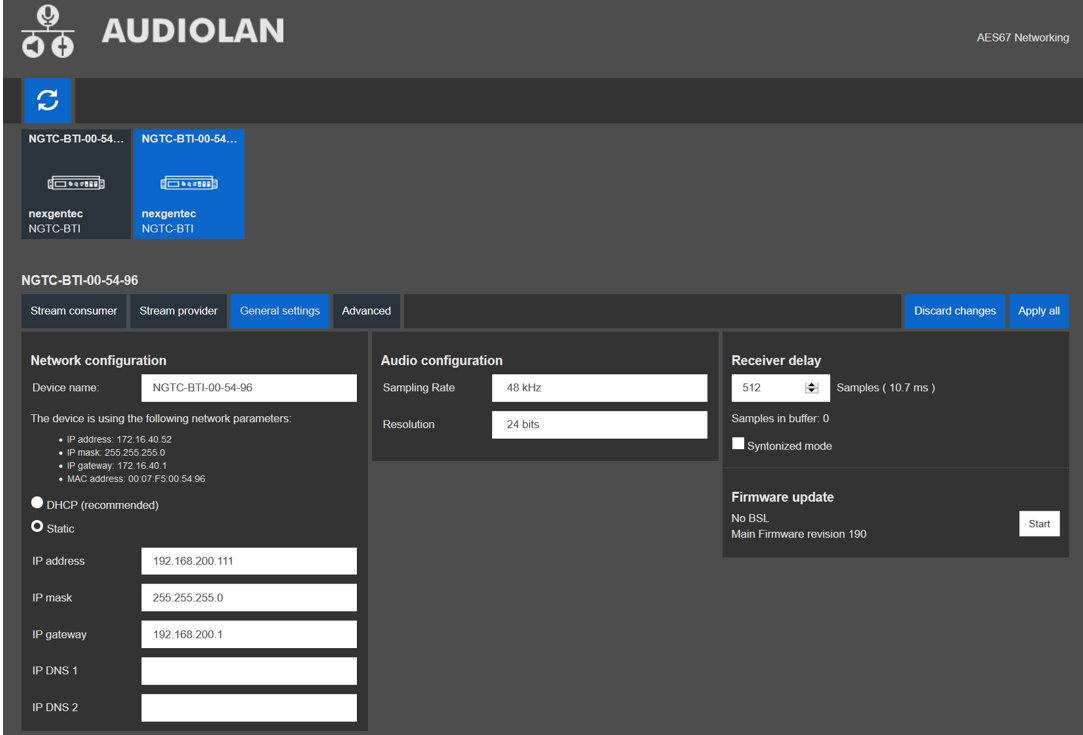
AES67 Network Setup (Audiolan)
AES67 Network Address Setup
There are two methods to configure AES67, depending on the AES67 daughter board in the MCP4KR2. Refer to the following instructions to configure it with the AudioGrid controller, especially if the setup provided below does not work for you.
To configure the AES67 network address use the built in Audiolan web UI. Your PC needs to be connected to the AES67 network and have its addressing set in the same IP range.
By default the AES67 network interface is set to the static IP address (192.168.4.233)
To avoid an IP conflicts, connect one device after another and change each units IP to a different one
Avoid any special characters and spaces in the device name
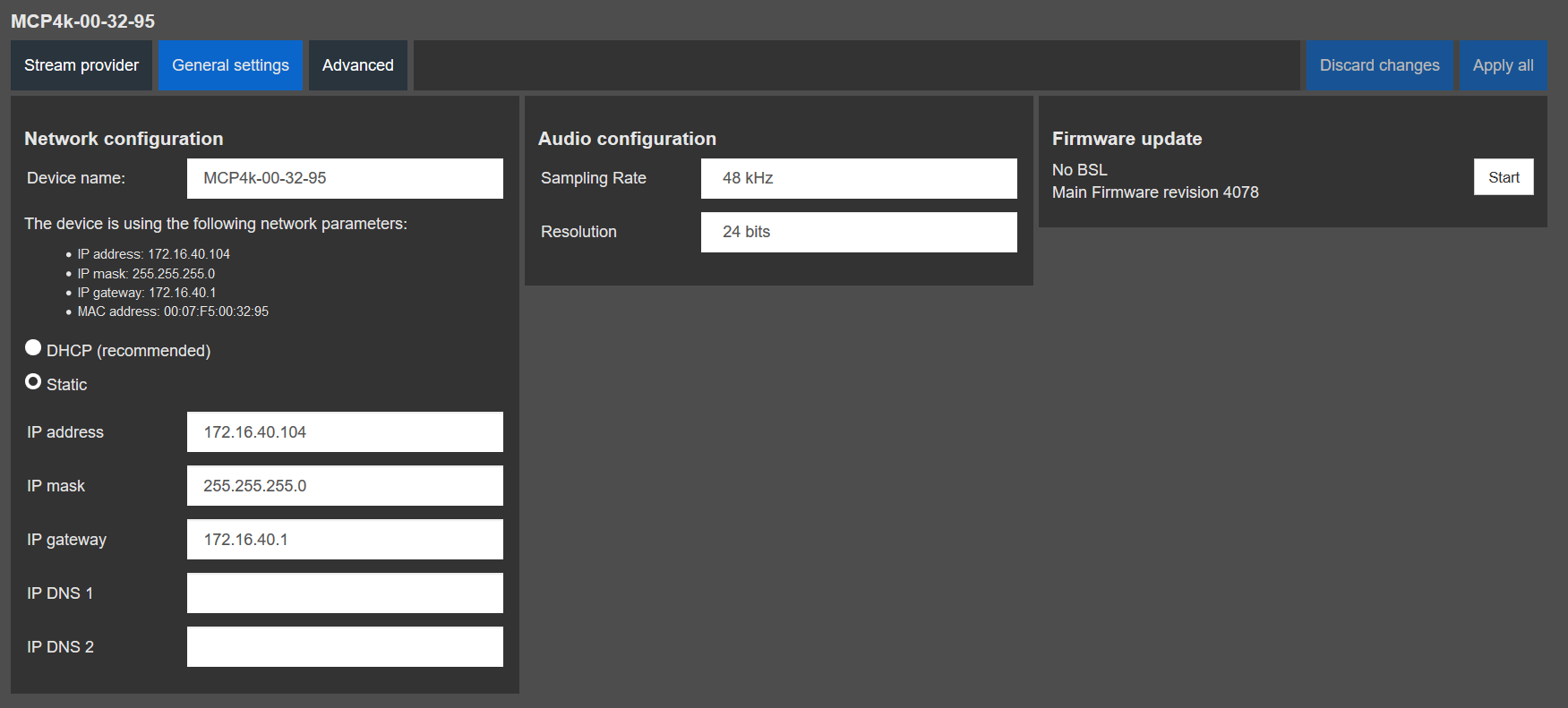
- Open a browser and enter the devices AES67 network address in the address bar, press enter
- Select the “General settings” tab in the web UI to change the devices IP address
- The NGTC-MCP4kR2 should have an IP and Subnet address in the same range as the Dante devices
- Apply all settings and reboot the device
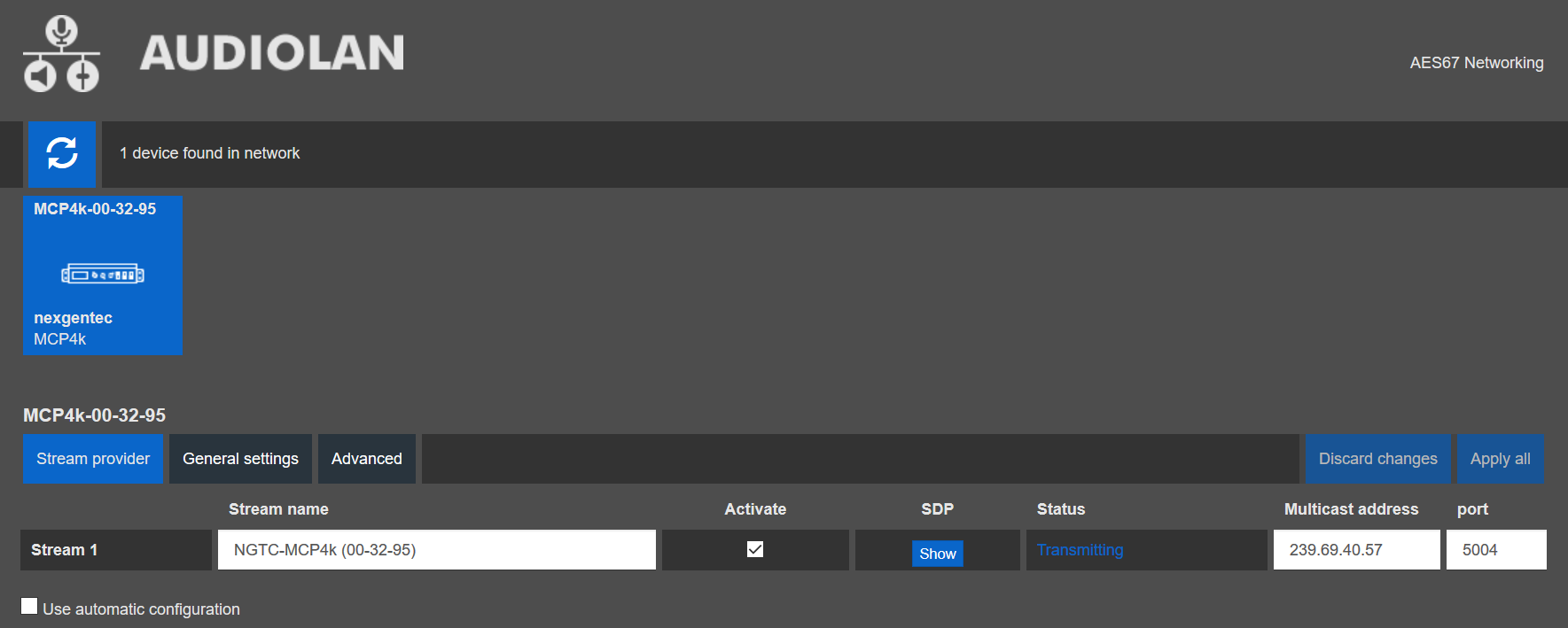
AES67 Stream Address Setup
The AES67 stream of each device needs to be configured to be received by the Dante/AES67 devices
Avoid any special characters and spaces in the stream name
- Open a browser and enter the devices AES67 network address in the address bar, press enter
- Select the “Stream provider” tab in the web UI and uncheck the “Use automatic configuration” checkbox
- Make sure that the first 2 octets matches the Multicast Address Prefix given in the Dante Controller (239.69.xxx.xxx in the example below). Set the last 2 octets to unique values. always avoid duplicated IP addresses. Best practice is to set them to the same value as the last 2 octets of the AES67 network address
- Make sure that the “Activate” checkbox for the stream is checked
- Select the “Advanced” tab and ensure that the SAP browsing is enabled
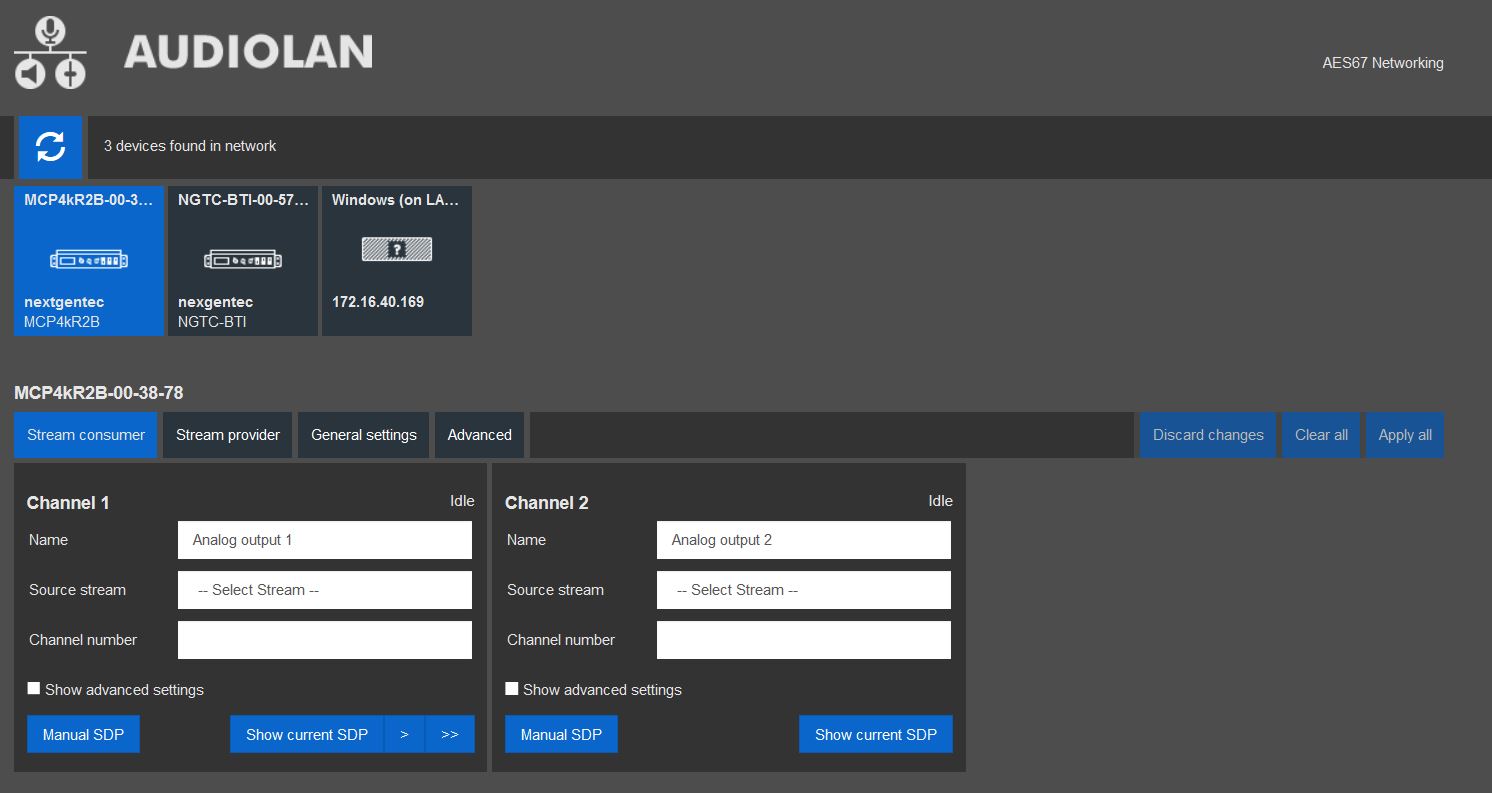
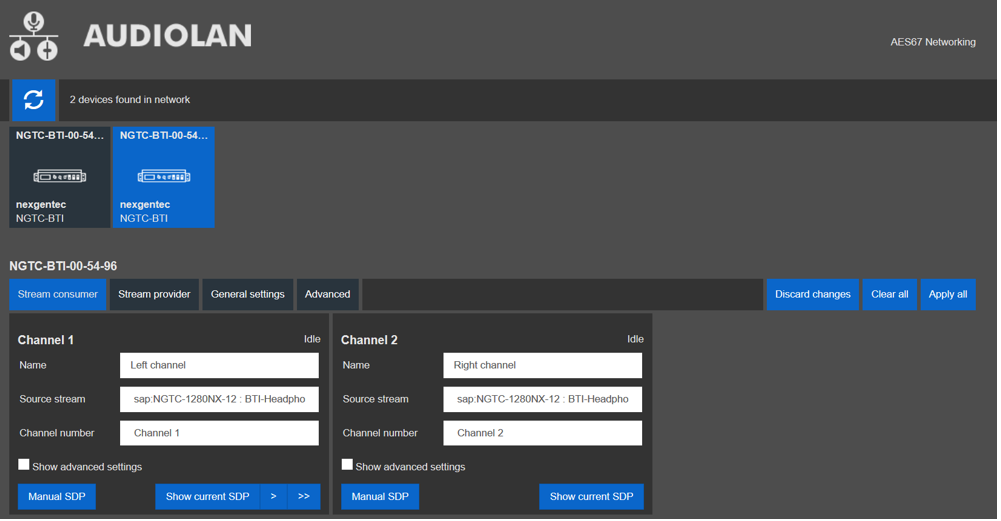
AES67 Receiving Stream Setup*
- Open a browser and enter the devices AES67 network address in the address bar, press enter
- Select the “Stream consumer” tab in the web UI and insert the AES Channel information for Channel 1 and Channel 2.
*Hardware revision B (MCP4kR2B) only
AES67 Network Setup (AudioGrid)
There are two methods to configure AES67, depending on the AES67 daughter board in the MCP4KR2. Refer to the following instructions to configure it using the Audiolan Integrated website, especially if the setup provided below does not work for you.
To configure the AES67 download latest generation Audio Grid Controller Software. Your PC needs to be connected to the AES67 network and have its addressing set in the same IP range.
AES67 Network Address Setup
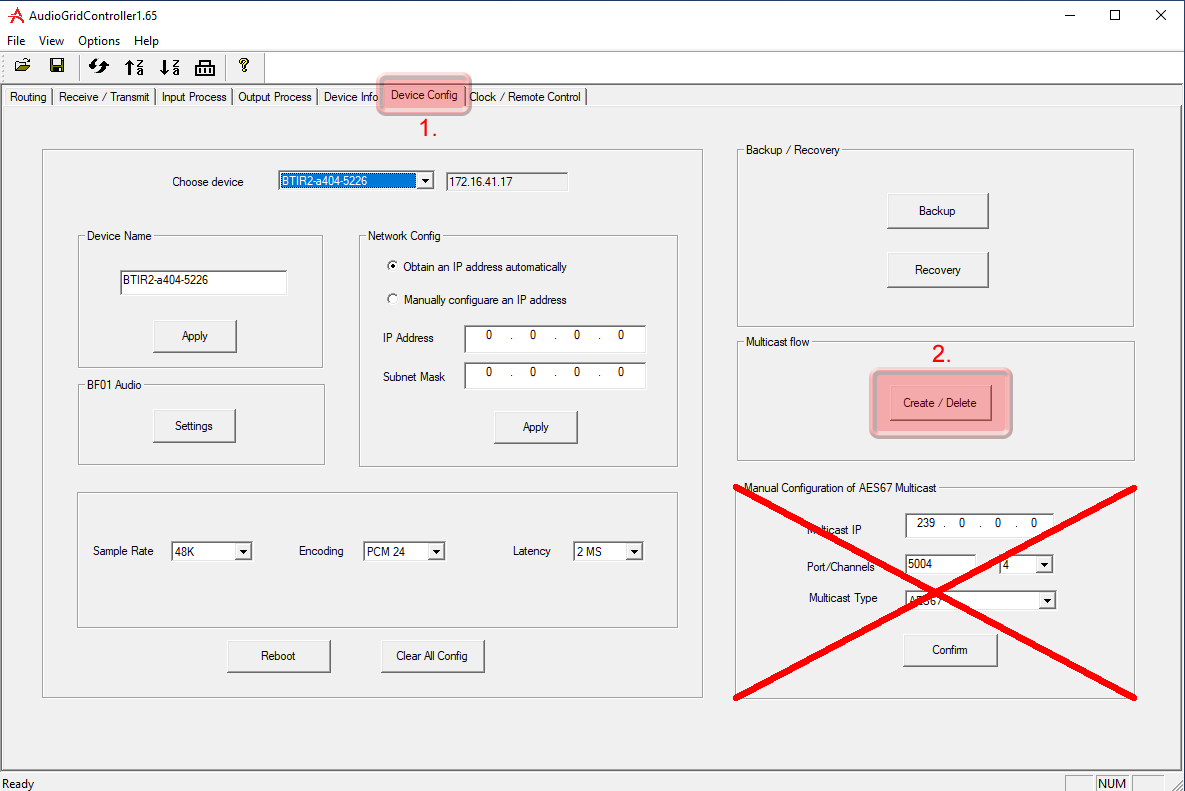
Start the software and go to the “Device Config” tab
- Select the device to be configured
- Enter “IP Address” and “Subnet Mask”
- Hit “Apply”
AES67 Stream Address Setup
The AES67 stream of each device needs to be configured to be received by the Dante/AES67 devices
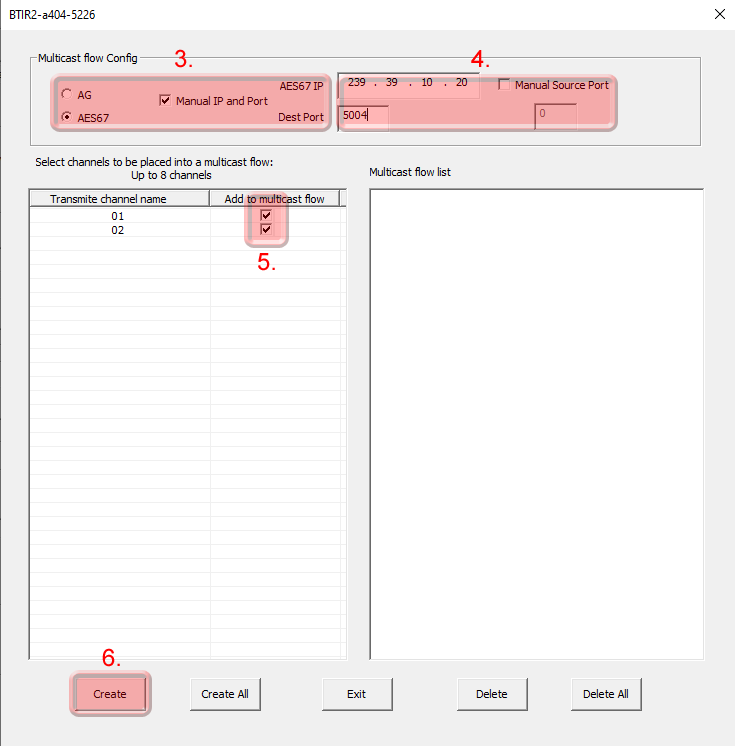
Start the software and go to the “Device Config” tab
- Select the device to be configured
- Select “Create / Delete” in the “Multicst flow” selection
- In the Multicast flow config, click on “AG” first and then on “AES67”. Next, select the “Manual IP and Port” option.
- You can set your desired multicast IP. Typically in combination with Dante Audio products, the multicast IP starts with “239.69.”, port 5004.
- Select the channels that should be multicast.
- Click on “Create”.
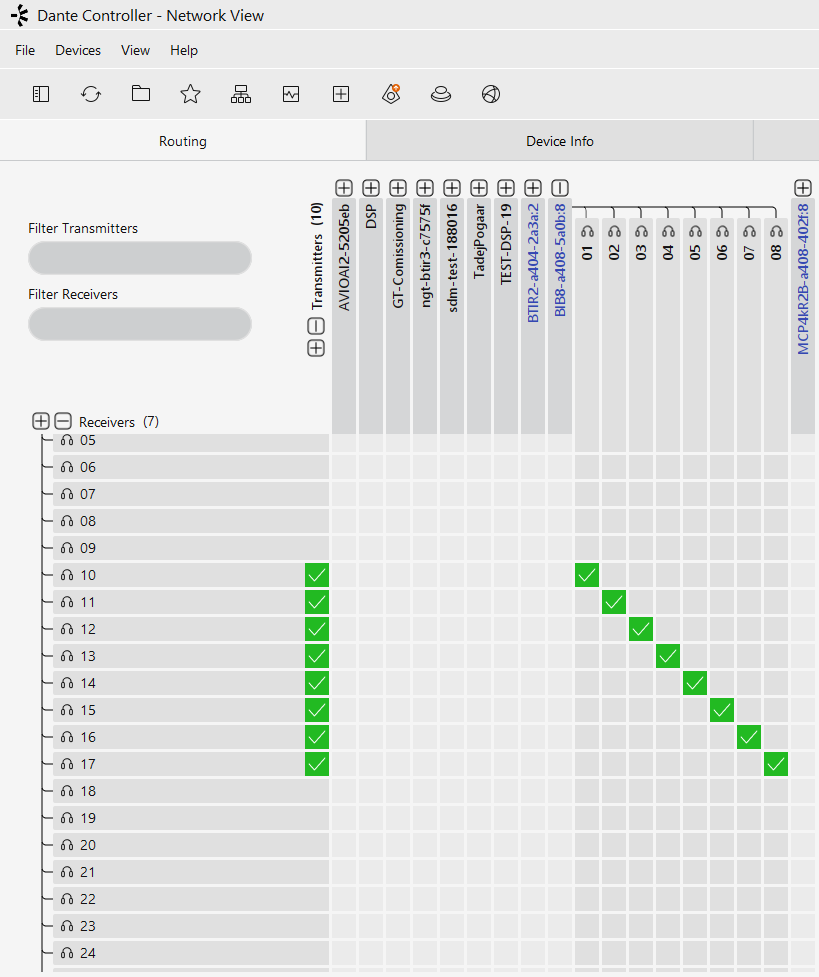
Audio Routing using Audinate’s Dante Controller
Global site parameters
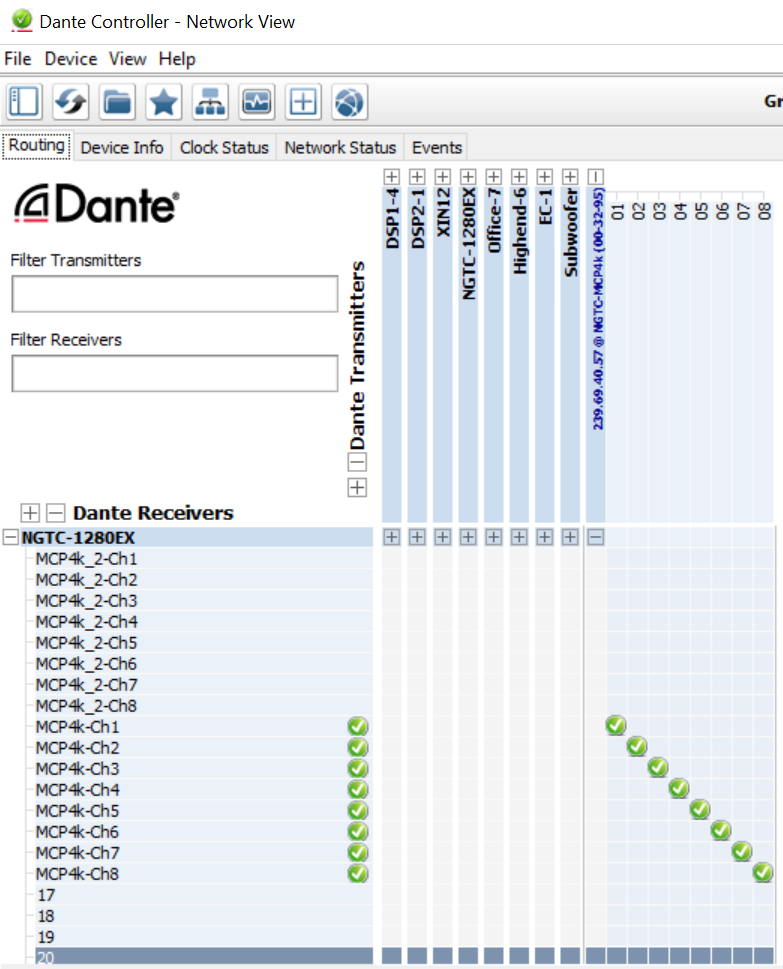
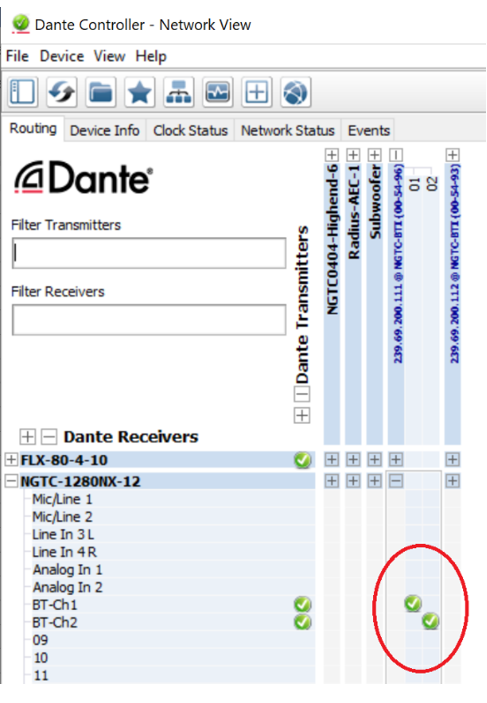
Natively the audio routing can be done by using Audinate’s Dante Controller in case if its not auto configured by the DSP’s management software. In Dante Controller all your Dante and AES67 devices that are connected to the network will show up automatically.
The MCP4kR2 will be shown at the ‘‘Dante Transmitters’’ part, using its multicast address@hostname-HH-HH-HH where ‘‘HH-HH-HH’’ are the last three bytes of the devices MAC address.
- Make the audio connections in the Dante controller
Audio Routing using Symnet Composer
In case of NGTC DSP hardware, the audio routing is done by using the Symetrix Symnet Composer. Please make sure all your Dante and AES67 devices that are connected to the network and are online. You might check this using Dante Controller.
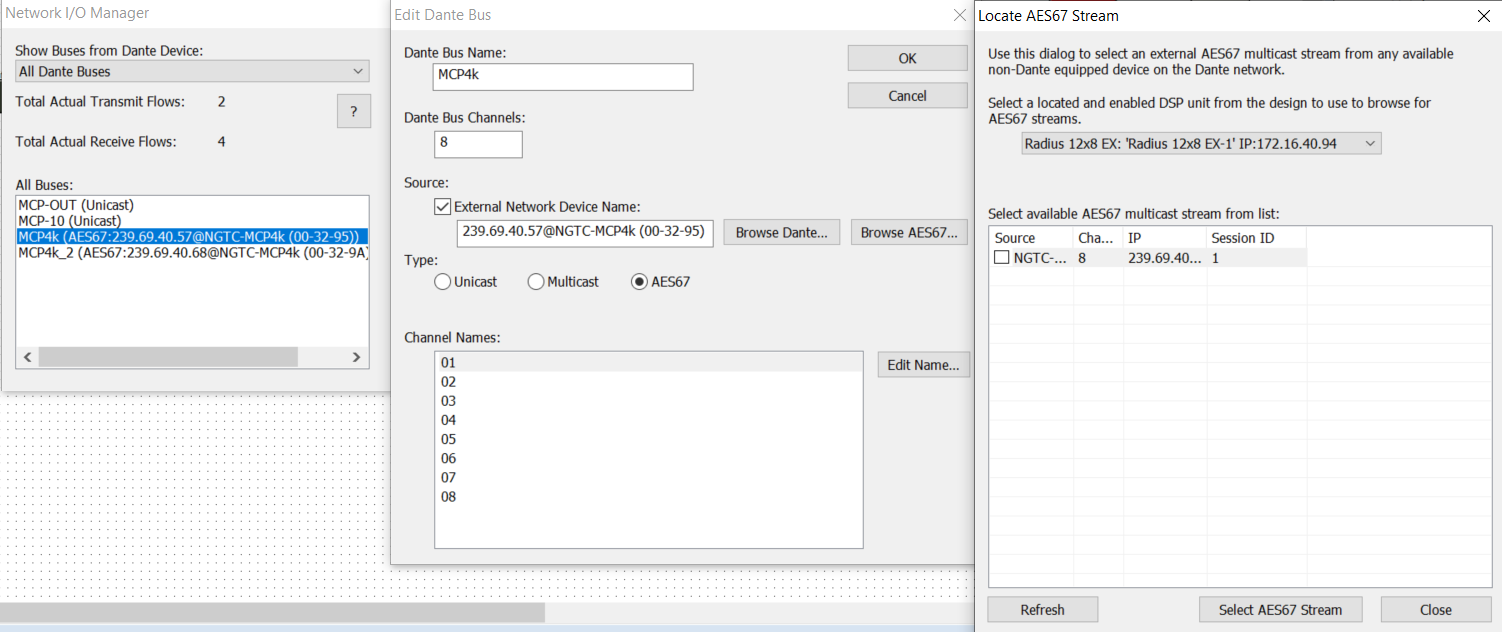
Create a 8 channel network AES67 receive module:
- In “Tools” open “Network I/O Manager”
- Select the corresponding bus and select “Edit Dante Bus”
- Check “External Network Device Name” and Browse AES67
- Pick the stream and Select AES67 Stream
- Insert the stream receiving module in the DSP’s configuration and connects its audio connections
This will connect the MCP4kR2 AES67 stream to the DSP while going online. There is no need to use the Dante Controller to do the connection.
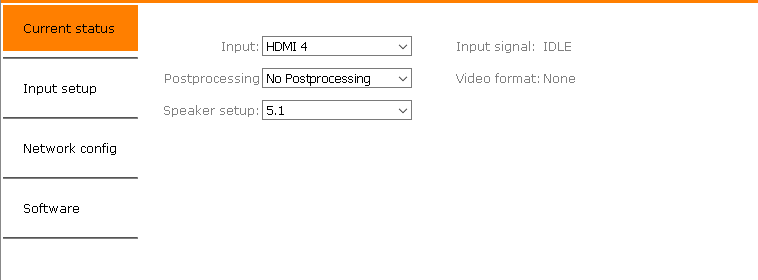
Audio Setup
Audio Configuration
The current input, post processing and specker setup can be set via WebUI on the control network interface. All audio settings can be overwritten on the fly by the control protocol
Speaker Setup
Available speaker Setup:
- 2.0
- 2.1
- 5.1
- 7.1
Post processing
Available post processing:
- None/direct
- PROLOGIC
- PROLOGIC II MUSIC
- PROLOGIC II MOVIE
- DTS NEO6 MUSIC
- DTS NEO6 CINEMA
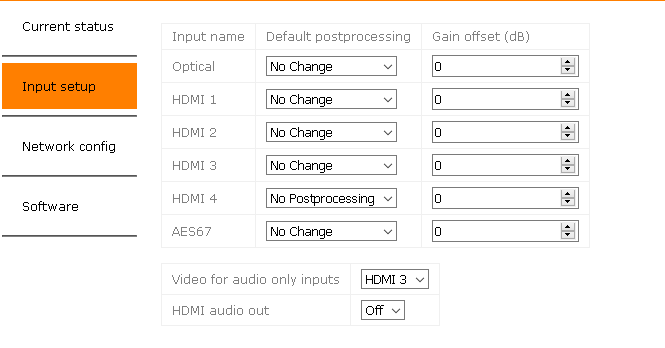
Current settings
Preset settings
These settings are recalled each time the input is selected
- Gain offset (dB) and Default Postprosessing: On each input a post processing preset and a gain offset can be defined.
- AES67 Input: Ability to switch input to the 2 channel AES67 input stream.*
- Video for audio only inputs: On use of an audio only input (optical or AES67) video will be switched to this input.*
- HDMI audio out: Enables/Disables the the audio signal on the HDMI output.*
*Hardware revision B (MCP4kR2B) only
Control API
Definitions
This section describes the communication protocol between the control system and the MCP4kR2
| Connection | TCP (NGTC-MCP4kR2 is server), Port 84 |
| Command Format | !Command(parameter)<cr> or !Command?<cr> |
All commands start with “!”, end with <CR>
<CR>stands for “carriage return”, corresponding hex is 0x0D
<LF> stands for “line feed”, corresponding hex is 0x0A
If a command has a parameter, the parameter is in between “(” “)”
If a command is a “set” command “(parameter)”, then there is no reply
If a command is a “request” command “?”,the value will be in the reply
Send only one command at the time and wait for reply before sending the next one
Ping
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !PING<CR> |
||
| Reply | !PONG<CR><LF> |
Verbosity
Select verbosity
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !VERB(Parameter)<CR> |
||
| 0: (default) Only send requested datal | |||
| 1: Send requested data plus status changes | |||
| 2: Send requested data, status and echo commands | |||
!VERB(2)<CR> |
|||
| Reply |
Request active verbosity
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !VERB?<CR> |
||
!VERB?<CR> |
|||
| Reply | !VERB(2)<CR><LF> |
Post processing
Select post processing
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !POSTP(Parameter)<CR> |
||
| 0: None | |||
| 1: PROLOGIC | |||
| 2: PROLOGIC II MUSIC | |||
| 3: PROLOGIC II MOVIE | |||
| 4: DTS NEO6 MUSIC | |||
| 4: DTS NEO6 CINEMA | |||
!POSTP(2)<CR> |
|||
| Reply |
Request active post processing number
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !POSTP?<CR> |
||
!POSTP?<CR> |
|||
| Reply | !POSTP(3)<CR><LF> |
Request active post processing name
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !POSTPNAME?<CR> |
||
!POSTPNAME?<CR> |
|||
| Reply | !POSTPNAME(Music)<CR><LF> |
Audio format
Request active audio format
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !AUDIOSTATUS?<CR> |
||
!AUDIOSTATUS?<CR> |
|||
| Reply | !AUDIOSTATUS(TRUEHD)<CR><LF> |
HDMI audio output
Enable HDMI audio output
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !HDMIAUDON<<CR> |
||
!HDMIAUDON<<CR> |
|||
| Reply |
Disable HDMI audio output
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !HDMIAUDOFF<<CR> |
||
!HDMIAUDOFF<<CR> |
|||
| Reply |
Request HDMI audio output
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !HDMIAUD?<CR> |
||
!HDMIAUD<CR> |
|||
| Reply | !HDMIAUDOFF()<CR><LF> |
Source
Select source
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !SRC(Parameter)<CR> |
||
| 0: Optical | |||
| 1: HDMI 1 | |||
| 2: HDMI 2 | |||
| 3: HDMI 3 | |||
| 4: HDMI 4 | |||
| 5: AES67* | |||
!SRC(3)<CR> |
|||
| Reply |
*Hardware revision B (MCP4kR2B) only
Request active source number
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !SRC?<CR> |
||
!SRC?<CR> |
|||
| Reply | !SRC(3)<CR><LF> |
Request active source name
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !SRCNAME?<<CR> |
||
!SRCNAME?<<CR> |
|||
| Reply | !HDMI 3<CR><LF> |
Select next source
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !SRCUP?<<CR> |
||
!SRCUP?<<CR> |
|||
| Reply |
Select previous source
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !SRCDN?<<CR> |
||
!SRCDN?<<CR> |
|||
| Reply |
Select video source for audio only input (optical or AES67)*
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !OPTVID(Parameter)<CR> |
||
| 0: No Input | |||
| 1: HDMI 1 | |||
| 2: HDMI 2 | |||
| 3: HDMI 3 | |||
| 4: HDMI 4 | |||
!OPTVID(3)<CR> |
|||
| Reply |
*Hardware revision B (MCP4kR2B) only
Request active video source for audio only input (optical or AES67)*
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !OPTVID?<CR> |
||
!OPTVID?<CR> |
|||
| Reply | !SRC(3)<CR><LF> |
*Hardware revision B (MCP4kR2B) only
Speaker setup
Select speaker setup
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !SPKSETUP(Parameter)<CR> |
||
| 2.0: 2ch, full range | |||
| 2.1: 2ch, full range, LFE | |||
| 5.1: 5ch, full range, LFE | |||
| 7.1: 5ch, full range, LFE | |||
!SPKSETUP(5.1)<<CR> |
|||
| Reply |
Request active speaker setup
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !SPKSETUP?<CR> |
||
!SPKSETUP?<CR> |
|||
| Reply | !SPKSETUP(5.1)<CR><LF> |
Request video status
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | !VIDEOSTATUS?<CR> |
||
!VIDEOSTATUS?<CR> |
|||
| Reply | !VIDEOSTATUS(2160p)<CR><LF> |
Specifications
| HDMI | |
| Type | HDMI 2.0/HDCP 2.2 |
| Matrix | 1 x 1 Input selector, no scaling |
| Digital Audio Input | |
| Type | TOSLINK |
| Format | PCM, LPCM, DD, DTS up to 6 channels. 24Bit/96kHz Audio |
| Digital Audio Output | |
| Type | 8 channels, full range |
| Format | Aes67 |
| Audio Performance | |
| Format | PCM, LPCM, DD, DTS, Dolby True HD, DTS Master HD, DD+ |
| EIN | -115dBu |
| System THD+N | <100dB, unweighted; 1kHz@+22dBu with 0dB gain |
| Freq. Response | 20Hz – 20kHz, +/- 1dB |
| AES67 Network with WebUI | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 100 Mbps Full Duplex |
| Control Network with WebUI | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 100 Mbps Full Duplex |
| General | |
| Power | POE, 10W max |
| Total heat dissipation | 20.00 BTU/hr |
| Operating temp | 0°C – 60°C |
| Dimensions | L: 250mm, W: 208mm, H:44mm |
| Compliance | CE, ROHS |
Audio Channel Assignment
| Channel | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 1 | Left Front |
| 2 | Right Front |
| 3 | Left Surround |
| 4 | Right Surround |
| 5 | Center Front |
| 6 | LFE |
| 7 | Left Rear |
| 8 | Right Rear |
Accessories
Mounting
The MCP4kR2 is half rack width and one rack unit high. If positioned in the rack, it can be mounted the rack shelf that is available. A half rack filler panel is available as well.
Firmware
Firmware
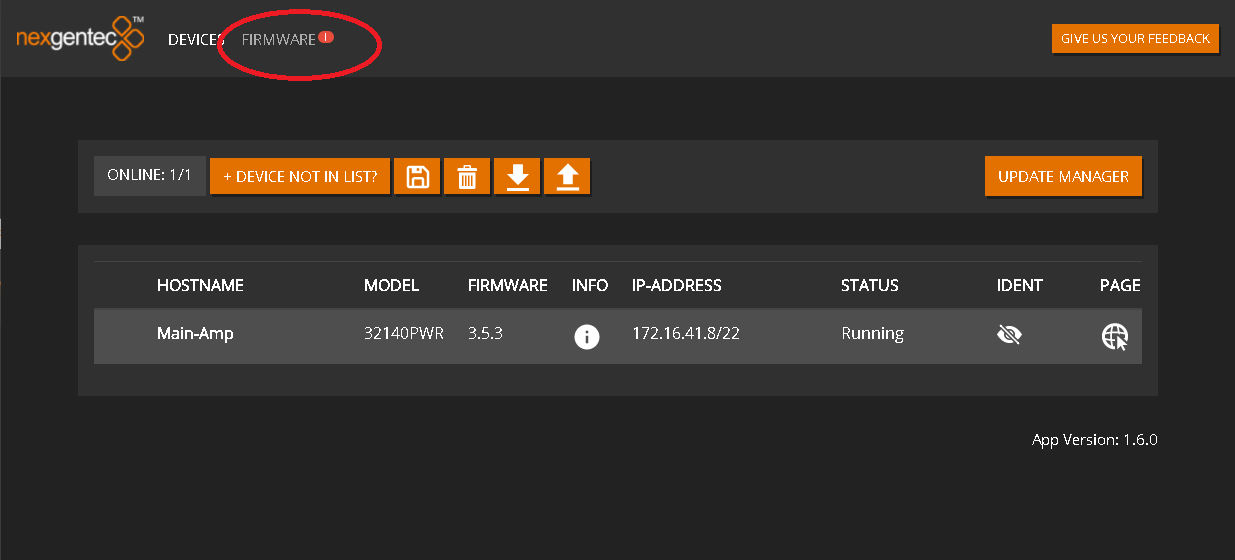
Welcome to the Firmware section!
If you are not redirected automatically, click here.
Subsections of Firmware
Device
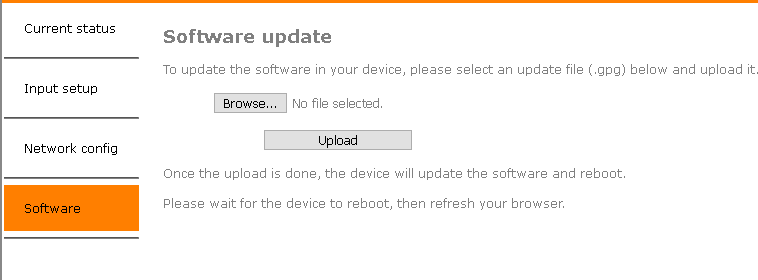
Device Firmware Updates
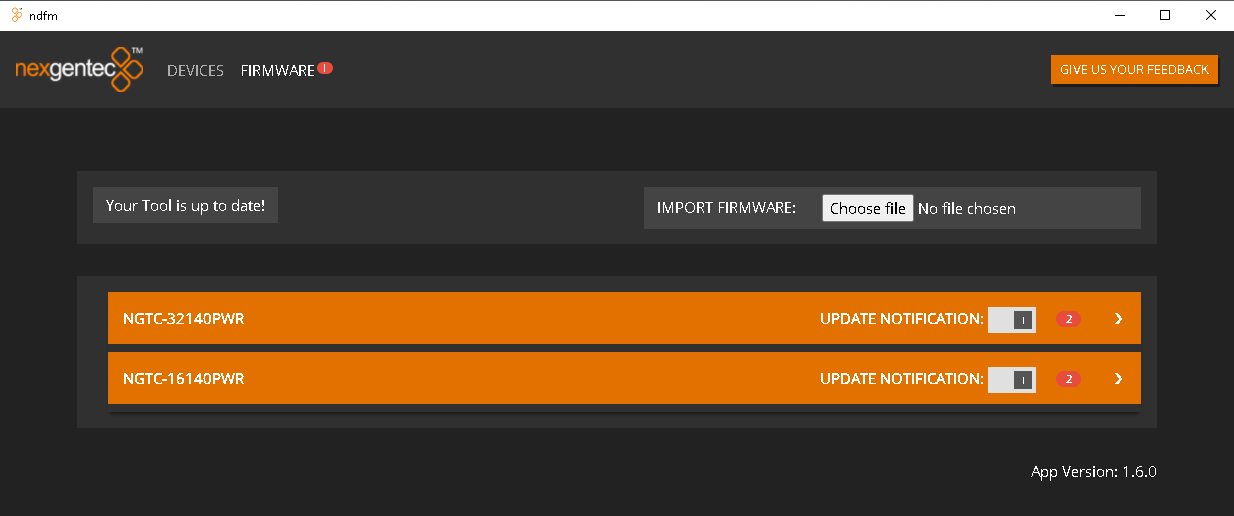
Firmware updates will be published on this site once a new release has passed all tests. To update download the latest version and upload it to the MCP4kR2
Release notes:
mcp4k-1.0.6-8-g186ea03
- Fixed audio drop outs
mcp4k_mcp4k-1.0.7-5-g39aa7b8;
- Fixed audio drop outs using ATV
- Fixed various HDMI issues
- New hardware support
update-mcp4k_mcp4k-1.0.7-37-g542985a
- New logo
update-mcp4k_mcp4k-1.0.8-1-gd4b5594
- Nivida Shield, fixed playback lock issue for HD audio formats.
- PCM 2.0, error fixed
Audio Card
Audio Card Firmware Update
The latest generation of MCP4kR2 features an AES67 daughter board that fully supports AES67, ensuring compatibility with Dante™. Additionally, these devices have mDNS discovery enabled, allowing them to be detected in the Dante Controller, similar to a Dante product.
However, starting with Dante Controller V12, a pop-up message may appear indicating that unlicensed Dante™ products are being used. To address this, the new firmware will disable Dante™ discovery, and all R2 units will be recognized as AES67 devices.
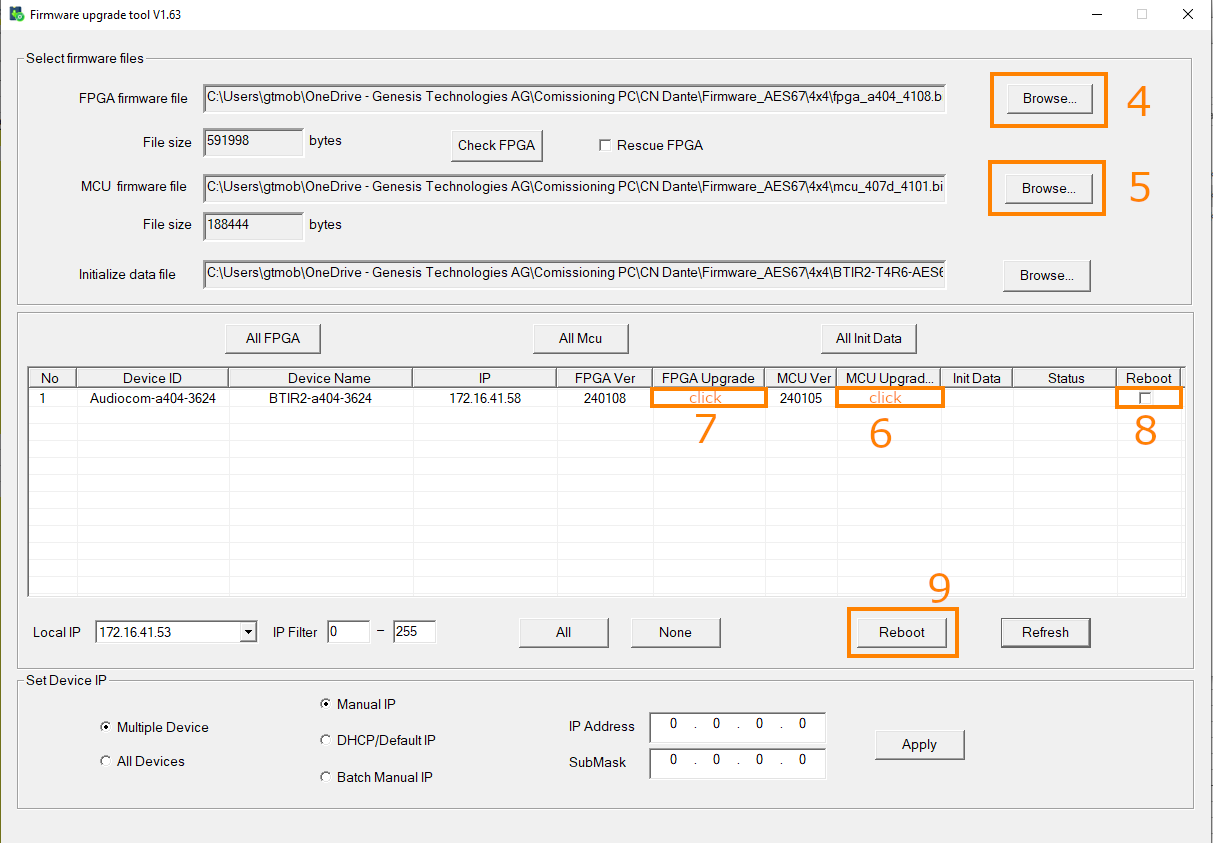
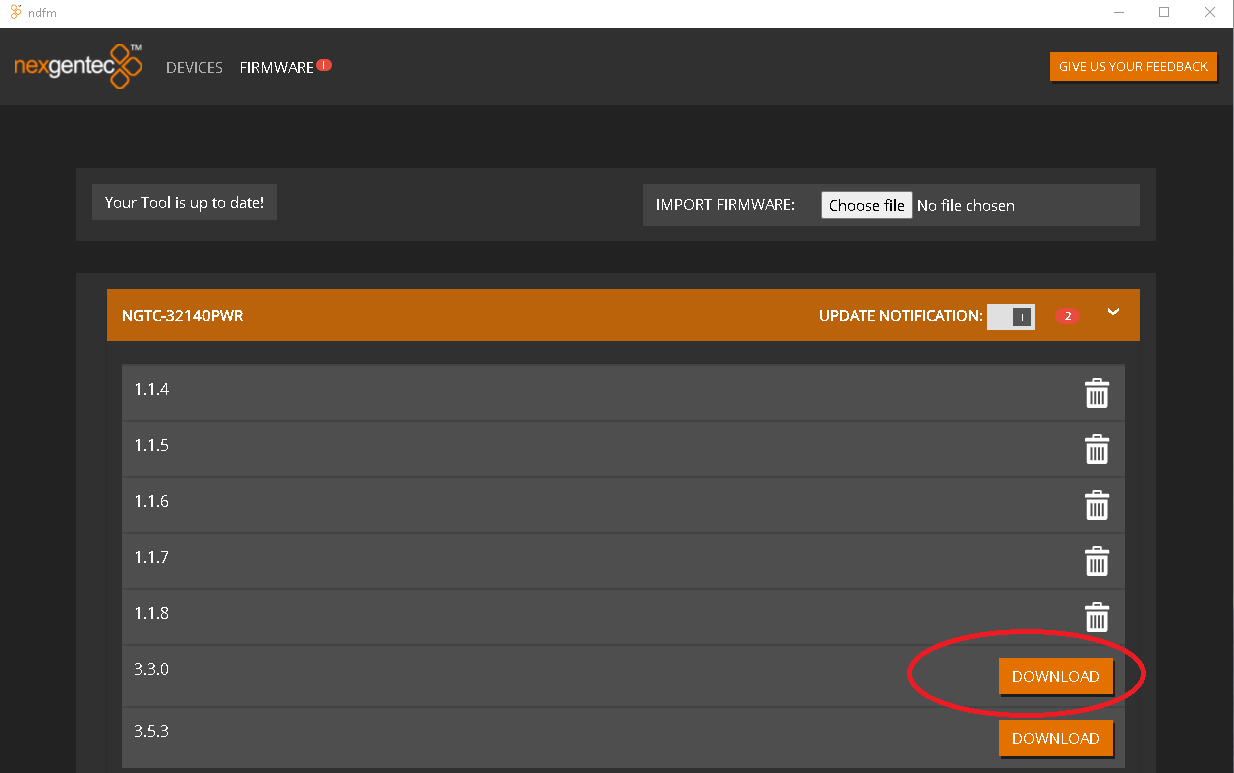
Update to the Latest AES67 only Firmware Release
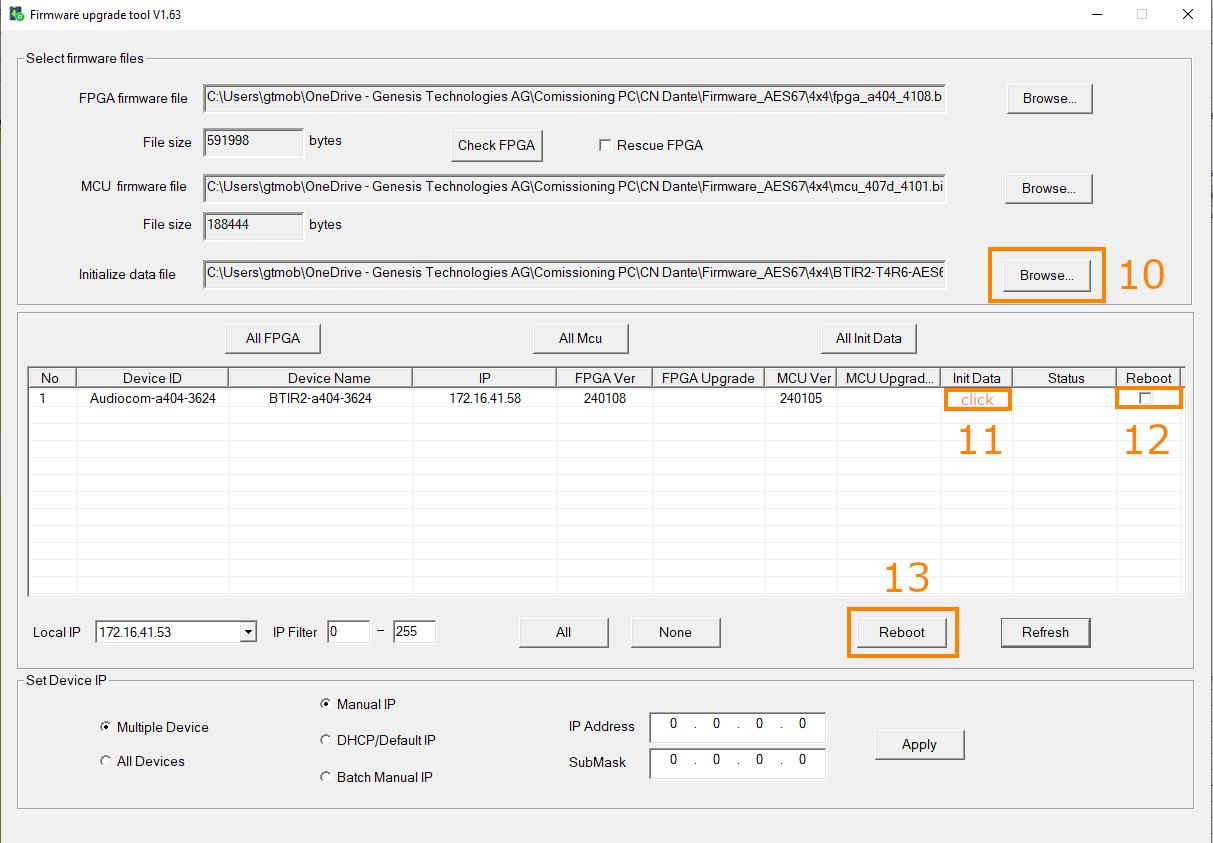
- Download the latest programmer and firmware files
- Unzip the firmware files (MCP4kR2B-FW_4102-4108.zip) into a folder.
- Run the updater tool (Fdt_factory1.63.exe). Note that the discovery function works for up to 10 units. If you have more units, use the IP address filter for efficient navigation.
- Open the FPGA firmware file with the updater tool (fpga_a408_4108.bit).
- Open the MCU firmware file with the updater tool (mcu_407d_4102.bin).
- Update all units with the new MCU by clicking in the field MCU Upgrade.
- Update all units with the new FPGA by clicking in the field FPGA Upgrade.
- Select all updated units in the latest row for reboot.
- Click “Reboot”.
After the reboot, click “Refresh” to update the device list. If the devices appear as expected, you can proceed with the update process.
- Open the Initialize data file with the updater tool (MCP4kR2B-AES67.c).
- Update all units with the new Init data fle by clicking in the field Init Data.
- Select all updated units in the latest row for reboot.
- Click “Reboot”.
After the reboot, you need to set the multicast address for AES67 to work. Use the Audio Grid Controller to do this.
Refer to the following instructions to configure it with the AudioGrid controller
MCP4k
The NGTC-MCP4k is an AES67 enabled multichannel audio processor for the nexgentec™ audio distribution solution.
The NGTC-MCP4k multichannel audio processor is capable of decoding all common digital audio formats delivering up to 8 AES67 channels of audio for processing by the NGTC digital signal processor.
The NGTC-MCP4k can be easily interfaced with 3rd party control systems via the control network port.
The NGTC-MCP4k is powered by a POE on the AES67 port. Its own Web UI is used to configure the AES67 interface. The additional LAN port is only used control. It can be configured by Web UI.
Subsections of MCP4k
Application Note
Hardware
The NGTC-MCP4k is an AES67 enabled multichannel audio processor for the Genesis TechnologiesTM audio distribution solution. It is capable of decoding all common digital audio formats, delivering up to 8 AES67 channels of audio for processing by the NGTC digital signal processors. It can be easily interfaced with 3rd party control systems via the control network port. The small form factor makes it very flexible in its application.
Application 1 – In Room, Zone assigned
The MCP4k audio processor will be placed in the zone. It will accept local sources, central feed and the audio return from the TV (ARC,TOSLINK). The unit will decode, post process and sent out 8 discrete channels via AES67 to the audio network. The bass management, time alignment and channel mapping will be done in the DSP’s for maximum flexibility and performance. To have in the master zone a full 7.1 system while the master bath and dressing may run 2.0 or 1.0 no more an issue. The NGTC DSP super modules by nexgentecTM enable efficient design and deployment of NGTC AVOIP systems, featuring the highest levels of functionality and performance.
Application 2 – In Rack, Zone assigned
The MCP4k audio processor will be placed in the rack and does accept the feed from the central matrix. Each zone has its own MCP. The unit will decode, post process and sent out 8 discrete channels via AES67 to the audio network. The bass management, time alignment and channel mapping will be done in the DSP’s for maximum flexibility and performance. To have in the master zone a full 7.1 system while the master bath and dressing may run 2.0 or 1.0 no more an issue. The NGTC DSP super modules by nexgentecTM enable efficient design and deployment of NGTC AVOIP systems, featuring the highest levels of functionality and performance.
Application 3 – In Rack, Source assigned
The MCP4k audio processor will be placed in the rack, connected to each source and the output of the processor will run into the central matrix. Audio and Video will be separated from the beginning. The MCP4k will decode, post process and sent out 8 discrete channels via AES67 to the audio network. The bass management, time alignment and channel mapping will be done in the DSP’s for maximum flexibility and performance. To have in the master zone a full 7.1 system while the master bath and dressing may run 2.0 or 1.0 no more an issue. The NGTC DSP super modules by nexgentecTM enable efficient design and deployment of NGTC AVOIP systems, featuring the highest levels of functionality and performance.
Installation
- 4 x HDMI inputs
- 2 x mirrored HDMI outputs
- 1 x Toslink digital input
- 1 x AES67 network interface (POE) – please use UTP cabling
- 1 x Control network interface – please use UTP cabling
All connections to the MCP4k should be made before power is applied
• Attach any multimedia sources that will be used, to the inputs
• Attach the LAN network port to the control network switch, using an UTP CAT-5 cable
• Attach the AES67 network port to the AES67/Dante POE network switch, using an UTP CAT-5 cable.
Configuration
Setup interoperability between MCP4k and Dante devices
AES67 interoperability settings are required for every Dante device that should receive a AES67 stream
To enable your Dante devices to receive an AES67 stream, AES67 interoperability must be enabled. This is done by using Audinate’s Dante Controller, which can be obtained from the Audinate website or any other manufacturer specific software tool.
In Dante controller all your Dante devices that are connected to the network will show up automatically.
- Start the Dante Controller Software and wait for it to be synchronized with the network
- Select the “device info” tab in the software
- Double click on the DSP you would like to configure for AES67, a new window will open
- Select the “AES67 config” tab
- Enable AES67 mode and make a note of the Tx multicast prefix. You will need this number later, even if you are not using the DSP as a transmitter. This must be the same for all DSP’s that are ready for AES67.
- Reboot the Dante device
- This needs to be done with every Dante device that will receive an AES67 stream
Subsections of Configuration
Control Network Setup
Control Network Address Setup
The setup of the control network of the MCP4k will be done via it’s Web UI. It is self-explaining
By default the interface is set to DHCP
Please make sure your computer network address is in the same network range to access the setup pages
Default web UI username and password
admin
To reset the control network address use the USR IOT tool
The tool does allow you to search and reset the network settings
AES67 Network Setup
AES67 Network Address Setup
To configure the AES67 network address use the built in Audiolan web UI. Your PC needs to be connected to the AES67 network and have its addressing set in the same IP range.
By default the AES67 network interface is set to the static IP address (192.168.4.233)
To avoid an IP conflicts, connect one device after another and change each units IP to a different one
Avoid any special characters and spaces in the device name
- Open a browser and enter the devices AES67 network address in the address bar, press enter
- Select the “General settings” tab in the web UI to change the devices IP address
- The NGTC-MCP4kR2 should have an IP and Subnet address in the same range as the Dante devices
- Apply all settings and reboot the device
AES67 Stream Address Setup
The AES67 stream of each device needs to be configured to be received by the Dante/AES67 devices
Avoid any special characters and spaces in the stream name
- Open a browser and enter the devices AES67 network address in the address bar, press enter
- Select the “Stream provider” tab in the web UI and uncheck the “Use automatic configuration” checkbox
- Make sure that the first 2 octets matches the Multicast Address Prefix given in the Dante Controller (239.69.xxx.xxx in the example below). Set the last 2 octets to unique values. always avoid duplicated IP addresses. Best practice is to set them to the same value as the last 2 octets of the AES67 network address
- Make sure that the “Activate” checkbox for the stream is checked
- Select the “Advanced” tab and ensure that the SAP browsing is enabled
Audio Routing using Audinate’s Dante Controller
Natively the audio routing can be done by using Audinate’s Dante Controller in case if its not auto configured by the DSP’s management software. In Dante Controller all your Dante and AES67 devices that are connected to the network will show up automatically.
The MCP4kR2 will be shown at the ‘‘Dante Transmitters’’ part, using its multicast address@hostname-HH-HH-HH where ‘‘HH-HH-HH’’ are the last three bytes of the devices MAC address.
- Make the audio connections in the Dante controller
Audio Routing using Symnet Composer
In case of NGTC DSP hardware, the audio routing is done by using the Symetrix Symnet Composer. Please make sure all your Dante and AES67 devices that are connected to the network and are online. You might check this using Dante Controller.
Create a 8 channel network AES67 receive module:
- In “Tools” open “Network I/O Manager”
- Select the corresponding bus and select “Edit Dante Bus”
- Check “External Network Device Name” and Browse AES67
- Pick the stream and Select AES67 Stream
- Insert the stream receiving module in the DSP’s configuration and connects its audio connections
This will connect the MCP4kR2 AES67 stream to the DSP while going online. There is no need to use the Dante Controller to do the connection.
Audio Setup
Audio Configurations
The audio configurations can be set via the control protocol
Available speaker Setup:
- 2.1
- 3.1
- 5.1
- 7.1
Available post processing:
- None/direct
- Stereo
- PROLOGIC II MUSIC
- PROLOGIC II MOVIE
- DTS NEO6 MUSIC
- DTS NEO6 CINEMA
Control API
This section describes the communication protocol between the control system and the MCP4k
| Connection | TCP (NGTC-MCP4k is server), Port 20108 |
| Command Format | h07CommandParameter)hB3h0Dh0A or h07CommandhB3 h0D h0A |
All commands start with h07 which is hex 07, end with hB3h0Dh0A which is in hex B3, 0D and 0A
If a command has a parameter, the parameter is right after the command, with no whitespaces inbetween
Send only one command at the time and wait for reply before sending the next one
Example
| Communication | Get Version |
|---|---|
| Request | h07GVERhB3h0Dh0A |
| Reply | h07RVER000hB3h0Dh0A |
Subsections of Control API
General
Version
| Communication | Get Version |
|---|---|
| Request | h07GVERhB3h0Dh0A |
| Reply | h07RVER000hB3h0Dh0A |
Source
Version
Select source
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | h07SINPhB3h0Dh0A |
||
| 000: HDMI 1 | |||
| 001: HDMI 2 | |||
| 002: HDMI 3 | |||
| 003: HDMI 4 | |||
| 004: SPDIF | |||
| 005: Analog | |||
h07SINP002hB3h0Dh0A |
|||
| Reply |
Request active source number
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | h07GINP000hB3h0Dh0A |
||
h07GINP000hB3h0Dh0A |
|||
| Reply | h07RINP002hB3h0Dh0A |
Speaker Setup
Select speaker setup
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | h07SMODhB3h0Dh0A |
||
| 2.1: 2ch, full range | |||
| 3.1: 2ch, full range, LFE | |||
| 5.1: 5ch, full range, LFE | |||
| 7.1: 5ch, full range, LFE | |||
h07SMOD003hB3h0Dh0A |
|||
| Reply |
Request active speaker setup
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | h07GMODhB3h0Dh0A |
||
h07GMODhB3h0Dh0A |
|||
| Reply | h07RMOD003hB3h0Dh0A |
Audio
Select post processing
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | h07SDSPhB3h0Dh0A |
||
| 0: None | |||
| 1: STEREO | |||
| 2: PROLOGIC II MUSIC | |||
| 3: PROLOGIC II MOVIE | |||
| 4: DTS NEO6 MUSIC | |||
| 4: DTS NEO6 MOVIE | |||
h07SDSP004hB3h0Dh0A |
|||
| Reply |
Request active post processing number
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | h07GDSP000hB3h0Dh0A |
||
h07GDSP000hB3h0Dh0A |
|||
| Reply | h07RDSP004hB3h0Dh0A |
Request active audio format
Request active post processing number
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | h07GSFO000hB3h0Dh0A |
||
| 1: Idle | |||
| 2: PCM | |||
| 4: Bitstream compressed 1 | |||
| 8: Bitstream compressed 2 | |||
| 32: HD Audio | |||
h07GSFO000hB3h0Dh0A |
|||
| Reply | h07RSFO001hB3h0Dh0A |
Specifications
| HDMI | |
| Type | HDMI 1.4/HDCP 1.0 |
| Matrix | 1 x 1 Input selector, no scaling |
| Digital Audio Input | |
| Type | TOSLINK |
| Format | PCM, LPCM, DD, DTS up to 6 channels. 24Bit/192kHz Audio |
| Digital Audio Output | |
| Type | 8 channels, full range |
| Format | Aes67 |
| Audio Performance | |
| Format | PCM, LPCM, DD, DTS |
| Freq. Response | 20Hz – 20kHz, +/- 1dB |
| Video Performance | |
| Format | Up to 4k, 3D, 48Bit deep color |
| AES67 Network with WebUI | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 100 Mbps Full Duplex |
| Control Network with WebUI | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 100 Mbps Full Duplex |
| General | |
| Power | POE, 10W max |
| Total heat dissipation | <50.00 BTU/hr |
| Operating temp | 0°C – 60°C |
| Dimensions | L: 250mm, W: 208mm, H:44mm |
| Compliance | CE, ROHS |
| Weight | 2kg |
Audio Channel Assignment
| Channel | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 1 | Center Front |
| 2 | LFE |
| 3 | Left Rear |
| 4 | Right Rear |
| 5 | Left Front |
| 6 | Right Front |
| 7 | Left Surround |
| 8 | Right Surrounc |
Accessories
Mounting
The MCP4k is half rack width and one rack unit high. If positioned in the rack, it can be mounted the rack shelf that is available. A half rack filler panel is available as well.
BTIR3
The NGT-BTIR3 is a universal Bluetooth® Dante™/AES67-enabled audio interface designed for the nexgentec™ audio distribution solution.
It features a robust API for navigation, configuration, and management, making it highly versatile for integration into various systems.
The NGT-BTIR3 operates exclusively in sink mode, supporting all current audio codecs and ensuring compatibility with a wide range of Bluetooth sources. It provides two AES67/Dante™ output channels for seamless audio distribution.
The device can be easily integrated with third-party control systems via its API, accessible through the communication control network port. Configuration is straightforward using its built-in web UI, which allows full control over all aspects of the interface.
Key Features
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) on the first network port for simplified installation.
- A manageable integrated 2-port switch for flexible networking.
- The nexgentec ngtOS operating system, offering advanced control API, configuration, and monitoring capabilities.
Subsections of BTIR3
Apps
Configure Installed Apps of the Unit
Each installed app can be configured to a certain level via the web interface.
The default login for the web interface is: Username: admin Password: nexgentec
Open a browser and enter the device’s network address in the address bar, then press Enter.
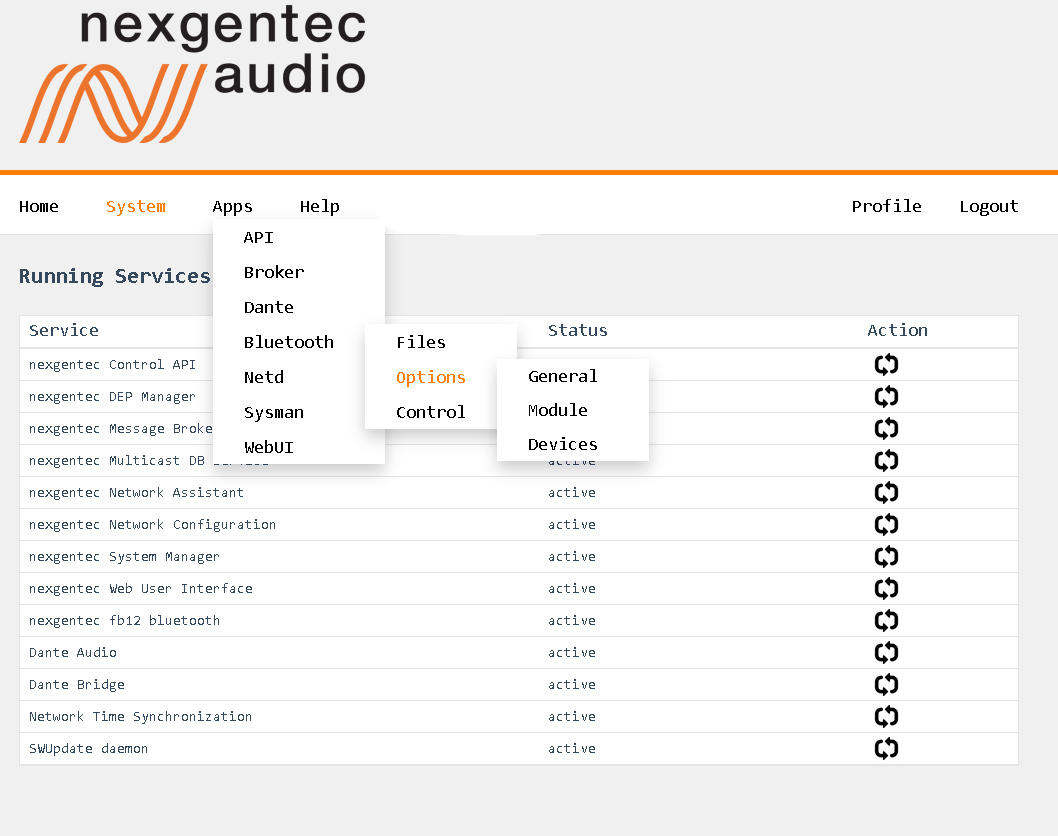
Use the top menu bar to navigate to Apps and select the app to be configured.
Subsections of Apps
API
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > API.
Files
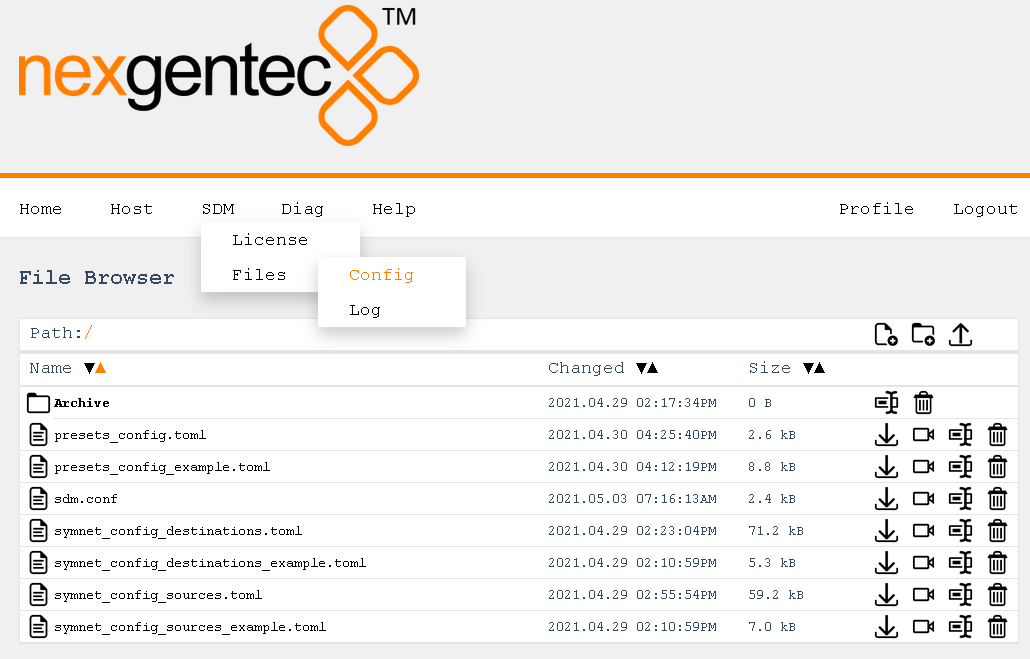
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
transport
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
api
- Use the dropdown menus to select the Endpoint and the port to use for each protocol that the API can communicate with.
Bluetooth
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > Bluetooth.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
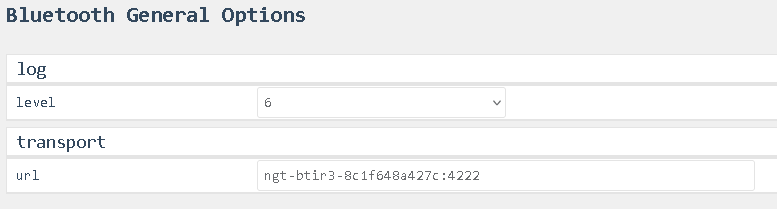
Options > General
log Level
- Select the log level for the app.
transport url
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
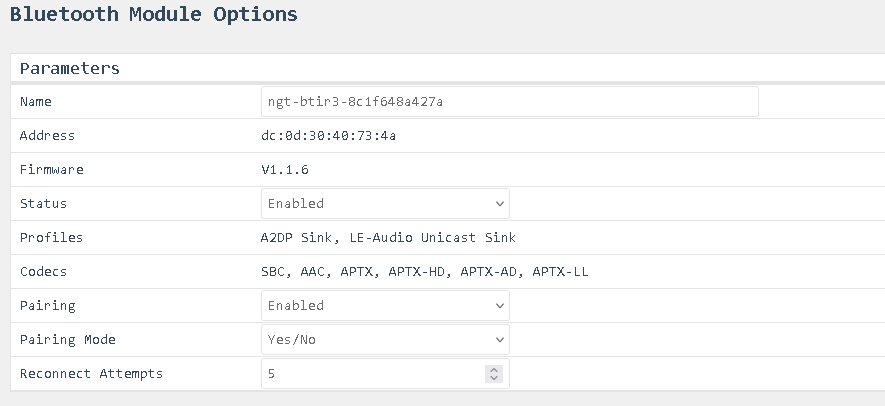
Options > Module
Name
Address
- The name of the Bluetooth device. This name is broadcasted as the device name over Bluetooth.
Firmware
- Read-only: Displays the firmware version of the Bluetooth chip.
Status
- Enables or disables the Bluetooth antenna.
Profiles
- Read-only: Lists the available and activated Bluetooth profiles.
Codecs
- Read-only: Lists the available and activated Bluetooth audio codecs.
Pairing
- Read-only: Indicates whether pairing is enabled or disabled. If pairing is disabled, no new devices can connect. If a device is already connected, pairing is always disabled until the device disconnects.
Pairing Mode
- Options: Yes, No, or Auto.
- Auto: Allows silent pairing without showing any pop-ups or prompts.
- Yes/No: May display a pairing code and ask for confirmation.
Reconnect Attempts
- Specifies whether Bluetooth should automatically reconnect after a BRIR3 restart and how many attempts should be made.
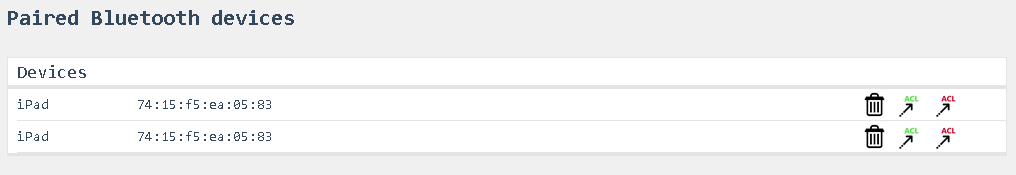
Options > Devices
Paired Bluetooth devices
- This is the list of the currently paired Bluetooth devices.
- To delete a device, click the trashcan icon next to the device you want to remove
- Select the green ACL symbol to add this device to the allowed devices in the access control list.
- Select the red ACL symbol to add this device to the denied devices in the access control list.
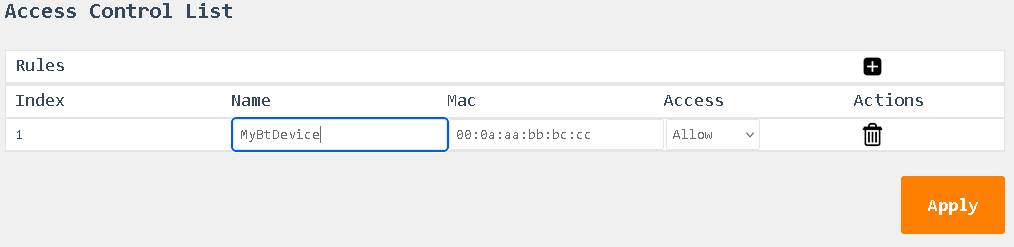
Access Control List
The Access Control List (ACL) displays a table of devices with the following details for each entry:
-
Name: The name of the Bluetooth device, as identified during pairing.
-
MAC Address: The unique MAC address of the Bluetooth device.
-
Access:
Indicates whether the device is allowed or denied access.- Allow: The device is permitted to connect.
- Deny: The device is blocked from connecting.
-
Delete Option:
Each entry includes a trashcan icon that allows you to delete the device from the list.
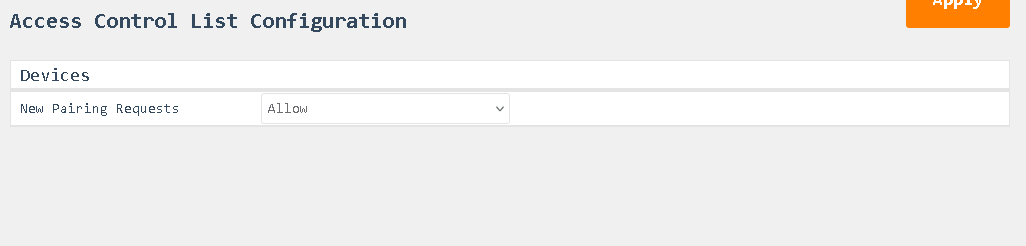
Access Control List Configuration
- New Pairing Requests:
This setting determines whether new devices are allowed to pair and stay connected with the Bluetooth module.- Allow: The device can connect and is granted access automatically.
- Deny: The device will connect but will immediately be disconnected.
Broker
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > Broker.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
transport
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
Dante
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > Broker.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
network
- Select the interface to be used for Dante audio. This interface will be used for audio data transmission.
Display
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > Display.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
transport
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
time
- Select the time format to be shown on the display, 24h or AM/PM.
temperature
- Select the temperature format to be shown on the display in Celsius or Fahrenheit.
backlight
- Select the brightness level. Possible values range from 0 to 255. At 0, the display on the front is completely dark and appears to be turned off.
Netd
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > WebUI.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
WebUI
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > WebUI.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
transport
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
web
- This is the address of the web UI to run on. The default is on all interfaces and port 80, therefore “:80”. Be careful when changing this setting.
Configuration
Configure Hardware and Software Properties
All configuration tasks can be performed via the web interface.
The default login for the web interface is: Username: admin Password: nexgentec
Open a browser and enter the device’s network address in the address bar, then press Enter.
Use the top menu bar to navigate to the option you want.
Subsections of Configuration
Network
This guide applies to all units running ngtOS >= version 1.0.16 (beta-rc6)
Status
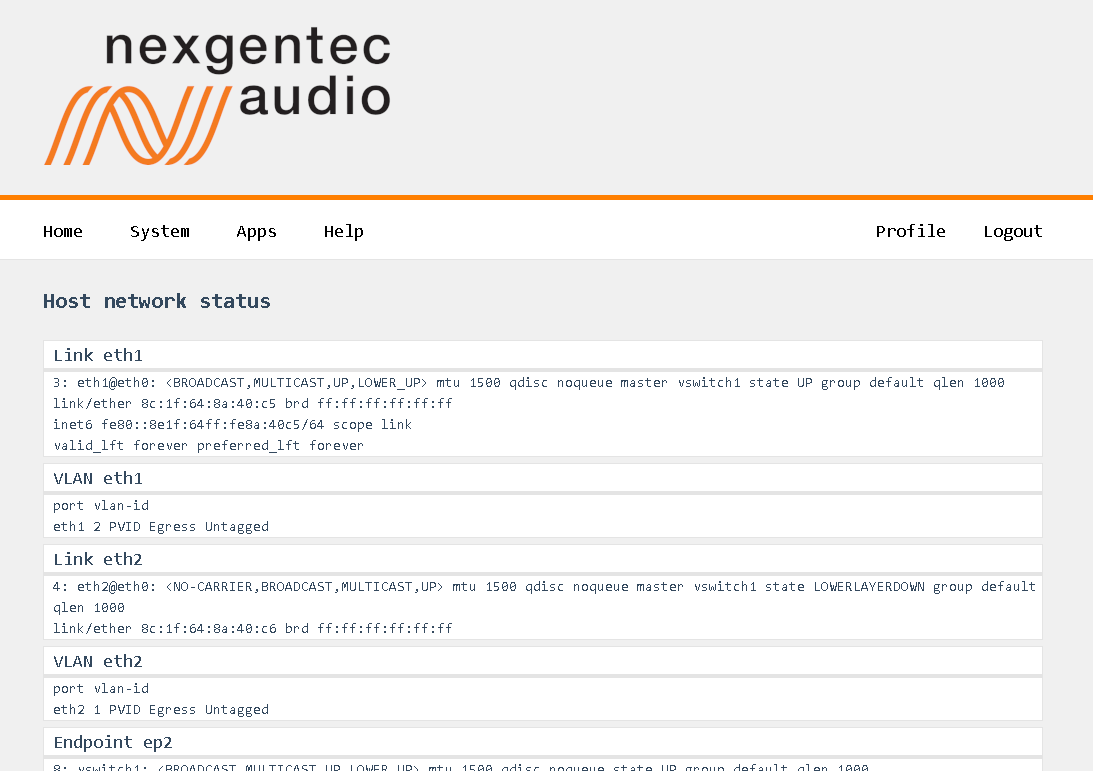
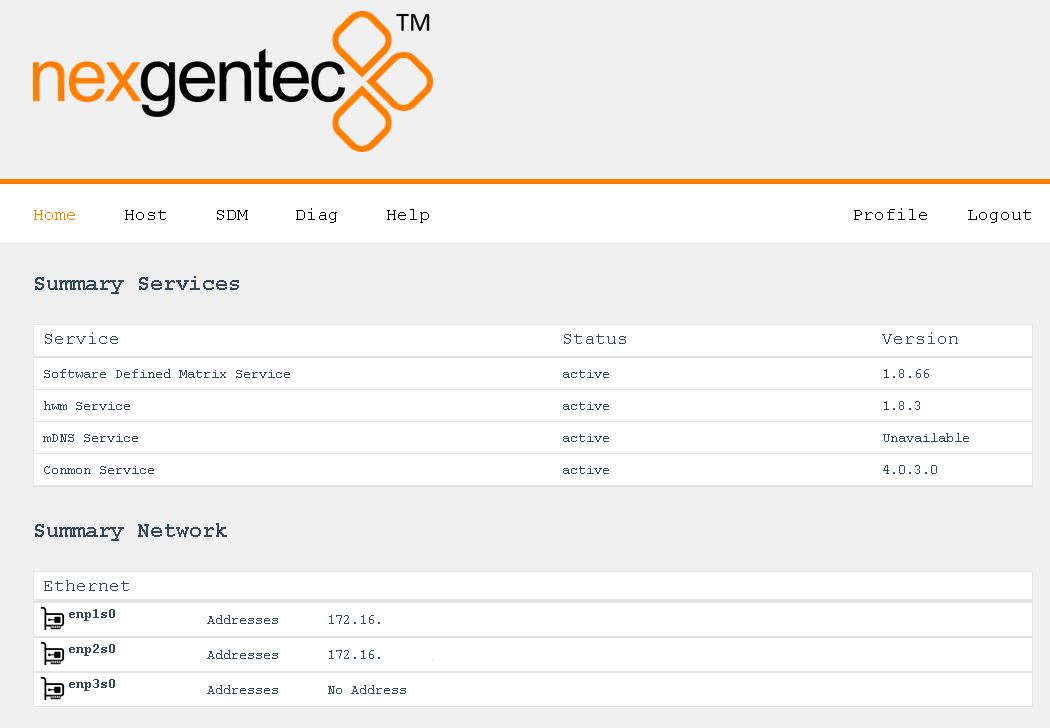
The status of the network connections can be viewed on the status page System > Network > Status
General
Points to consider:
- Never assign a gateway to more than one connection.
- Never place more than one connection in the same IP address range.
- Use DNS servers that are reachable.
- Avoid leaving two interfaces connected to the network on DHCP.
- The unit requires internet access. This is necessary in case service personnel need to access the unit using the built-in support tool.
If things go wrong:
- Try to locate the device using your DHCP server. Attempt this on all available Ethernet interfaces.
- The display on the unit shows the full configuration for each interface, including the path to access the IP address.
Basic Functionality
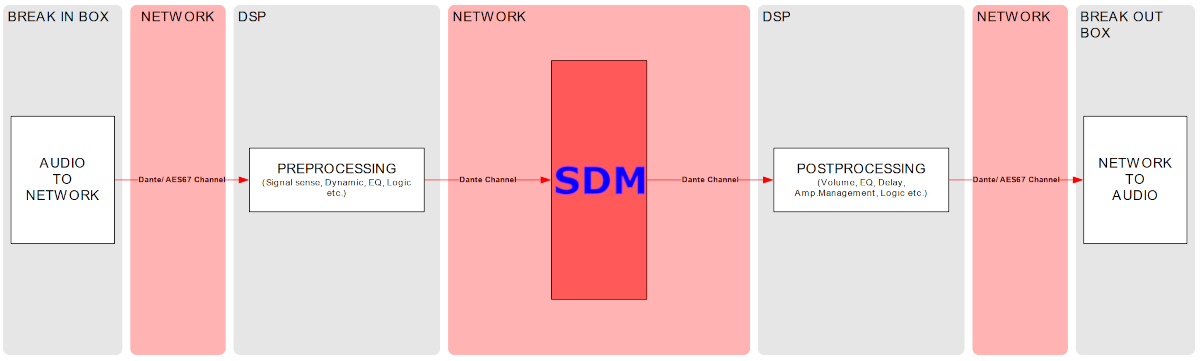
In general, the physical network interfaces and the internal endpoints should be understood as a managed switch infrastructure. Each physical port can take untagged and tagged VLANs, each VLAN can be used to connect an “Endpoint” for Audio and/or Control. Finally, VLANs can be forwarded tagged or untagged between the physical interfaces, keeping the tagging or even untagging during forwarding.
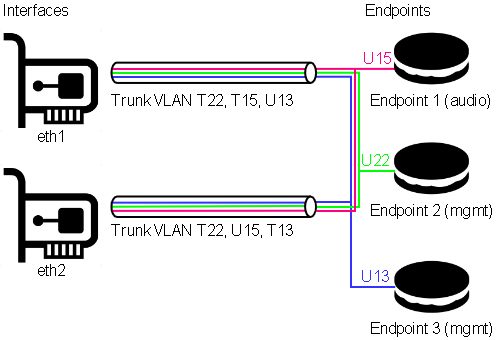
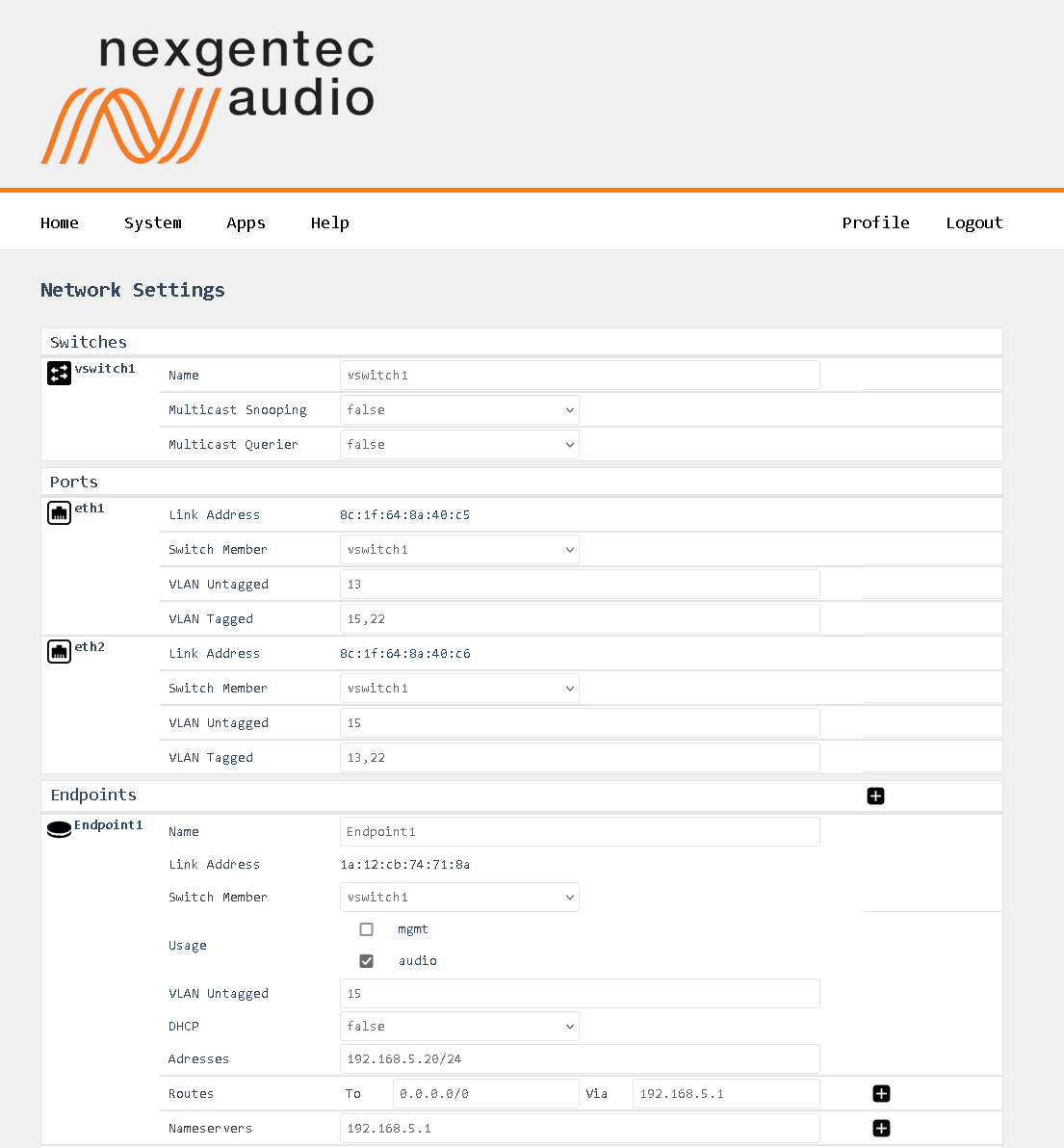
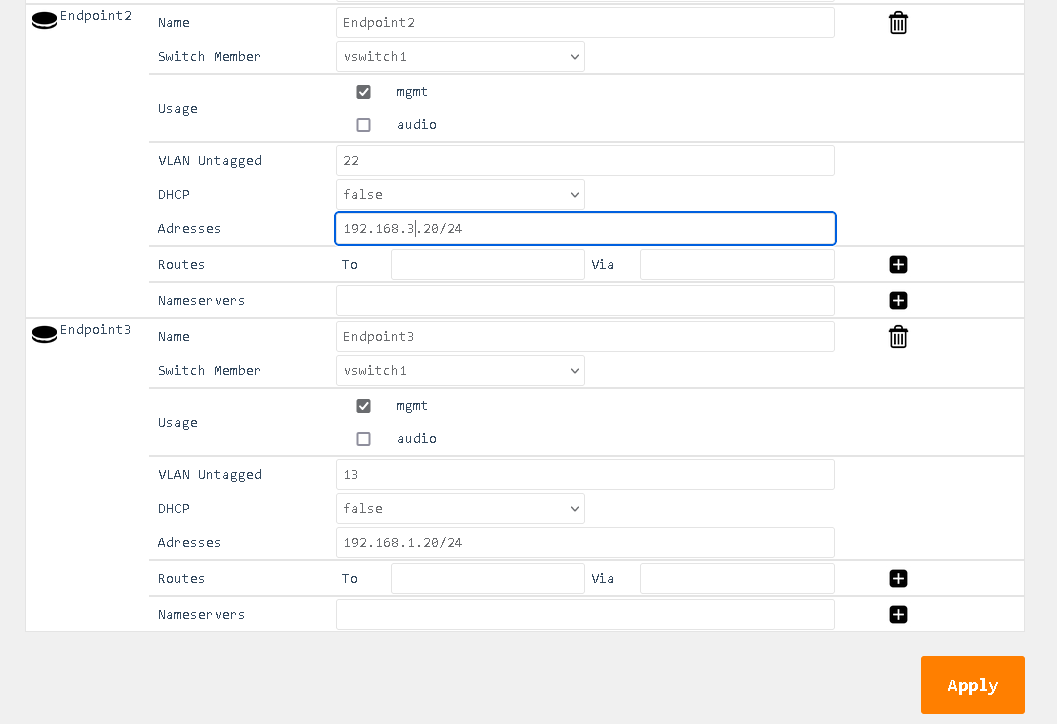
 In this example, both physical ports are carrying VLANs 13, 15, and 22.
In this example, both physical ports are carrying VLANs 13, 15, and 22.
-
VLAN 13 is the untagged (native) VLAN on eth1 and gets tagged while flowing towards eth2, and vice versa. It’s also received by Endpoint 3, which is a management endpoint. The IP address (fixed or statically assigned) of Endpoint 3 can be reached on eth1 using no VLAN tag and on eth2 using a VLAN tag 13.
-
VLAN 15 is the tagged VLAN on eth1 and gets untagged while flowing towards eth2 (native), and vice versa. It’s also received by Endpoint 1, which is the audio endpoint. The IP address (fixed or statically assigned) of Endpoint 1 can be reached on eth1 using VLAN tag 15 and on eth2 using no VLAN tag.
-
VLAN 22 is a tagged VLAN which flows over both physical interfaces. It’s also received by Endpoint 2, which is a management endpoint. The IP address (fixed or statically assigned) of Endpoint 2 can be reached on any of the two physical interfaces using a VLAN tag 22.
On the Front Display
The front panel display shows the current network configuration, including how to access the shown IP address. If multiple endpoints exist, the line scrolls every 5 seconds to display all endpoints.
Syntax: physical[:Tagged VLAN]>Endpoint name > IP Address (CIDR notation).
Examples
Following the example above:
- eth1 > Endpoint 3 > 192.168.1.20/24 (See the description above on how to access 192.168.1.20)
- eth1:15 > Endpoint 1 > 192.168.5.20/24 (See the description above on how to access 192.168.5.20)
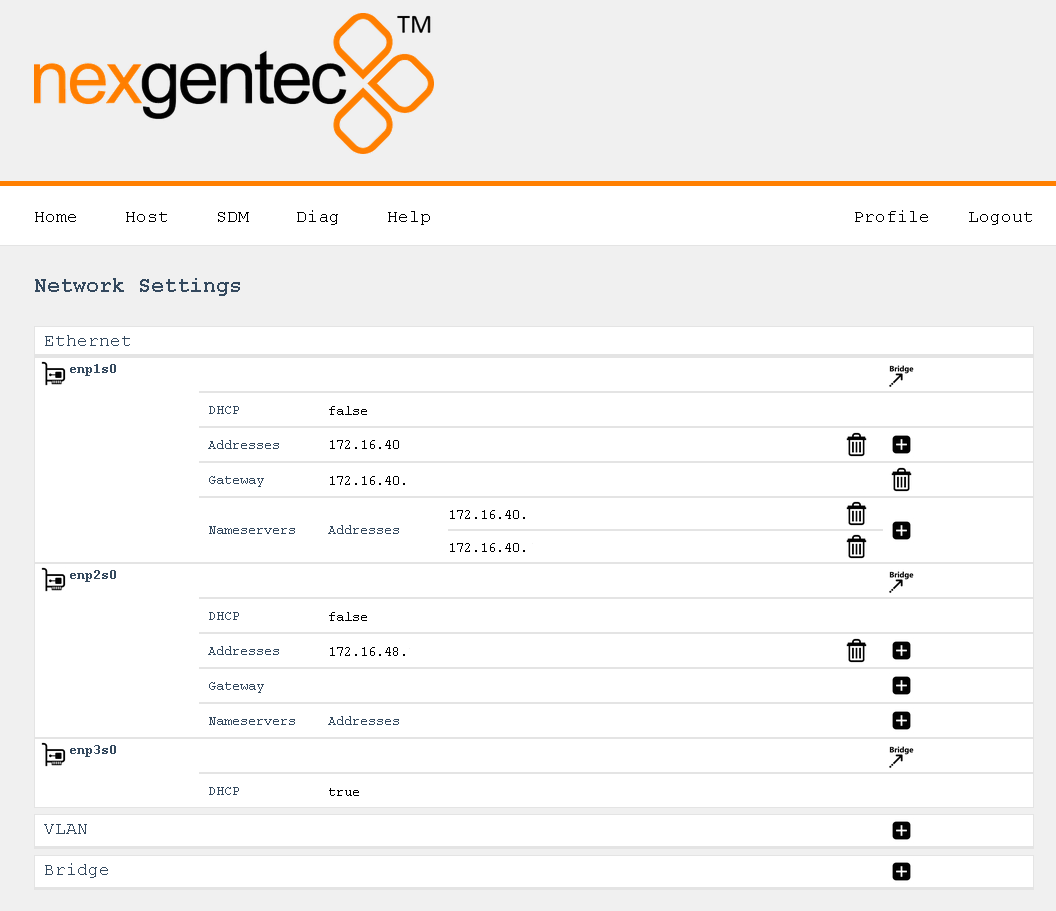
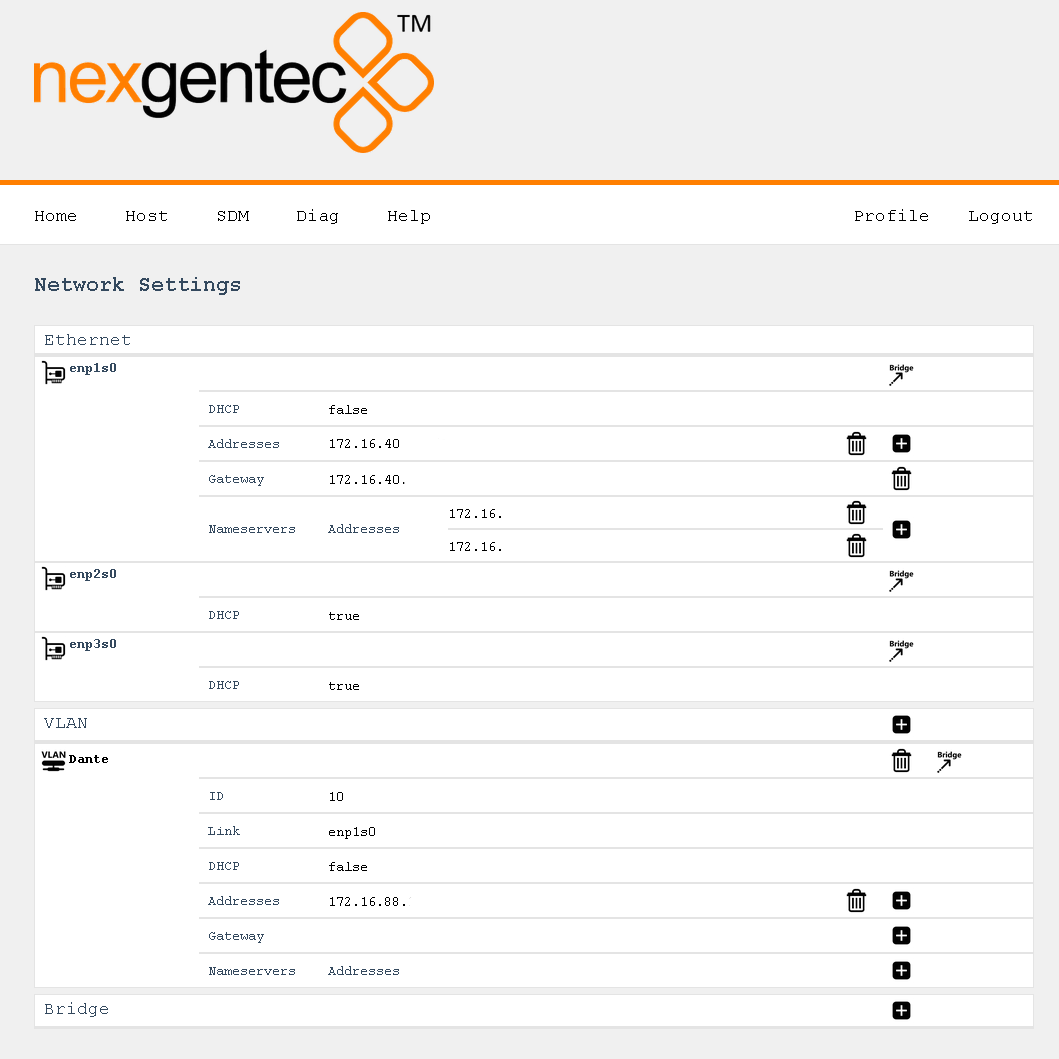
Configure
Select in the top menu System > Network > Settings
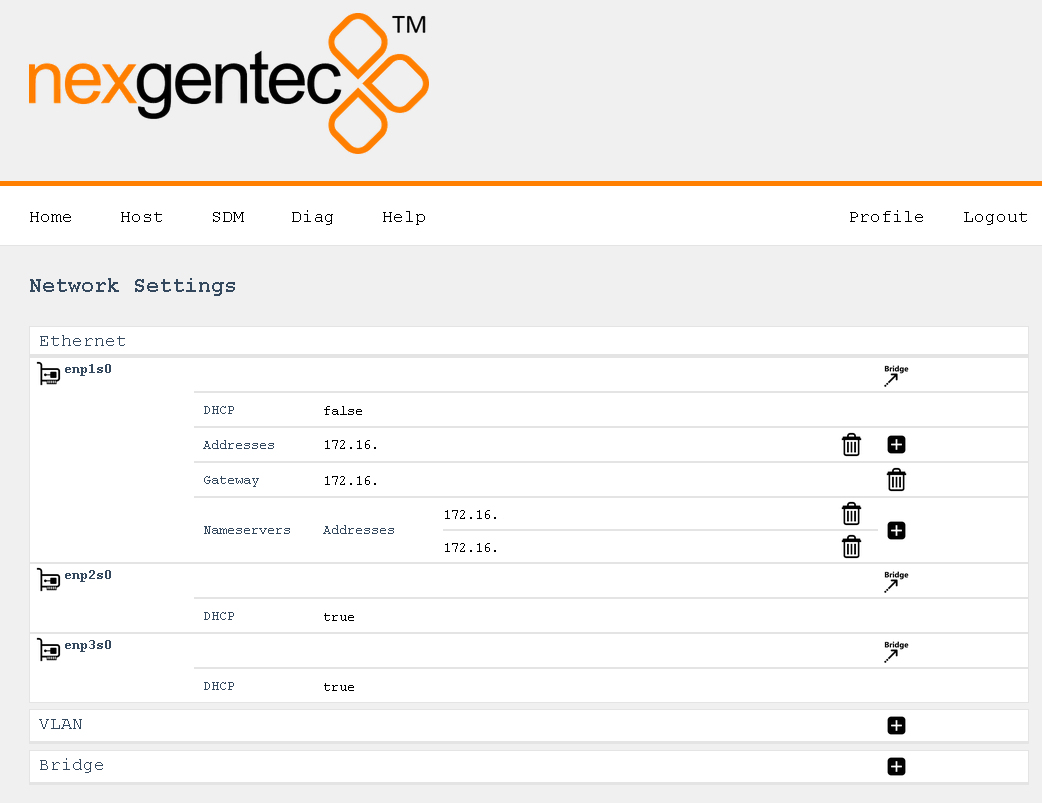
Continuing with the example above, this would look like:
Detailed Field Descriptions for “Switches”
Name
- Read-only: This field displays the name of the switch to be configured. “vswitch1” is the switch to be configured. Currently, only one virtual switch is allowed.
Multicast Snooping
- This setting allows the switch to observe and learn the multicast groups and associated members to limit the forwarding of multicast traffic. Use with caution. If you experience any problems with multicast streams flowing towards the unit or passing through it, turn this setting off.
Multicast Querier
- This setting allows the switch to send out network queries to determine which hosts belong to which multicast groups. It will be automatically set to false once the Endpoint for Audio is included in a tagged VLAN on any of the physical ports. Use it only when there is no managed switch in the network that could send out the query.
Detailed Field Descriptions for “Ports”
Link Address
- Read-only: This field displays the MAC address assigned to the port.
Switch Member
- This setting determines whether to include or exclude the physical port from being used by the managed switch.
VLAN Untagged
- This setting allows you to specify which VLANs should have their tags removed when traffic is sent out of this port.
VLAN Tagged
- This setting allows you to specify which VLANs should retain their tags when traffic is sent out of this port.
Detailed Field Descriptions for “Endpoints”
Name
- Read-only: This field displays the name of the endpoint.
Link Address
- This field displays the MAC address assigned to the endpoint.
Switch Member
- This setting determines in which virtual switch the endpoint should be included.
Usage
- This field indicates how the endpoint is being used in the network setup, either for Control, Audio, or both.
VLAN Untagged
- This setting allows you to specify which VLANs should be included and have their tags removed when traffic is sent out of this endpoint.
DHCP
- This setting enables or disables the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for the endpoint. If enabled, the endpoint will automatically receive an IP address from the DHCP server in the network.
Addresses
- This field displays the IP addresses assigned to the endpoint. The notation is in CIDR notation.
Routes (To)
- This field displays the routing table for the endpoint, showing where traffic will be directed. To add a default route (gateway), enter To: 0.0.0.0/0 Via: Gateway Address.
Nameservers
- This field displays the IP addresses of the DNS servers that the endpoint is configured to use.
Time
Status
You can view the status of the time on the status page by navigating to System > Time > Status.

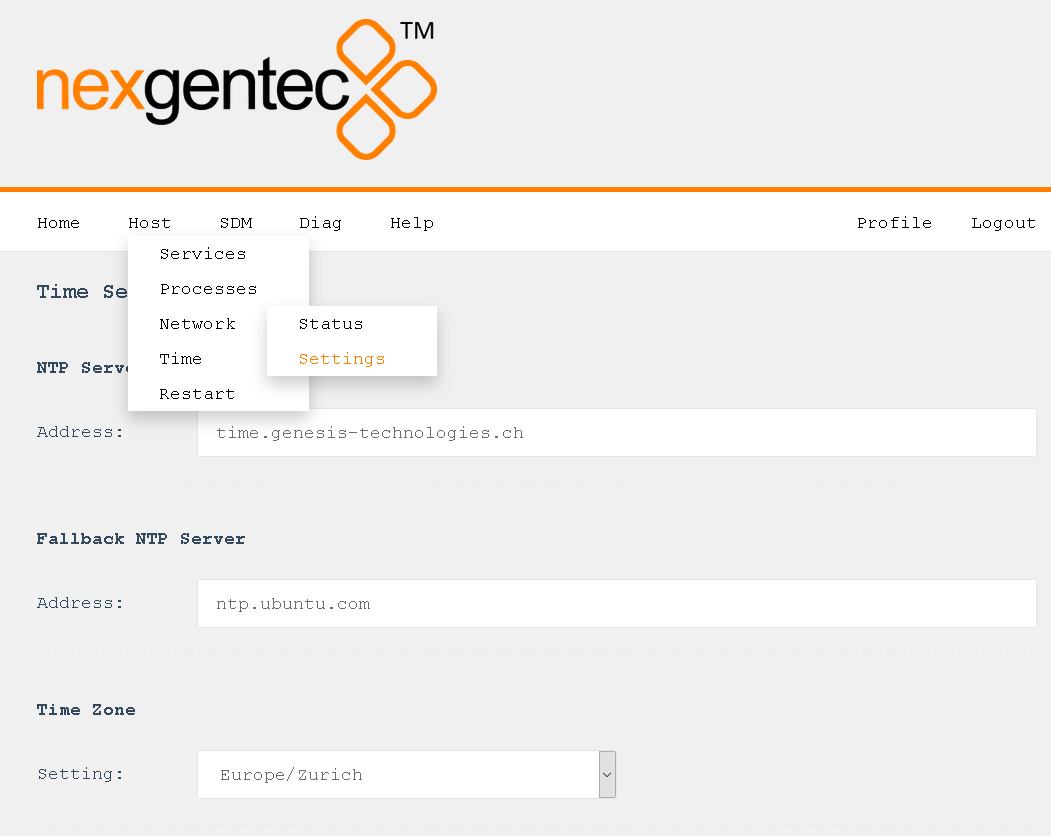
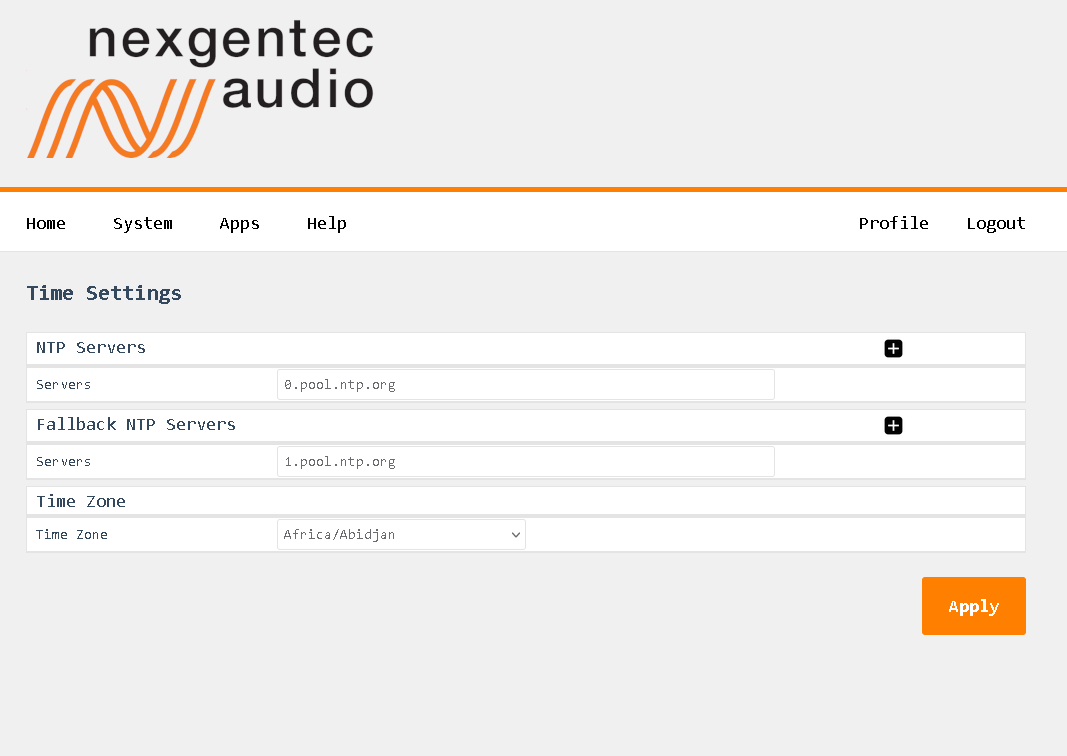
Configuration
Select in the top menu System > Network > Settings

Detailed Field Description
NTP Server
- Enter a reachable NTP server that is geographically close to you.
Fallback NTP Server
- Enter another reachable NTP server that is geographically close to you. This server will be queried if the first server becomes unreachable.
Time Zone
- Select the time zone that you are in.
Control APIs
Control the Bluetooth Interface over TCP and HTTP using JSON-RPC 2.0
This is a preliminary api documentation, subject to change
Subsections of Control APIs
JSON RPC 2.0 API
This section describes the communication protocol between the control system and the BTIR3 using RPC calls using the JSON-RPC 2.0 protocol
Definitions
Commands must be formatted as defined in the JSON-RPC 2.0 protocol
All commands sent over TCP transport must end with <LF>
All replies are formatted as defined in the JSON-RPC 2.0 protocol
All replies over TCP transport end up with <LF>
<LF> stands for “line feed”, corresponding hex is 0x0A
Transport protocols
JSON-RPC 2.0 commands can flow over different transport protocols, they need to be enabled in the config file of the installed api service. Per default they might not be enabled.
| Transport | Config | Datatype | Example | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCP | jrpc2TCPInterface | string | eth1 | >v1.0.1 |
| TCP | jrpc2TCPPort | int | 64823 | >v1.0.1 |
| TCP | jrpc2HTTPInterface | string | eth1 | >v1.0.1 |
| TCP | jrpc2HTTPPort | int | 64880 | >v1.0.1 |
In subsequent pages all methods are described that can be used.
Concurrency
All JSON-RPC 2.0 services do support asynchronous message processing. 3rd party control Systems must keep tracking of the id’s to determine whether a request was successful or not
TCP transport
Any TCP capable application can be used to test commands. Do not forget to end up with <LF>
HTTP transport
The body of the HTTP POST request must contain the complete JSON-RPC request message, encoded with Content-Type: application/json. Either a single request object or a list of request objects is supported. If the request completes, whether or not there is an error, the HTTP response is 200 (OK) for ordinary requests or 204 (No Response) for notifications, and the response body contains the JSON-RPC response. If the HTTP request method is not “POST”, BTIR3 reports 405 (Method Not Allowed). If the Content-Type is not application/json, BTIR3 reports 415 (Unsupported Media Type).
Test from a linux shell:
curl -i -X POST -H ‘Content-Type: application/json’ -d ‘{“jsonrpc”:“2.0”,“id”:1,“method”:“rpc.serverInfo”}’ http://host:64880
Subsections of JSON RPC 2.0 API
bluetooth
bluetooth commands are generic commands for all nexgentec™ devices that support Bluetooth. These commands utilize the generic Bluetooth protocol, enabling seamless integration and control across supported devices.
bluetooth.config.set
Change the Bluetooth configuration
Request
The mute function only works if playback is currently active.
The defaults parameter clears all configurations and ignores all other parameters sent with it.
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.config.set | >=v1.0.16 | |||
| name | string | Bluetooth Name | >=v1.0.16 | |
| status | 0,1 | Power on (1) or off (0) | >=v1.0.16 | |
| pairing | 0,1 | activate pairing (1) or deactivate (0) | >=v1.0.16 | |
| reconnect | 0-15 | activate and retry reconnect (1-15) or deactivate (0) | >=v1.0.16 | |
| pairingMode | 0,1 | Yes/no (1) or auto (0) | >=v1.0.16 | |
| mute | 0,1 | Mute (1) or Unmute (0) | >=v1.0.16 | |
| defaults | 1 | All Settings to Default (1) | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"method": "bluetooth.config.set",
"params": {
"pairing": 1,
"status": 1,
"pairingMode": 1,
"name": "MyBTDev",
"reconnect": 1
},
"id": 1,
"jsonrpc": "2.0"
}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}bluetooth.config.get
Get the Bluetooth configuration
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.config.get | >=v1.0.16 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"bluetooth.config.get"}Reply
| Result | Key | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| config | ||
| pairing | 1 if pairing is active, 0 if pairing is deactivated | |
| media | Read only max refresh rate of media info | |
| status | 1 if bluetooth antenna is active, 0 if not active | |
| pairingMode | 1 for Yes/No, 0 for Auto pairing | |
| codecs | Read only activated codecs | |
| address | Read only Bluetooth MAC Address | |
| error | null if there is no error on the channel; otherwise, displays the error message. | |
| profiles | Read only activated profiles | |
| name | Bluetooth Name | |
| firmware | Firmware version of Bluetooth Interface | |
| reconnect | 1-15 if active and retry, 0 no reconnect |
{
"result": {
"pairing": 0,
"media": {
"playProgRate": 5,
"trackID3Info": 1
},
"status": 1,
"pairingMode": 1,
"codecs": {
"sbc": 1,
"aac": 1,
"aptxLL": 1,
"aptxHD": 1,
"aptxAD": 1,
"aptx": 1
},
"defaults": null,
"address": "dc:0d:30:40:73:4a",
"error": null,
"profiles": {
"a2dpSource": 0,
"bisSink": 0,
"cisSink": 1,
"a2dpSink": 1
},
"name": "ngt-btir3-8c1f648a427a",
"mute": null,
"firmware": "V1.1.6",
"reconnect": 5
},
"id": 481,
"jsonrpc": "2.0"
}bluetooth.config.subscribe
This method enables push notifications for configuration changes of the Bluetooth chip. The pushed status messages follow the same format as the bluetooth.config.get replies.
Subscribe to receive real-time updates about configuration changes of the Bluetooth chip.
Push messages over HTTP transport are not supported.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.config.subscribe | >=v1.0.16 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"bluetooth.config.subscribe"}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}bluetooth.config.unsubscribe
Unsubscribe all Bluetooth config change push messages
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| amplifier.channels.unsubscribe | >=v1.0.16 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"bluetooth.config.unsubscribe"}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}bluetooth.peer.set
Set various aspects of the peer (connected Bluetooth device).
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.peer.set | volume | 0-15 | Set the volume. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "bluetooth.peer.set",
"params": {
"volume": 10
}
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": null
}bluetooth.peer.get
Retrieve all information about the connected peer (connected Bluetooth device).
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.peer.get | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "bluetooth.peer.get"
}Reply
| Result | Key | Comment |
|---|---|---|
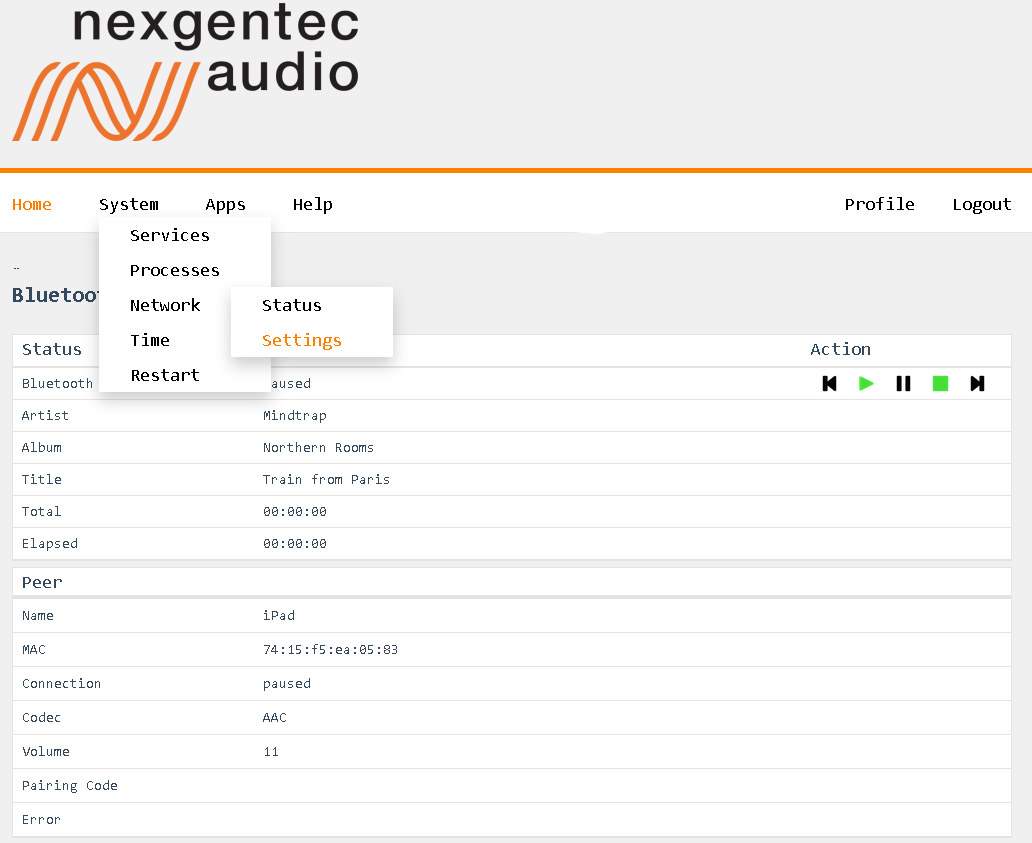
| peer | ||
| mac | Bluetooth MAC address of the connected device. | |
| media | All media information, including artist, title, album, elapsed time, and total duration. | |
| connection | The current connection state: unsupported, standby, connecting, connected, paused, streaming. | |
| volume | The current volume level of the Bluetooth device. | |
| error | null if there is no error; otherwise, displays the error message. | |
| node | The unique identifier of the Bluetooth module. | |
| name | The name of the connected Bluetooth device. | |
| codec | The audio codec being used (e.g., AAC, SBC). | |
| pairCode | The pairing code, if applicable; otherwise, null. |
{
"result": {
"mac": "74:15:f5:ea:05:83",
"media": {
"artist": "Hosini & Jones",
"elapsed": 3754,
"total": 288011,
"title": "Grön",
"state": "playing",
"album": "Cafe del Mar ChillWave 3"
},
"connection": "streaming",
"volume": 11,
"error": null,
"node": "ngt-btir3-8c1f648a427c",
"name": "iPad",
"codec": "AAC",
"pairCode": null
},
"id": 180,
"jsonrpc": "2.0"
}bluetooth.peer.subscribe
This method enables push notifications for status changes of the connected Bluetooth peer. The pushed status messages follow the same format as the bluetooth.peer.get replies.
Subscribe to receive real-time updates about the connected peer’s status.
Push messages over HTTP transport are not supported.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.peer.subscribe | Subscribe to peer status changes. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "bluetooth.peer.subscribe"
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": null
}bluetooth.peer.unsubscribe
Unsubscribe from all status change messages for the connected Bluetooth peer (connected Bluetooth device).
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.peer.unsubscribe | Unsubscribe from peer status changes. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "bluetooth.peer.unsubscribe"
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": null
}bluetooth.peer.transport
Control playback and transport actions for the connected Bluetooth device.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.peer.transport | play | 1 | Start playback. | >=v1.0.16 |
| bluetooth.peer.transport | stop | 1 | Stop playback. | >=v1.0.16 |
| bluetooth.peer.transport | pause | 1 | Pause playback. | >=v1.0.16 |
| bluetooth.peer.transport | skipfwd | 1 | Skip to the next track. | >=v1.0.16 |
| bluetooth.peer.transport | skiprev | 1 | Skip to the previous track. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "bluetooth.peer.transport",
"params": {
"play": 1
}
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": null
}bluetooth.peer.release
Release the currently connected Bluetooth peer (connected Bluetooth device).
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.peer.release | Release the connected Bluetooth peer. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "bluetooth.peer.release"
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": null
}bluetooth.peers.release
Release all currently connected Bluetooth peers (connected Bluetooth devices).
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.peers.release | Release all connected Bluetooth peers. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "bluetooth.peers.release"
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": null
}bluetooth.pairedlist.get
Retrieve a list of all paired Bluetooth devices.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.pairedlist.get | Retrieve the list of paired devices. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 68,
"method": "bluetooth.pairedlist.get"
}Reply
| Result | Key | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| result | peers | A list of paired devices, each containing the following details: |
| index: The index of the paired device. | ||
| name: The name of the paired Bluetooth device. | ||
| mac: The MAC address of the paired Bluetooth device. | ||
| error | null if there is no error; otherwise, displays the error message. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 68,
"result": {
"node": "ngt-btir3-8c1f648a427c",
"peers": [
{
"index": 1,
"name": "iPad",
"mac": "74:15:f5:ea:05:83"
},
{
"index": 2,
"name": "MyPhone",
"mac": "16:15:f5:44:2a:ab"
}
],
"error": null
}
}bluetooth.pairedlist.clear
Clear the list of all paired Bluetooth devices.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.pairedlist.clear | Clear all paired devices. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 69,
"method": "bluetooth.pairedlist.clear"
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 69,
"result": null
}bluetooth.pairedlist.remove
Remove specific devices from the paired Bluetooth devices list.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.pairedlist.remove | peers | Array of paired device objects | Specify devices to remove by index, name, or MAC address. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 71,
"method": "bluetooth.pairedlist.remove",
"params": {
"peers": [
{
"index": 2
},
]
}
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 71,
"result": null
}bluetooth.pairedlist.subscribe
Subscribe to push notifications for changes in the paired Bluetooth devices list. This is useful for receiving real-time updates when devices are added or removed from the paired list. The pushed status messages follow the same format as the bluetooth.pairedlist.get replies.
Subscribe to receive real-time updates about paired list changes.
Push messages over HTTP transport are not supported.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.pairedlist.subscribe | Subscribe to paired list changes. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 232,
"method": "bluetooth.pairedlist.subscribe"
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 232,
"result": null
}bluetooth.pairedlist.unsubscribe
Unsubscribe from push notifications for changes in the paired Bluetooth devices list, stopping any further updates about paired list changes.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.pairedlist.unsubscribe | Unsubscribe from paired list changes. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 233,
"method": "bluetooth.pairedlist.unsubscribe"
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 233,
"result": null
}bluetooth.acl.get
Retrieve the current Access Control List (ACL) for Bluetooth devices.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.acl.get | Retrieve the current ACL. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 101,
"method": "bluetooth.acl.get"
}Reply
| Result | Key | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| result | rules | A list of ACL rules, each containing the following details: |
| mac: The MAC address of the device. | ||
| name: Name of the device. | ||
| access: 1 for allowed devices, 0 for denied devices. | ||
| error | null if there is no error; otherwise, displays the error message. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 101,
"result": {
"rules": [
{
"mac": "90:B1:44:9A:C2:5F",
"name": "MySuperPhone1",
"access": 1
},
{
"mac": "90:B1:44:9A:C2:5E",
"name": "MySuperPhone2",
"access": 0
}
],
"error": null
}
}bluetooth.acl.clear
Clear all entries from the Access Control List (ACL).
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.acl.clear | Clear all ACL entries. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 102,
"method": "bluetooth.acl.clear"
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 102,
"result": null
}bluetooth.acl.add
Add new rules to the Access Control List (ACL).
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.acl.add | rules | Array of ACL rule objects | Specify devices to add by MAC address and access type, name not mandatory | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 103,
"method": "bluetooth.acl.add",
"params": {
"rules": [
{
"mac": "90:B1:44:9A:C2:5F",
"name": "MySuperPhone1",
"access": 1
},
]
}
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 103,
"result": null
}bluetooth.acl.remove
Remove specific rules from the Access Control List (ACL).
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.acl.remove | rules | Array of ACL rule objects | Specify devices to remove by MAC address or Name | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 104,
"method": "bluetooth.acl.remove",
"params": {
"rules": [
{
"mac": "90:B1:44:9A:C2:5E"
}
]
}
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 104,
"result": null
}bluetooth.acl.subscribe
Subscribe to push notifications for changes in the Access Control List (ACL). This is useful for receiving real-time updates about modifications to the ACL, such as adding or removing devices.
The pushed status messages follow the same format as the bluetooth.acl.get replies.
Subscribe to receive real-time updates about ACL changes.
Push messages over HTTP transport are not supported.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.acl.subscribe | Subscribe to ACL changes. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 240,
"method": "bluetooth.acl.subscribe"
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 240,
"result": null
}bluetooth.acl.unsubscribe
Unsubscribe from push notifications for changes in the Access Control List (ACL), stopping any further updates about ACL changes.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.acl.unsubscribe | Unsubscribe from ACL changes. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 241,
"method": "bluetooth.acl.unsubscribe"
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 241,
"result": null
}bluetooth.acl.config.get
Retrieve the current Access Control List (ACL) configuration.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.acl.config.get | Retrieve the ACL configuration. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 119,
"method": "bluetooth.acl.config.get"
}Reply
| Result | Key | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| result | defaultLevel | 1 if new devices are allowed after pairing, 0 if they are rejected. |
| error | null if there is no error; otherwise, displays the error message. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 119,
"result": {
"defaultLevel": 1,
"error": null
}
}bluetooth.acl.config.set
Set the default Access Control List (ACL) configuration.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.acl.config.set | defaultLevel | 1, 0 | 1 to allow new devices after pairing, 0 to reject them. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 105,
"method": "bluetooth.acl.config.set",
"params": {
"defaultLevel": 0
}
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 105,
"result": null
}If the default level is set to 0, all new paired devices are rejected by default. Ensure to manually add allowed devices to the ACL using the web interface or the API.
Similarly, if the default level is set to 1, all devices are allowed by default. You can later restrict access by modifying the ACL.
bluetooth.acl.config.subscribe
Subscribe to push notifications for changes in the Access Control List (ACL) configuration.
The pushed status messages follow the same format as the bluetooth.acl.config.get replies.
Subscribe to receive real-time updates about ACL configuration changes.
Push messages over HTTP transport are not supported.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.acl.config.subscribe | Subscribe to ACL configuration changes. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 236,
"method": "bluetooth.acl.config.subscribe"
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 236,
"result": null
}bluetooth.acl.config.unsubscribe
Unsubscribe from push notifications for changes in the Access Control List (ACL) configuration.
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bluetooth.acl.config.unsubscribe | Unsubscribe from ACL configuration changes. | >=v1.0.16 |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 237,
"method": "bluetooth.acl.config.unsubscribe"
}Reply
| Result | Comment |
|---|---|
| null | null means the request was successful, with no errors. |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 237,
"result": null
}fb12 bluetooth service
fb12 commands are specific to BTIR3 nexgentec™ devices. These commands are used to control the fb12 Bluetooth service, which is a chip-specific service designed for BTIR3 devices.
fb12.app.log.level.get
Get the log level for the fb12 Bluetooth service running on the BTIR3
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fb12.app.log.level.get | >=v1.0.16 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"fb12.app.log.level.get"}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| x | Active log level |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":20,"result":{"level":3}}fb12.app.log.level.set
Set the log level for fb12 service and associated processes
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fb12.app.log.level.set | level | 0-7 | Log level to set | >=v1.0.16 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"fb12.app.log.level.set","params":{"level":6}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}api
api commands are generic commands for all nexgentec™ devices that have an API. These commands utilize the generic API protocol, enabling seamless integration and control across supported devices.
api.app.log.level.get
Get the log level for the api service running on the api
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| api.app.log.level.get | >=v1.0.16 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"api.app.log.level.get"}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| x | Active log level |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":20,"result":{"level":3}}api.app.log.level.set
Set the log level
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| api.app.log.level.set | level | 0-7 | Log level to set | >=v1.0.16 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"api.app.log.level.set","params":{"level":6}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}server
server commands are generic commands for all Nexgentec™ devices that support a JSON-RPC 2.0 API. These commands provide a standard JSON-RPC method to retrieve the list of supported methods available on the device.
rpc.server.info.get (serverInfo)
Get all supported RCP methods
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rpc.serverInfo | >1.0.1 | |||
| rpc.server.info.get | >=1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"rpc.serverInfo"}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"rpc.server.info.get"}Reply
| Result | Key | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| methods | All supported methods that can be used by a 3rd party control system | |
| counters | Server counters | |
| startTime | Server start time |
{
"result": {
"startTime": "2025-04-01T12:45:20.908934559Z",
"metrics": {
"bytes_written": 364,
"rpc_requests": 3,
"bytes_read": 165,
"notifications_pushed": 0,
"rpc_errors": 1,
"servers_active": 2,
"calls_pushed": 0
},
"methods": [
"api.app.log.level.get","api.app.log.level.set","api.app.version.get","api.appLogLevelGet","api.appLogLevelSet","api.appVersionGet","bluetooth.acl.add","bluetooth.acl.clear","bluetooth.acl.config.get","bluetooth.acl.config.set","bluetooth.acl.config.subscribe","bluetooth.acl.config.unsubscribe","bluetooth.acl.get","bluetooth.acl.remove","bluetooth.acl.subscribe","bluetooth.acl.unsubscribe","bluetooth.config.get","bluetooth.config.set","bluetooth.config.subscribe","bluetooth.config.unsubscribe","bluetooth.pairedlist.clear","bluetooth.pairedlist.get","bluetooth.pairedlist.remove","bluetooth.pairedlist.subscribe","bluetooth.pairedlist.unsubscribe","bluetooth.peer.get","bluetooth.peer.release","bluetooth.peer.set","bluetooth.peer.subscribe","bluetooth.peer.transport","bluetooth.peer.unsubscribe","bluetooth.peers.release","bluetooth.pl.clear","bluetooth.pl.get","bluetooth.pl.remove","fb12.app.log.level.get","fb12.app.log.level.set","fb12.app.version.get","rpc.server.info.get","rpc.serverInfo"]
},
"id": 2,
"jsonrpc": "2.0"
}Specifications
| OS Support | |
| OS | iOS, PC, MAC and Android |
| Bluetooth | |
| Standards | V5.4 down to V1.1, Class 1.5 |
| Band | 2.402 – 2.480 GHz |
| Audio Format | SBC, AAC, APTX, APTX-HD, APTX-AD, APTX-LL |
| Profiles | A2DP Sink, LE-Audio Unicast Sink |
| Digital Audio Output | |
| Type | 8 channels, full range |
| Format | Dante™, Aes67 |
| Network Port eth1 | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 10/100/1000 Mbps Full Duplex |
| PoE Standards | IEEE 802.3at |
| PoE Classes | 0 |
| Network Port eth2 | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 10/100/1000 Mbps Full Duplex |
| General | |
| Power | POE, 10W max |
| Total heat dissipation | max 10.00 BTU/hr |
| Operating temp | 5°C – 30°C |
| Dimensions | L: 110mm, W: 74mm, H:25mm |
| Compliance | CE, ROHS |
Audio Channel Assignment
| Channel | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 1 | Left Channel |
| 2 | Right Channel |
CAD step file
ngtOS
Never downgrade to an older ngtOS, as it will result in a factory return of the unit in every case.
If you have multiple units to update, try the update on one and if it’s working as expected, proceed with all others.
Update Path
- All units must be updated to 1.0.16 (beta-rc6) before upgrading to any higher version of ngtOS.
- Future update paths will be published when available.
Update Notes
Version 1.0.16 (beta-rc6)
- Initial version of ngtOS that supports Bluetooth
Plan the Update
- Ensure that the unit you plan to update is connected to a network with unfiltered internet access. This is necessary in case service personnel need to access the unit using the built-in support tool.
- Make sure that you are within the office hours of Nexgentec Audio AG Switzerland (8am to 4pm CET +1).
- Ensure that no one else is working on the network during the time of the update.
Run the Update
The default login for the web interface is: Username: admin Password: nexgentec
- Open a browser and enter the IP address of the unit into the address bar.
- Log into the web interface using username and the chosen password.
- In the top menu bar, select ‘Help’ > ‘Update’.
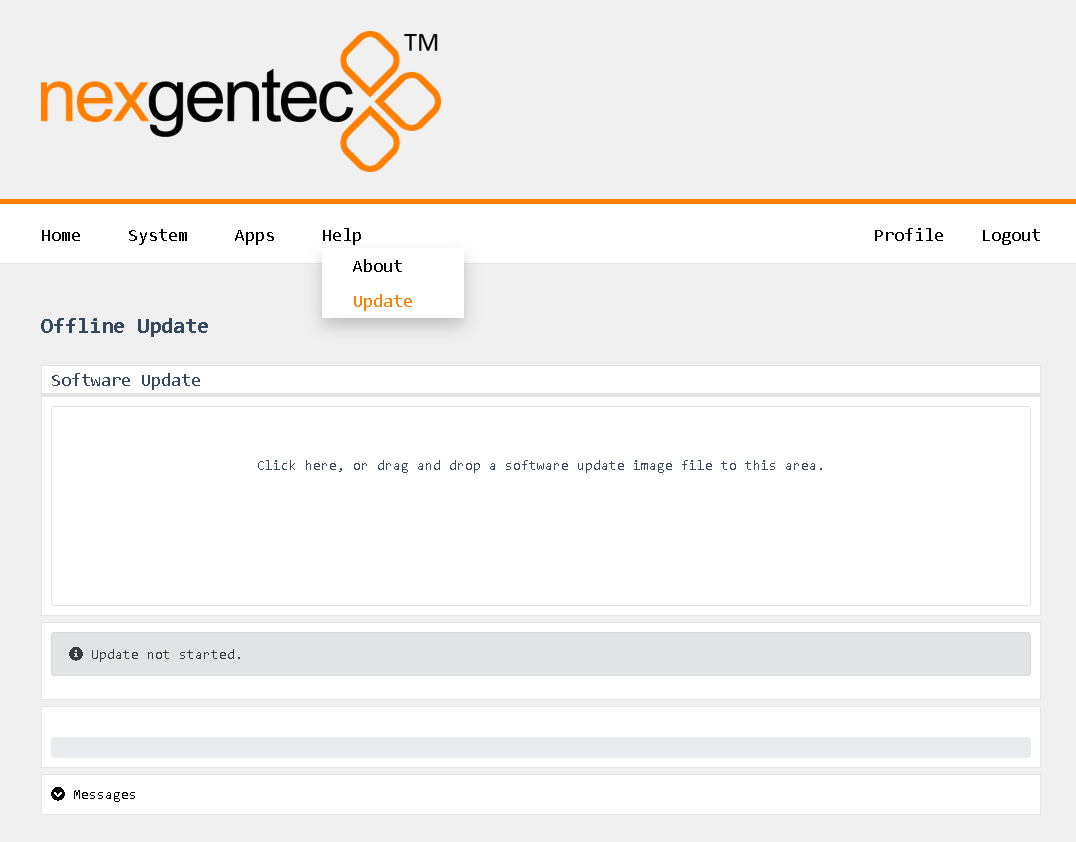

- Follow the instructions shown.
- Wait for the unit to reboot
Change Log
Version 1.0.16 (beta-rc6)
- Initial version of ngtOS that supports Bluetooth
Known Issues
Version 1.0.16 (beta-rc6)
- WebUI: Clustering configuration is missing
- WebUI: Mandatory password change feature is missing
- SNMP: Missing
Upcoming Features
Features Awaiting Implementation:
- User configuration support for clustering
- SNMP support
BTIR2
The NGTC-BTIR2 is a universal Bluetooth® AES67 enabled audio interface for the nexgentec™ audio distribution solution.
It features an API for navigation, configuration and management.
The NGTC-BTIR2 is a Bluetooth 5.0 to AES67 audio gateway that can be used in sink or source mode. It supports all current audio codes and it is compatible with all the different Bluetooth sources and sinks. It has 2x2 AES67 channels with an interface for audio processing by the NGTC digital signal processor.
It can be easily interfaced with 3rd party control systems via the API on the communication control network port.
It is powered by POE on the AES67 port. Its own web UI is used to configure the AES67 interface. The additional LAN port is only used for control and can be configured by web UI.
Subsections of BTIR2
Installation
The NGTC-BTI Bluetooth interface is working in the 2.4Ghz band. It is essential to mount it as “free” are possible in the space to not reduce reception. Any metal shielding should be avoided!
The BTI should be mounted on a flat surface with it’s two mounting brackets
- AES67 network interface (POE)
- Control network interface
- Blutooth Area, keep clear!
- Mounting Bracket Positions
All connections to the NGTC-BTI should be made before power is applied
• Attach the LAN network port to the control network switch, using an UTP CAT-5 cable
• Attach the AES67 network port to the AES67/Dante POE network switch, using an UTP CAT-5 cable.
Configuration
Setup interoperability between BTI and Dante devices
AES67 interoperability settings are required for every Dante device that should receive a AES67 stream
To enable your Dante devices to receive an AES67 stream, AES67 interoperability must be enabled. This is done by using Audinate’s Dante Controller, which can be obtained from the Audinate website or any other manufacturer specific software tool.
In Dante controller all your Dante devices that are connected to the network will show up automatically.
- Start the Dante Controller Software and wait for it to be synchronized with the network
- Select the “device info” tab in the software
- Double click on the DSP you would like to configure for AES67, a new window will open
- Select the “AES67 config” tab
- Enable AES67 mode and make a note of the Tx multicast prefix. You will need this number later, even if you are not using the DSP as a transmitter. This must be the same for all DSP’s that are ready for AES67.
- Reboot the Dante device
- This needs to be done with every Dante device that will receive an AES67 stream
Subsections of Configuration
Control Network Setup
Control Network Address Setup
The setup of the control network of the BTI will be done via it’s Web UI. It is self-explaining
By default the interface is set to DHCP
Please make sure your computer network address is in the same network range to access the setup pages
Default web UI username and password
admin
Refer to the MAC address if multiple MCP’s are in the network to identify the right unit. The MAC address is also printed on each units bottom cover as QR Code.
To reset the control network address use the USR IOT tool
The tool does allow you to search and reset the network settings
AES67 Network Setup
To configure the AES67 download latest generation Audio Grid Controller Software. Your PC needs to be connected to the AES67 network and have its addressing set in the same IP range.
AES67 Network Address Setup
Start the software and go to the “Device Config” tab
- Select the device to be configured
- Enter “IP Address” and “Subnet Mask”
- Hit “Apply”
AES67 Stream Address Setup
The AES67 stream of each device needs to be configured to be received by the Dante/AES67 devices
Start the software and go to the “Device Config” tab
- Select the device to be configured
- Select “Create / Delete” in the “Multicst flow” selection
- In the Multicast flow config, click on “AG” first and then on “AES67”. Next, select the “Manual IP and Port” option.
- You can set your desired multicast IP. Typically in combination with Dante Audio products, the multicast IP starts with “239.69.”, port 5004.
- Select the channels that should be multicast.
- Click on “Create”.
Audio Routing using Audinate’s Dante Controller
Natively the audio routing can be done by using Audinate’s Dante Controller in case if its not auto configured by the DSP’s management software. In Dante Controller all your Dante and AES67 devices that are connected to the network will show up automatically.
The BTI will be shown at the ‘‘Dante Transmitters’’ part, using its multicast address@hostname-HH-HH-HH where ‘‘HH-HH-HH’’ are the last three bytes of the devices MAC address.
- Make the audio connections in the Dante controller
Control API
This section describes the communication protocol between the control system and the BTI
The BTI Configurator does use the same protocol, see its debug window for more information
Please use >80ms between each command sent
| Connection | TCP (NGTC-BTI is server), Port 20108 |
| Command Format | AT+ Command {=Param1{, Param2{, Param3…}}}<CR><LF> |
| Reply Format | <CR><LF>+reply {=Param1{, Param2{, Param3…}}} <CR><LF> |
<CR> stands for “carriage return”, corresponding hex is 0x0D
<LF> stands for “line feed”, corresponding hex is 0x0A
Command Format Details
All commands start with “AT”, end with <CR><LF>
If a command has a parameter, the parameter is behind the “=”
If a command has multiple parameters, the parameters must be separated by “,”
Reply Format Details
All replies start with <CR><LF> and end with <CR><LF>
If a reply has a parameter, the parameter is behind the “=”
If a reply has multiple parameters, the parameters must be separated by “,”
The interface will always report the execution result using “OK” for success or “ERROR” for failure
Examples
Read BTI’s Bluetooth name
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+NAME<CR><LF> |
||
AT+NAME<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+NAME=NGTC-BTI<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Set BTI’s Bluetooth name
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+NAME=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| NGTC-BTI | |||
AT+NAME=NGTC-BTI<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Subsections of Control API
General
Request firmware version
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+VER<CR><LF> |
||
AT+VER<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>>+VER=20171125,NGTC-BTI<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Bluetooth General
Request Bluetooth MAC address
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+ADDR<CR><LF> |
||
AT+ADDR<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>>+ADDR=DC0D30123456<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request Bluetooth name
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+NAME<CR><LF> |
||
AT+NAME<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+NAME=NGTC-BTI<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Set Bluetooth name
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+NAME=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| NGTC-BTI | |||
AT+NAME=NGTC-BTI<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Release all Bluetooth connections
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+DSCA<CR><LF> |
||
AT+DSCA<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Release all Bluetooth connections and reboot
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+REBOOT<CR><LF> |
||
AT+REBOOT<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Set Bluetooth discoverability and connection
- Undiscoverable = disconnect all devices connected and set’s the NGTC-BTI into an unconnectable and undiscoverable mode
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+BTEN=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Undiscoverable | |||
| 1: operational | |||
AT+BTEN=1<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request Bluetooth discoverability and connection
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+BTEN<CR><LF> |
||
AT+BTEN<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+BTEN=1<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request operation status
Status parameter will be reported in bit representation
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+DEVSTAT<CR><LF> |
||
| BIT[0]: PWR OFF; 1: PWR ON | |||
| BIT[1]: Non Discoverable; 1: Discoverable | |||
| BIT[2]: Non Advertising; 1: Advertising | |||
| BIT[3]: Non Scanning; 1: Scanning | |||
AT+DEVSTAT<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+DEVSTAT=9<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Set auto connect
This command needs a reboot to activate
- The NGTC-BTI will attempt to reconnect last device after power on
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+AUTOCONN=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Off | |||
| 1: 15 Attempts | |||
AT+AUTOCONN=0<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request auto connect
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+AUTOCONN<CR><LF> |
||
AT+AUTOCONN<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+AUTOCONN=1<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Restore all Bluetooth parameters to factory default
BTI module needs to be power cycled afterwards
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+RESTORE<CR><LF> |
||
AT+RESTORE<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Bluetooth Audio
Set volume of connected Bluetooth device
Please watch the volume carefully
There is no real standard for the source volume.
If you all the way to 15, you may overload the interface and it will result in distortion
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+SPKVOL=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| +: UP | |||
| -: DOWN | |||
AT+SPKVOL=+<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request volume of connected Bluetooth device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+SPKVOL<CR><LF> |
||
AT+SPKVOL<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+SPKVOL=10<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Operation Mode
Set operation mode
BTI module will reboot and all device profiles will be deleted
- Set’s the NGTC-BTI to sink(stream from device to BTI or source) or source(stream from BTI to headphone)
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPROLE=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Sink | |||
| 1: Source | |||
AT+A2DPROLE=0<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request operation mode
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPROLE<CR><LF> |
||
AT+A2DPROLE<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPROLE=1<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Sink Mode
To use the commands below the BTI needs to be switched to sink mode first
Set pairing active/inactive
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PAIR=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Off | |||
| 1: On | |||
AT+PAIR=1<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request pairing active/inactive status
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PAIR<CR><LF> |
||
AT+PAIR<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+PAIR=1<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Activate simple/secure pairing
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+SSP=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Off | |||
| 1: On | |||
AT+SSP=1<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request simple/secure pairing status
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+SSP<CR><LF> |
||
AT+SSP<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+SSP=0<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Set BTI’s pin code
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PIN=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 4-15 ASCII numbers | |||
AT+PIN=1234<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request BTI’s pin code
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PIN<CR><LF> |
||
AT+PIN<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+PIN=1234<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Clear a paired record
If the device (headphone/speaker) is deleted in the BTI it needs to be reconnected to work
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PLIST=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Clear list | |||
| x: Clear index (x) | |||
AT+PLIST=E<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request paired records
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PLIST<CR><LF> |
||
AT+PLIST<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+PLIST=1,123456ABCDEF <CR><LF><CR><LF>+PLIST=1,ABCDEF123456 <CR><LF><CR><LF>+PLIST=E <CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Reconnect to Bluetooth device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPCONN=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| No parameter: To last device | |||
| MAC: Mac of target device (12 Bytes ASCII) | |||
AT+A2DPCONN=123456ABCEDF<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPCONN=123456ABCEDF<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Release Bluetooth connection to device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPDISC<CR><LF> |
||
AT+A2DPDISC<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request status of connected device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPSTAT<CR><LF> |
||
AT+A2DPSTAT<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPSTAT=4<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Unsupported | |||
| 1: Standby | |||
| 2: Connecting | |||
| 3: Connected | |||
| 4: Streaming | |||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Nofification address of connected device
Event at device connection only, cannot be requested by control system
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPDEV=123456ABCDEF <CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request codex used by the connected device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPDEC<CR><LF> |
||
AT+A2DPDEC<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPDEC=1<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Invalid | |||
| 1: SBC | |||
| 2: MP3 | |||
| 3: AAC | |||
| 4: FASTSTREAM | |||
| 5: APTX | |||
| 6: APTX-Sprint | |||
| 7: APTX-HD | |||
| 8: APTX-LL | |||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Set ID track feedback
This command needs a reboot to activate
- Parameter: Default is 11, Base 10 representation of a bit
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+AVRCPCFG<CR><LF> |
||
| BIT[0]: Auto get rack ID3 information (title, artist, album) on track changed (default 1) | |||
| BIT[1-3]: Auto get track state (play progress) if value >0 (default 5sec) | |||
AT+AVRCPCFG=11<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request status of connected device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+AVRCPSTAT<CR><LF> |
||
AT+AVRCPSTAT<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+AVRCPSTAT=4<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Unsupported | |||
| 1: Standby | |||
| 2: Connecting | |||
| 3: Connected | |||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Nofification Mediaplayer play progress
Event at device connection only, cannot be requested by control system
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Param1: (0-4) Media Player State – please see PLAYSTAT parameters | |||
| Param2:(Decimal ASCII), Elapsed time of current track in ms | |||
| Param3:(Decimal ASCII), Total time of track in ms | |||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+TRACKSTAT=1,142000,248000 <CR><LF> |
Nofification Mediaplayer track info
Event at device connection only, cannot be requested by control system
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Param1: Title | |||
| Param2: Artist | |||
| Param3: Album | |||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+TRACKINFO=Creep<FF>Radiohead<FF>Pablo Honey <CR><LF> |
Nofification Mediaplayer status of the connected device
Event at device connection only, cannot be requested by control system
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0: Stopped | |||
| 1: Playing | |||
| 2: Paused | |||
| 3: Fast Forward | |||
| 4: Fast Rewind | |||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+PLAYSTAT=1<CR><LF> |
Transport Play/Pause
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PLAYPAUSE<CR><LF> |
||
AT+PLAYPAUSE<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Transport Play
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PLAY<CR><LF> |
||
AT+PLAY<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Transport Pause
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PAUSE<CR><LF> |
||
AT+PAUSE<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Transport Stop
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+STOP<CR><LF> |
||
AT+STOP<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Transport Track Forward
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+FORWARD<CR><LF> |
||
AT+FORWARD<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Transport Track Backward
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+BACKWARD<CR><LF> |
||
AT+BACKWARD<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Source Mode
To use the commands below the BTI needs to be switched to source mode first
Set autoscan
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+INQCFG=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Off | |||
| 1: On | |||
AT+INQCFG=1<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request autoscan status
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+INQCFG<CR><LF> |
||
AT+INQCFG<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+INQCFG=10<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Clear a paired record
If the device (headphone/speaker) is deleted in the BTI it needs to be reconnected to work
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PLIST=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Clear list | |||
| x: Clear index (x) | |||
AT+PLIST=E<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request paired records
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PLIST<CR><LF> |
||
AT+PLIST<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+PLIST=1,123456ABCDEF <CR><LF><CR><LF>+PLIST=1,ABCDEF123456 <CR><LF><CR><LF>+PLIST=E <CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Reconnect to Bluetooth device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPCONN=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| No parameter: To last device | |||
| MAC: Mac of target device (12 Bytes ASCII) | |||
AT+A2DPCONN=123456ABCEDF<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPCONN=123456ABCEDF<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Release Bluetooth connection to device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPDISC<CR><LF> |
||
AT+A2DPDISC<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request status of connected device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPSTAT<CR><LF> |
||
AT+A2DPSTAT<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPSTAT=4<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Unsupported | |||
| 1: Standby | |||
| 2: Connecting | |||
| 3: Connected | |||
| 4: Streaming | |||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Nofification address of connected device
Event at device connection only, cannot be requested by control system
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPDEV=123456ABCDEF <CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request codex used by the connected device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPDEC<CR><LF> |
||
AT+A2DPDEC<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPDEC=1<CR><LF> |
||
| 1: SBC | |||
| 5: APTX | |||
| 6: APTX-LL | |||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Specifications
| OS Support | |
| OS | iOS, PC, MAC and Android |
| Bluetooth | |
| Standards | V5 down to V1.1, Class 1.5 |
| Band | 2.402 – 2.480 GHz |
| Audio Format | All (SBC,aptx HD,LL) |
| AES67 Network with WebUI | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 100 Mbps Full Duplex |
| Control Network with WebUI | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 100 Mbps Full Duplex |
| General | |
| Power | POE, 3W max |
| Total heat dissipation | max 10.00 BTU/hr |
| Operating temp | 5°C – 30°C |
| Dimensions | L: 110mm, W: 74mm, H:25mm |
| Compliance | CE, ROHS |
Audio Channel Assignment
| Channel | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 1 | Left Channel |
| 2 | Right Channel |
CAD step file
Bluetooth facts and figures
How does Bluetooth work
The simplest explanation for how Bluetooth works is that data/audio is continuously transferred from a paired Bluetooth transmitter to a paired receiver. Pairing is just the bonding procedure between devices so that you don’t have to enter access or security information, like passwords or passkeys, each time the devices need to establish a connection. Bluetooth operates in the frequency range of (2.402 -2.480GHz). Once a secure connection is established between a transmitter and receiver, data is split into small packets, which are then transferred at alternating frequencies. The type of Bluetooth and profiles may vary, but the core architecture remains the same. To avoid interference with other devices that may also use the ISM (industrial, science, and medical) bandwidth of 2.4Ghz, Bluetooth devices randomly hop between frequencies 1600 times per second until all the packets are transferred.
Bluetooth version and profiles
The NGTC-BTI supports Bluetooth 5.x, the most recent iteration of Bluetooth. It has twice the bandwidth of V4.x. The NGTC-BTI supports only audio related transmission, no data communication or phone/handsfree functionality.
Stereo audio transmission. This is the most important profile for Bluetooth as mono audio is not suited for listening to music.
Adds control for media playback such as skipping tracks, play/pause, and meta data.
Which Bluetooth Codec is the best?
Codecs are encoding and decoding algorithms that compress audio into manageable data packets for faster or wireless transmission. The efficiency of the codec will determine the quality and rate at which the audio data is sent. SBC is the default sub-band coding for most Bluetooth devices. However, since this codec has a relatively high latency and may be a bit lossy, companies have developed their own encoding algorithms.
The mandatory and default codec for all stereo Bluetooth headphones with the Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP). It is capable of bit rates up to 328 kbps with a sampling rate of 44.1kHz. It provides fairly good audio quality without requiring a lot of processing power to encode or decode. However, the audio quality can be a bit inconsistent at times. This is especially noticeable with a cheap Bluetooth transmitter.
Similar to SBC, but with better sound quality. This codec is mostly popular with Apple’s iTunes platform and some other non-wireless applications. However, it’s not very common, especially for headphones.
It’s ideal for demanding audio applications since it encodes audio more efficiently and at a slightly higher rate than SBC. There are also two additional variations, aptX Low Latency and aptX HD, that either drastically reduces the latency of the connection or significantly improves its audio quality. However, it’s a bit limiting, as both the Bluetooth transmitter and receiver must have aptX or its variations for the codec to work.
Latency
Codecs have a bigger impact on latency than on sound quality for most listeners. The default SBC connection typically has more than 100ms of latency, which is noticeable when listening to music but may be severe enough to ruin your movie experience. To fix some of the sync issues caused by latency, CSR developed the aptX and subsequently the aptX Low Latency codec. Regular aptX does somewhat improve latency due to its more efficient encoding algorithm than SBC. However, aptX-LL has the most noticeable impact on latency.
| Codec | Latency |
|---|---|
| SBC | 173ms |
| aptX | 166ms |
| aptx LL | 34ms |
Codecs are the algorithms that compress data for easier and faster transmission. Better encoding and decoding algorithms mean less lossy transmission which can help with audio quality. We have noticed that codecs have a bigger impact on latency than on audio quality. The subtle changes in audio quality due to a codec like aptX are negligible when compared to the reduced latency aptX Low Latency connection. However, since both Bluetooth devices (source/sink) have to support the codec for it to work, you will most often rely on the default sub-band coding (SBC), as there are not many Bluetooth devices that support aptX and even less for aptX-LL.
Firmware
Firmware
Welcome to the Firmware section!
If you are not redirected automatically, click here.
Subsections of Firmware
Firmware
Known Firmware issues
- V4.0.3: AT+PLIST command is faulty, No Audio in Master/Source mode
- V4.04: AT+PLIST command is faulty
- V4.05: Module does turn off after 10min if no source connected
Audio Card
Audio Card Firmware Update
The latest generation of BTIR2 features an AES67 daughter board that fully supports AES67, ensuring compatibility with Dante™. Additionally, these devices have mDNS discovery enabled, allowing them to be detected in the Dante Controller, similar to a Dante product.
However, starting with Dante Controller V12, a pop-up message may appear indicating that unlicensed Dante™ products are being used. To address this, the new firmware will disable Dante™ discovery, and all R2 units will be recognized as AES67 devices.
Update to the Latest AES67 only Firmware Release
- Download the latest programmer and firmware files
- Unzip the firmware files (BTI-FW_4101-4108.zip) into a folder.
- Run the updater tool (Fdt_factory1.63.exe). Note that the discovery function works for up to 10 units. If you have more units, use the IP address filter for efficient navigation.
- Open the FPGA firmware file with the updater tool (fpga_a404_4108.bit).
- Open the MCU firmware file with the updater tool (mcu_407d_4101.bin).
- Update all units with the new MCU by clicking in the field MCU Upgrade.
- Update all units with the new FPGA by clicking in the field FPGA Upgrade.
- Select all updated units in the latest row for reboot.
- Click “Reboot”.
After the reboot, click “Refresh” to update the device list. If the devices appear as expected, you can proceed with the update process.
- Open the Initialize data file with the updater tool (BTIR2-T4R6-AES67.c).
- Update all units with the new Init data fle by clicking in the field Init Data.
- Select all updated units in the latest row for reboot.
- Click “Reboot”.
After the reboot, you need to set the multicast address for AES67 to work. Use the Audio Grid Controller to do this.
Refer to the following instructions to configure it with the AudioGrid controller
Software
Configuration Software
Control4 Bluetooth Experience Button driver
BTI
The NGTC-BTI is a universal Bluetooth® AES67 enabled audio interface for the nexgentec™ audio distribution solution.
It features an API for navigation, configuration and management.
The NGTC-BTI is a Bluetooth 5.0 to AES67 audio gateway that can be used in sink or source mode. It supports all current audio codes and it is compatible with all the different Bluetooth sources and sinks. It has 2x2 AES67 channels with an interface for audio processing by the NGTC digital signal processor.
It can be easily interfaced with 3rd party control systems via the API on the communication control network port.
It is powered by POE on the AES67 port. Its own web UI is used to configure the AES67 interface. The additional LAN port is only used for control and can be configured by web UI.
Subsections of BTI
Installation
The NGTC-BTI Bluetooth interface is working in the 2.4Ghz band. It is essential to mount it as “free” are possible in the space to not reduce reception. Any metal shielding should be avoided!
The BTI should be mounted on a flat surface with it’s two mounting brackets
- AES67 network interface (POE)
- Control network interface
- Blutooth Area, keep clear!
- Mounting Bracket Positions
All connections to the NGTC-BTI should be made before power is applied
• Attach the LAN network port to the control network switch, using an UTP CAT-5 cable
• Attach the AES67 network port to the AES67/Dante POE network switch, using an UTP CAT-5 cable.
Configuration
Setup interoperability between BTI and Dante devices
AES67 interoperability settings are required for every Dante device that should receive a AES67 stream
To enable your Dante devices to receive an AES67 stream, AES67 interoperability must be enabled. This is done by using Audinate’s Dante Controller, which can be obtained from the Audinate website or any other manufacturer specific software tool.
In Dante controller all your Dante devices that are connected to the network will show up automatically.
- Start the Dante Controller Software and wait for it to be synchronized with the network
- Select the “device info” tab in the software
- Double click on the DSP you would like to configure for AES67, a new window will open
- Select the “AES67 config” tab
- Enable AES67 mode and make a note of the Tx multicast prefix. You will need this number later, even if you are not using the DSP as a transmitter. This must be the same for all DSP’s that are ready for AES67.
- Reboot the Dante device
- This needs to be done with every Dante device that will receive an AES67 stream
Subsections of Configuration
Control Network Setup
Control Network Address Setup
The setup of the control network of the BTI will be done via it’s Web UI. It is self-explaining
By default the interface is set to 192.168.4.7
Please make sure your computer network address is in the same network range to access the setup pages
Default web UI username and passwordadmin
Refer to the MAC address if multiple MCP’s are in the network to identify the right unit. The MAC address is also printed on each units bottom cover as QR Code.
To reset the control network address use the USR IOT tool
The tool does allow you to search and reset the network settings
AES67 Network Setup
AES67 Network Address Setup
To configure the AES67 network address use the built in Audiolan web UI. Your PC needs to be connected to the AES67 network and have its addressing set in the same IP range.
By default the AES67 network interface is set to the static IP address (192.168.4.233)
Avoid any special characters and spaces in the device name
- Open a browser and enter the devices AES67 network address in the address bar, press enter
- Select the “General settings” tab in the web UI to change the devices IP address
- The NGTC-MCP4kR2 should have an IP and Subnet address in the same range as the Dante devices
- Apply all settings and reboot the device
AES67 Stream Address Setup
The AES67 stream of each device needs to be configured to be received by the Dante/AES67 devices
- Open a browser and enter the devices AES67 network address in the address bar, press enter
- Select the “Stream provider” tab in the web UI and uncheck the “Use automatic configuration” checkbox
- Make sure that the first 2 octets matches the Multicast Address Prefix given in the Dante Controller (239.69.xxx.xxx in the example below). Set the last 2 octets to unique values. always avoid duplicated IP addresses. Best practice is to set them to the same value as the last 2 octets of the AES67 network address
- Make sure that the “Activate” checkbox for the stream is checked
- Select the “Advanced” tab and ensure that the SAP browsing is enabled
AES67 Receiving Stream Setup
The receiving AES67 part of the NGTC-BTI device needs to be configured in the Audiolan Web UI.
- Open a browser and enter the devices AES67 network address in the address bar, press enter
- Select the “Stream consumer” tab in the web UI
- Select a source stream for both channels and the channel number (NGTC-1280NX: BTI-Headphone in the example below)
- Apply all settings
Audio Routing using Audinate’s Dante Controller
Natively the audio routing can be done by using Audinate’s Dante Controller in case if its not auto configured by the DSP’s management software. In Dante Controller all your Dante and AES67 devices that are connected to the network will show up automatically.
The BTI will be shown at the ‘‘Dante Transmitters’’ part, using its multicast address@hostname-HH-HH-HH where ‘‘HH-HH-HH’’ are the last three bytes of the devices MAC address.
- Make the audio connections in the Dante controller
Control API
This section describes the communication protocol between the control system and the BTI
The BTI Configurator does use the same protocol, see its debug window for more information
Please use >80ms between each command sent
| Connection | TCP (NGTC-BTI is server), Port 20108 |
| Command Format | AT+ Command {=Param1{, Param2{, Param3…}}}<CR><LF> |
| Reply Format | <CR><LF>+reply {=Param1{, Param2{, Param3…}}} <CR><LF> |
<CR> stands for “carriage return”, corresponding hex is 0x0D
<LF> stands for “line feed”, corresponding hex is 0x0A
Command Format Details
All commands start with “AT”, end with <CR><LF>
If a command has a parameter, the parameter is behind the “=”
If a command has multiple parameters, the parameters must be separated by “,”
Reply Format Details
All replies start with <CR><LF> and end with <CR><LF>
If a reply has a parameter, the parameter is behind the “=”
If a reply has multiple parameters, the parameters must be separated by “,”
The interface will always report the execution result using “OK” for success or “ERROR” for failure
Examples
Read BTI’s Bluetooth name
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+NAME<CR><LF> |
||
AT+NAME<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+NAME=NGTC-BTI<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Set BTI’s Bluetooth name
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+NAME=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| NGTC-BTI | |||
AT+NAME=NGTC-BTI<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Subsections of Control API
General
Request firmware version
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+VER<CR><LF> |
||
AT+VER<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>>+VER=20171125,NGTC-BTI<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Bluetooth General
Request Bluetooth MAC address
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+ADDR<CR><LF> |
||
AT+ADDR<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>>+ADDR=DC0D30123456<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request Bluetooth name
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+NAME<CR><LF> |
||
AT+NAME<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+NAME=NGTC-BTI<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Set Bluetooth name
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+NAME=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| NGTC-BTI | |||
AT+NAME=NGTC-BTI<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Release all Bluetooth connections
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+DSCA<CR><LF> |
||
AT+DSCA<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Release all Bluetooth connections and reboot
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+REBOOT<CR><LF> |
||
AT+REBOOT<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Set Bluetooth discoverability and connection
- Undiscoverable = disconnect all devices connected and set’s the NGTC-BTI into an unconnectable and undiscoverable mode
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+BTEN=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Undiscoverable | |||
| 1: operational | |||
AT+BTEN=1<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request Bluetooth discoverability and connection
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+BTEN<CR><LF> |
||
AT+BTEN<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+BTEN=1<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request operation status
Status parameter will be reported in bit representation
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+DEVSTAT<CR><LF> |
||
| BIT[0]: PWR OFF; 1: PWR ON | |||
| BIT[1]: Non Discoverable; 1: Discoverable | |||
| BIT[2]: Non Advertising; 1: Advertising | |||
| BIT[3]: Non Scanning; 1: Scanning | |||
AT+DEVSTAT<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+DEVSTAT=9<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Set auto connect
This command needs a reboot to activate
- The NGTC-BTI will attempt to reconnect last device after power on
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+AUTOCONN=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Off | |||
| 1: 15 Attempts | |||
AT+AUTOCONN=0<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request auto connect
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+AUTOCONN<CR><LF> |
||
AT+AUTOCONN<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+AUTOCONN=1<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Restore all Bluetooth parameters to factory default
BTI module needs to be power cycled afterwards
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+RESTORE<CR><LF> |
||
AT+RESTORE<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Bluetooth Audio
Set volume of connected Bluetooth device
Please watch the volume carefully
There is no real standard for the source volume.
If you all the way to 15, you may overload the interface and it will result in distortion
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+SPKVOL=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| +: UP | |||
| -: DOWN | |||
AT+SPKVOL=+<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request volume of connected Bluetooth device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+SPKVOL<CR><LF> |
||
AT+SPKVOL<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+SPKVOL=10<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Operation Mode
Set operation mode
BTI module will reboot and all device profiles will be deleted
- Set’s the NGTC-BTI to sink(stream from device to BTI or source) or source(stream from BTI to headphone)
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPROLE=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Sink | |||
| 1: Source | |||
AT+A2DPROLE=0<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request operation mode
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPROLE<CR><LF> |
||
AT+A2DPROLE<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPROLE=1<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Sink Mode
To use the commands below the BTI needs to be switched to sink mode first
Set pairing active/inactive
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PAIR=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Off | |||
| 1: On | |||
AT+PAIR=1<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request pairing active/inactive status
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PAIR<CR><LF> |
||
AT+PAIR<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+PAIR=1<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Activate simple/secure pairing
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+SSP=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Off | |||
| 1: On | |||
AT+SSP=1<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request simple/secure pairing status
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+SSP<CR><LF> |
||
AT+SSP<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+SSP=0<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Set BTI’s pin code
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PIN=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 4-15 ASCII numbers | |||
AT+PIN=1234<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request BTI’s pin code
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PIN<CR><LF> |
||
AT+PIN<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+PIN=1234<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Clear a paired record
If the device (headphone/speaker) is deleted in the BTI it needs to be reconnected to work
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PLIST=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Clear list | |||
| x: Clear index (x) | |||
AT+PLIST=E<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request paired records
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PLIST<CR><LF> |
||
AT+PLIST<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+PLIST=1,123456ABCDEF <CR><LF><CR><LF>+PLIST=1,ABCDEF123456 <CR><LF><CR><LF>+PLIST=E <CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Reconnect to Bluetooth device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPCONN=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| No parameter: To last device | |||
| MAC: Mac of target device (12 Bytes ASCII) | |||
AT+A2DPCONN=123456ABCEDF<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPCONN=123456ABCEDF<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Release Bluetooth connection to device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPDISC<CR><LF> |
||
AT+A2DPDISC<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request status of connected device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPSTAT<CR><LF> |
||
AT+A2DPSTAT<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPSTAT=4<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Unsupported | |||
| 1: Standby | |||
| 2: Connecting | |||
| 3: Connected | |||
| 4: Streaming | |||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Nofification address of connected device
Event at device connection only, cannot be requested by control system
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPDEV=123456ABCDEF <CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request codex used by the connected device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPDEC<CR><LF> |
||
AT+A2DPDEC<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPDEC=1<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Invalid | |||
| 1: SBC | |||
| 2: MP3 | |||
| 3: AAC | |||
| 4: FASTSTREAM | |||
| 5: APTX | |||
| 6: APTX-Sprint | |||
| 7: APTX-HD | |||
| 8: APTX-LL | |||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Set ID track feedback
This command needs a reboot to activate
- Parameter: Default is 11, Base 10 representation of a bit
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+AVRCPCFG<CR><LF> |
||
| BIT[0]: Auto get rack ID3 information (title, artist, album) on track changed (default 1) | |||
| BIT[1-3]: Auto get track state (play progress) if value >0 (default 5sec) | |||
AT+AVRCPCFG=11<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request status of connected device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+AVRCPSTAT<CR><LF> |
||
AT+AVRCPSTAT<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+AVRCPSTAT=4<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Unsupported | |||
| 1: Standby | |||
| 2: Connecting | |||
| 3: Connected | |||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Nofification Mediaplayer play progress
Event at device connection only, cannot be requested by control system
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Param1: (0-4) Media Player State – please see PLAYSTAT parameters | |||
| Param2:(Decimal ASCII), Elapsed time of current track in ms | |||
| Param3:(Decimal ASCII), Total time of track in ms | |||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+TRACKSTAT=1,142000,248000 <CR><LF> |
Nofification Mediaplayer track info
Event at device connection only, cannot be requested by control system
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Param1: Title | |||
| Param2: Artist | |||
| Param3: Album | |||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+TRACKINFO=Creep<FF>Radiohead<FF>Pablo Honey <CR><LF> |
Nofification Mediaplayer status of the connected device
Event at device connection only, cannot be requested by control system
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0: Stopped | |||
| 1: Playing | |||
| 2: Paused | |||
| 3: Fast Forward | |||
| 4: Fast Rewind | |||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+PLAYSTAT=1<CR><LF> |
Transport Play/Pause
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PLAYPAUSE<CR><LF> |
||
AT+PLAYPAUSE<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Transport Play
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PLAY<CR><LF> |
||
AT+PLAY<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Transport Pause
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PAUSE<CR><LF> |
||
AT+PAUSE<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Transport Stop
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+STOP<CR><LF> |
||
AT+STOP<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Transport Track Forward
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+FORWARD<CR><LF> |
||
AT+FORWARD<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Transport Track Backward
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+BACKWARD<CR><LF> |
||
AT+BACKWARD<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Source Mode
To use the commands below the BTI needs to be switched to source mode first
Set autoscan
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+INQCFG=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Off | |||
| 1: On | |||
AT+INQCFG=1<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request autoscan status
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+INQCFG<CR><LF> |
||
AT+INQCFG<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+INQCFG=10<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Clear a paired record
If the device (headphone/speaker) is deleted in the BTI it needs to be reconnected to work
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PLIST=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Clear list | |||
| x: Clear index (x) | |||
AT+PLIST=E<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request paired records
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+PLIST<CR><LF> |
||
AT+PLIST<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+PLIST=1,123456ABCDEF <CR><LF><CR><LF>+PLIST=1,ABCDEF123456 <CR><LF><CR><LF>+PLIST=E <CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Reconnect to Bluetooth device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPCONN=Parameter<CR><LF> |
||
| No parameter: To last device | |||
| MAC: Mac of target device (12 Bytes ASCII) | |||
AT+A2DPCONN=123456ABCEDF<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPCONN=123456ABCEDF<CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Release Bluetooth connection to device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPDISC<CR><LF> |
||
AT+A2DPDISC<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request status of connected device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPSTAT<CR><LF> |
||
AT+A2DPSTAT<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPSTAT=4<CR><LF> |
||
| 0: Unsupported | |||
| 1: Standby | |||
| 2: Connecting | |||
| 3: Connected | |||
| 4: Streaming | |||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Nofification address of connected device
Event at device connection only, cannot be requested by control system
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPDEV=123456ABCDEF <CR><LF> |
||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Request codex used by the connected device
| Communication | Command | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | AT+A2DPDEC<CR><LF> |
||
AT+A2DPDEC<CR><LF> |
|||
| Reply #1 | <CR><LF>+A2DPDEC=1<CR><LF> |
||
| 1: SBC | |||
| 5: APTX | |||
| 6: APTX-LL | |||
| Reply #2 | <CR><LF>OK<CR><LF> |
Specifications
| OS Support | |
| OS | iOS, PC, MAC and Android |
| Bluetooth | |
| Standards | V5 down to V1.1, Class 1.5 |
| Band | 2.402 – 2.480 GHz |
| Audio Format | All (SBC,aptx HD,LL) |
| AES67 Network with WebUI | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 100 Mbps Full Duplex |
| Control Network with WebUI | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 100 Mbps Full Duplex |
| General | |
| Power | POE, 3W max |
| Total heat dissipation | max 10.00 BTU/hr |
| Operating temp | 5°C – 30°C |
| Dimensions | L: 130mm, W: 65mm, H:25mm |
| Compliance | CE, ROHS |
Audio Channel Assignment
| Channel | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 1 | Left Channel |
| 2 | Right Channel |
CAD step file
Bluetooth facts and figures
How does Bluetooth work
The simplest explanation for how Bluetooth works is that data/audio is continuously transferred from a paired Bluetooth transmitter to a paired receiver. Pairing is just the bonding procedure between devices so that you don’t have to enter access or security information, like passwords or passkeys, each time the devices need to establish a connection. Bluetooth operates in the frequency range of (2.402 -2.480GHz). Once a secure connection is established between a transmitter and receiver, data is split into small packets, which are then transferred at alternating frequencies. The type of Bluetooth and profiles may vary, but the core architecture remains the same. To avoid interference with other devices that may also use the ISM (industrial, science, and medical) bandwidth of 2.4Ghz, Bluetooth devices randomly hop between frequencies 1600 times per second until all the packets are transferred.
Bluetooth version and profiles
The NGTC-BTI supports Bluetooth 5.x, the most recent iteration of Bluetooth. It has twice the bandwidth of V4.x. The NGTC-BTI supports only audio related transmission, no data communication or phone/handsfree functionality.
Stereo audio transmission. This is the most important profile for Bluetooth as mono audio is not suited for listening to music.
Adds control for media playback such as skipping tracks, play/pause, and meta data.
Which Bluetooth Codec is the best?
Codecs are encoding and decoding algorithms that compress audio into manageable data packets for faster or wireless transmission. The efficiency of the codec will determine the quality and rate at which the audio data is sent. SBC is the default sub-band coding for most Bluetooth devices. However, since this codec has a relatively high latency and may be a bit lossy, companies have developed their own encoding algorithms.
The mandatory and default codec for all stereo Bluetooth headphones with the Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP). It is capable of bit rates up to 328 kbps with a sampling rate of 44.1kHz. It provides fairly good audio quality without requiring a lot of processing power to encode or decode. However, the audio quality can be a bit inconsistent at times. This is especially noticeable with a cheap Bluetooth transmitter.
Similar to SBC, but with better sound quality. This codec is mostly popular with Apple’s iTunes platform and some other non-wireless applications. However, it’s not very common, especially for headphones.
It’s ideal for demanding audio applications since it encodes audio more efficiently and at a slightly higher rate than SBC. There are also two additional variations, aptX Low Latency and aptX HD, that either drastically reduces the latency of the connection or significantly improves its audio quality. However, it’s a bit limiting, as both the Bluetooth transmitter and receiver must have aptX or its variations for the codec to work.
Latency
Codecs have a bigger impact on latency than on sound quality for most listeners. The default SBC connection typically has more than 100ms of latency, which is noticeable when listening to music but may be severe enough to ruin your movie experience. To fix some of the sync issues caused by latency, CSR developed the aptX and subsequently the aptX Low Latency codec. Regular aptX does somewhat improve latency due to its more efficient encoding algorithm than SBC. However, aptX-LL has the most noticeable impact on latency.
| Codec | Latency |
|---|---|
| SBC | 173ms |
| aptX | 166ms |
| aptx LL | 34ms |
Conclusion
Codecs are the algorithms that compress data for easier and faster transmission. Better encoding and decoding algorithms mean less lossy transmission which can help with audio quality. We have noticed that codecs have a bigger impact on latency than on audio quality. The subtle changes in audio quality due to a codec like aptX are negligible when compared to the reduced latency aptX Low Latency connection. However, since both Bluetooth devices (source/sink) have to support the codec for it to work, you will most often rely on the default sub-band coding (SBC), as there are not many Bluetooth devices that support aptX and even less for aptX-LL.
Firmware
Known Firmware issues
- V4.0.3: AT+PLIST command is faulty, No Audio in Master/Source mode
- V4.04: AT+PLIST command is faulty
- V4.05: Module does turn off after 10min if no source connected
Software
Configuration Software
Control4 Bluetooth Experience Button driver
TVI2.0R2
The NGTC-TVI2.0R2 is a Digital to Analog Audio Converter, that has been designed for either marine, residential or professional audio applications. It converts Coaxial or Toslink digital audio signals to analog L/R audio and it is available for connection to an external device, such as an amplifier, via standard RCA-style jacks. This
Converter is small in size and quite easy to install.
Subsections of TVI2.0R2
Installation
- Place the TVI2.0 behind the TV or wherever suited..
- Select via hardware switch the coaxial or Toslink digital audio input
Configuration
Setup interoperability between TVI2.0 and Dante devices
AES67 interoperability settings are required for every Dante device that should receive a AES67 stream
To enable your Dante devices to receive an AES67 stream, AES67 interoperability must be enabled. This is done by using Audinate’s Dante Controller, which can be obtained from the Audinate website or any other manufacturer specific software tool.
In Dante controller all your Dante devices that are connected to the network will show up automatically.
- Start the Dante Controller Software and wait for it to be synchronized with the network
- Select the “device info” tab in the software
- Double click on the DSP you would like to configure for AES67, a new window will open
- Select the “AES67 config” tab
- Enable AES67 mode and make a note of the Tx multicast prefix. You will need this number later, even if you are not using the DSP as a transmitter. This must be the same for all DSP’s that are ready for AES67.
- Reboot the Dante device
- This needs to be done with every Dante device that will receive an AES67 stream
Subsections of Configuration
AES67 Network Setup
To configure the AES67 download latest generation Audio Grid Controller Software. Your PC needs to be connected to the AES67 network and have its addressing set in the same IP range.
AES67 Network Address Setup
Start the software and go to the “Device Config” tab
- Select the device to be configured
- Enter “IP Address” and “Subnet Mask”
- Hit “Apply”
AES67 Stream Address Setup
The AES67 stream of each device needs to be configured to be received by the Dante/AES67 devices
Start the software and go to the “Device Config” tab
- Select the device to be configured
- Select “Create / Delete” in the “Multicst flow” selection
- In the Multicast flow config, click on “AG” first and then on “AES67”. Next, select the “Manual IP and Port” option.
- You can set your desired multicast IP. Typically in combination with Dante Audio products, the multicast IP starts with “239.69.”, port 5004.
- Select the channels that should be multicast.
- Click on “Create”.
Audio Routing using Audinate’s Dante Controller
Natively the audio routing can be done by using Audinate’s Dante Controller in case if its not auto configured by the DSP’s management software. In Dante Controller all your Dante and AES67 devices that are connected to the network will show up automatically.
The BTI will be shown at the ‘‘Dante Transmitters’’ part, using its multicast address@hostname-HH-HH-HH where ‘‘HH-HH-HH’’ are the last three bytes of the devices MAC address.
- Make the audio connections in the Dante controller
Specifications
- Converts coaxial or Toslink digital audio signals to 2CH audio on AES67 (Switchable by hardware switch)
- Supports sampling rate at 32, 44.1, 48, 96 KHz, 24-bit, all bitstream formats
- THD <0.008%@1kHz
- SNR >95dB
- Crosstalk >84dB@1kHz
- Frequency response 20-20kHz
- POE powered
Audio Channel Assignment
| Channel | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 1 | Left Channel |
| 2 | Right Channel |
CAD step file
Firmware
Firmware
Welcome to the Firmware section!
If you are not redirected automatically, click here.
Subsections of Firmware
Audio Card
Audio Card Firmware Update
The latest generation of TVI2.0R2 features an AES67 daughter board that fully supports AES67, ensuring compatibility with Dante™. Additionally, these devices have mDNS discovery enabled, allowing them to be detected in the Dante Controller, similar to a Dante product.
However, starting with Dante Controller V12, a pop-up message may appear indicating that unlicensed Dante™ products are being used. To address this, the new firmware will disable Dante™ discovery, and all R2 units will be recognized as AES67 devices.
Update to the Latest AES67 only Firmware Release
- Download the latest programmer and firmware files
- Unzip the firmware files (TVI-FW_4101-4108.zip) into a folder.
- Run the updater tool (Fdt_factory1.63.exe). Note that the discovery function works for up to 10 units. If you have more units, use the IP address filter for efficient navigation.
- Open the FPGA firmware file with the updater tool (fpga_a404_4108.bit).
- Open the MCU firmware file with the updater tool (mcu_407d_4101.bin).
- Update all units with the new MCU by clicking in the field MCU Upgrade.
- Update all units with the new FPGA by clicking in the field FPGA Upgrade.
- Select all updated units in the latest row for reboot.
- Click “Reboot”.
After the reboot, click “Refresh” to update the device list. If the devices appear as expected, you can proceed with the update process.
- Open the Initialize data file with the updater tool (TVI-T4R6-AES67.c).
- Update all units with the new Init data fle by clicking in the field Init Data.
- Select all updated units in the latest row for reboot.
- Click “Reboot”.
After the reboot, you need to set the multicast address for AES67 to work. Use the Audio Grid Controller to do this.
Refer to the following instructions to configure it with the AudioGrid controller
TVI2.0
The NGTC-TVI2.0 is a Digital to Analog Audio Converter, that has been designed for either marine, residential or professional audio applications. It converts Coaxial or Toslink digital audio signals to analog L/R audio and it is available for connection to an external device, such as an amplifier, via standard RCA-style jacks. This
Converter is small in size and quite easy to install.
Subsections of TVI2.0
Installation
- Place the TVI2.0 behind the TV or wherever suited..
- Select via hardware switch the coaxial or Toslink digital audio input
Configuration
Setup interoperability between TVI2.0 and Dante devices
AES67 interoperability settings are required for every Dante device that should receive a AES67 stream
To enable your Dante devices to receive an AES67 stream, AES67 interoperability must be enabled. This is done by using Audinate’s Dante Controller, which can be obtained from the Audinate website or any other manufacturer specific software tool.
In Dante controller all your Dante devices that are connected to the network will show up automatically.
- Start the Dante Controller Software and wait for it to be synchronized with the network
- Select the “device info” tab in the software
- Double click on the DSP you would like to configure for AES67, a new window will open
- Select the “AES67 config” tab
- Enable AES67 mode and make a note of the Tx multicast prefix. You will need this number later, even if you are not using the DSP as a transmitter. This must be the same for all DSP’s that are ready for AES67.
- Reboot the Dante device
- This needs to be done with every Dante device that will receive an AES67 stream
Subsections of Configuration
AES67 Network Setup
AES67 Network Address Setup
To configure the AES67 network address use the built in Audiolan web UI. Your PC needs to be connected to the AES67 network and have its addressing set in the same IP range.
By default the AES67 network interface is set to DHCP
To avoid an IP conflicts, connect one device after another and change each units IP to a different one
Avoid any special characters and spaces in the device name
- Open a browser and enter the devices AES67 network address in the address bar, press enter
- Select the “General settings” tab in the web UI to change the devices IP address
- The NGTC-MCP4kR2 should have an IP and Subnet address in the same range as the Dante devices
- Apply all settings and reboot the device
AES67 Stream Address Setup
The AES67 stream of each device needs to be configured to be received by the Dante/AES67 devices
Avoid any special characters and spaces in the stream name
- Open a browser and enter the devices AES67 network address in the address bar, press enter
- Select the “Stream provider” tab in the web UI and uncheck the “Use automatic configuration” checkbox
- Make sure that the first 2 octets matches the Multicast Address Prefix given in the Dante Controller (239.69.xxx.xxx in the example below). Set the last 2 octets to unique values. always avoid duplicated IP addresses. Best practice is to set them to the same value as the last 2 octets of the AES67 network address
- Make sure that the “Activate” checkbox for the stream is checked
- Select the “Advanced” tab and ensure that the SAP browsing is enabled
Audio Routing using Audinate’s Dante Controller
Natively the audio routing can be done by using Audinate’s Dante Controller in case if its not auto configured by the DSP’s management software. In Dante Controller all your Dante and AES67 devices that are connected to the network will show up automatically.
The BTI will be shown at the ‘‘Dante Transmitters’’ part, using its multicast address@hostname-HH-HH-HH where ‘‘HH-HH-HH’’ are the last three bytes of the devices MAC address.
- Make the audio connections in the Dante controller
Specifications
- Converts coaxial or Toslink digital audio signals to 2CH audio on AES67 (Switchable by hardware switch)
- Supports sampling rate at 32, 44.1, 48, 96 KHz, 24-bit, all bitstream formats
- THD <0.008%@1kHz
- SNR >95dB
- Crosstalk >84dB@1kHz
- Frequency response 20-20kHz
- POE powered
Audio Channel Assignment
| Channel | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 1 | Left Channel |
| 2 | Right Channel |
CAD step file
BIB8DR2
The NGTC-BIB8DR2 is an AES67 enabled Digital to Analog Audio Converter for the nexgentec™ audio distribution solution.
It features four digital inputs sets, each capable of converting multichannel audio signals to 2-channel audio on AES67.
Common Features
Key Features
- Converts coaxial or Toslink digital audio signals to 2-channel audio on AES67 (auto-switching with priority on Toslink)
- Supports sampling rates of 32, 44.1, 48, and 96 kHz, 24-bit, all bitstream formats
- Total Harmonic Distortion (THD): < 0.008% @ 1 kHz
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR): > 95 dB
- Crosstalk: > 84 dB @ 1 kHz
- Frequency Response: 20 Hz – 20 kHz
- Powered via Power over Ethernet (PoE)
Subsections of BIB8DR2
Installation
- AES67 network interface (POE) – please use UTP cabling
- Coax digital audio input
- Toslink digital audio input
All connections to the NGT-BIB8D should be made before power is applied
The BIB8D has 4 input pairs, and for each pair, only one input can be used at a time: Coax or Toslink. If both are connected within a pair, Toslink takes priority.
Configuration
Setup interoperability between MCP4kR2 and Dante devices
AES67 interoperability settings are required for every Dante device that should receive a AES67 stream
To enable your Dante devices to receive an AES67 stream, AES67 interoperability must be enabled. This is done by using Audinate’s Dante Controller, which can be obtained from the Audinate website or any other manufacturer specific software tool.
In Dante controller all your Dante devices that are connected to the network will show up automatically.
- Start the Dante Controller Software and wait for it to be synchronized with the network
- Select the “device info” tab in the software
- Double click on the DSP you would like to configure for AES67, a new window will open
- Select the “AES67 config” tab
- Enable AES67 mode and make a note of the Tx multicast prefix. You will need this number later, even if you are not using the DSP as a transmitter. This must be the same for all DSP’s that are ready for AES67.
- Reboot the Dante device
- This needs to be done with every Dante device that will receive an AES67 stream
Subsections of Configuration
AES67 Network Setup (AudioGrid)
To configure the AES67 download latest generation Audio Grid Controller Software. Your PC needs to be connected to the AES67 network and have its addressing set in the same IP range.
AES67 Network Address Setup
Start the software and go to the “Device Config” tab
- Select the device to be configured
- Enter “IP Address” and “Subnet Mask”
- Hit “Apply”
AES67 Stream Address Setup
The AES67 stream of each device needs to be configured to be received by the Dante/AES67 devices
Start the software and go to the “Device Config” tab
- Select the device to be configured
- Select “Create / Delete” in the “Multicst flow” selection
- In the Multicast flow config, click on “AG” first and then on “AES67”. Next, select the “Manual IP and Port” option.
- You can set your desired multicast IP. Typically in combination with Dante Audio products, the multicast IP starts with “239.69.”, port 5004.
- Select the channels that should be multicast.
- Click on “Create”.
Audio Routing using Audinate’s Dante Controller
Global site parameters
Natively the audio routing can be done by using Audinate’s Dante Controller in case if its not auto configured by the DSP’s management software. In Dante Controller all your Dante and AES67 devices that are connected to the network will show up automatically.
The BIB8DR2 will be shown at the ‘‘Dante Transmitters’’ part, using its multicast address@hostname-HH-HH-HH where ‘‘HH-HH-HH’’ are the last three bytes of the devices MAC address.
- Make the audio connections in the Dante controller
Specifications
General
• Converts coaxial or Toslink digital audio signals to 2CH audio on AES67 (autoswitch with priority on Toslink)
| Digital Audio Input | |
| Type | TOSLINK / COAX |
| Format | All Bitstream Formats |
| Sampling Rates | 32, 44.1, 48, 96 KHz |
| Bit Depth | Up to 24-bit |
| Audio Performance | |
| Crosstalk | >84dB@1kHz |
| System THD+N | <0.008%@1kHz |
| Freq. Response | 20Hz – 20kHz, +/- 1dB |
| Digital Audio Output | |
| Type | 8 channels, full range |
| Format | Aes67 |
| AES67 Network with WebUI | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 100 Mbps Full Duplex |
| General | |
| Power | POE, 15W max |
| Total heat dissipation | <50>.00 BTU/hr |
| Operating temp | 5°C – 30°C |
| Dimensions | L: 250mm, W: 208mm, H:44mm |
| Compliance | CE, ROHS |
Audio Channel Assignment
| Channel | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 1/2 | Input A Left/Right |
| 3/4 | Input B Left/Right |
| 5/6 | Input C Left/Right |
| 7/8 | Input D Left/Right |
Firmware
Audio Card Firmware Update
The latest generation of BIB8D features an AES67 daughter board that fully supports AES67, ensuring compatibility with Dante™. Additionally, these devices have mDNS discovery enabled, allowing them to be detected in the Dante Controller, similar to a Dante product.
However, starting with Dante Controller V12, a pop-up message may appear indicating that unlicensed Dante™ products are being used. To address this, the new firmware will disable Dante™ discovery, and all R2 units will be recognized as AES67 devices.
Update to the Latest AES67 only Firmware Release
- Download the latest programmer and firmware files
- Unzip the firmware files (BIB8D-FW_4102-4108.zip) into a folder.
- Run the updater tool (Fdt_factory1.63.exe). Note that the discovery function works for up to 10 units. If you have more units, use the IP address filter for efficient navigation.
- Open the FPGA firmware file with the updater tool (fpga_a408_4108.bit).
- Open the MCU firmware file with the updater tool (mcu_407d_4102.bin).
- Update all units with the new MCU by clicking in the field MCU Upgrade.
- Update all units with the new FPGA by clicking in the field FPGA Upgrade.
- Select all updated units in the latest row for reboot.
- Click “Reboot”.
After the reboot, click “Refresh” to update the device list. If the devices appear as expected, you can proceed with the update process.
- Open the Initialize data file with the updater tool (BIB8-AES67.c).
- Update all units with the new Init data fle by clicking in the field Init Data.
- Select all updated units in the latest row for reboot.
- Click “Reboot”.
After the reboot, you need to set the multicast address for AES67 to work. Use the Audio Grid Controller to do this.
Refer to the following instructions to configure it with the AudioGrid controller
2140PWRR3
The NGTC-2140PWRR3 is a Dante™ enabled network power amplifier for the nexgentec™ audio distribution solution
Key Features
- 2 x 140 Watt @ 4 Ohm – 1 x 200 Watt @ 4 Ohm bridged
- LAN control protocol
- only 1RU high
- Dante™ audio interface
- Stereo digital power amplifier
- Manageable integrated 2 port switch
- nexgentec ngtOS, operating system for control api, configuration and monitoring
Subsections of 2140PWRR3
Apps
Configure Installed Apps of the Unit
Each installed app can be configured to a certain level via the web interface.
The default login for the web interface is: Username: admin Password: nexgentec
Open a browser and enter the device’s network address in the address bar, then press Enter.
Use the top menu bar to navigate to Apps and select the app to be configured.
Subsections of Apps
Amplifier
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > Amplifier.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
transport
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
Control
Control > Channels
Status
- These icons show the status of the amplifier channel. Also, the temperature is displayed.
Action
- Use these buttons to turn the amplifier channel on and off. The amplifier channels can also be muted and unmuted. Be aware that due to a hardware limitation, channels 1 and 2 always follow the same power and mute settings, as do channels 3 and 4.
API
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > API.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
transport
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
api
- Use the dropdown menus to select the Endpoint and the port to use for each protocol that the API can communicate with.
Broker
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > Broker.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
transport
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
Dante
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > Broker.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
network
- Select the interface to be used for Dante audio. This interface will be used for audio data transmission.
Display
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > Display.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
transport
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
time
- Select the time format to be shown on the display, 24h or AM/PM.
temperature
- Select the temperature format to be shown on the display in Celsius or Fahrenheit.
backlight
- Select the brightness level. Possible values range from 0 to 255. At 0, the display on the front is completely dark and appears to be turned off.
Netd
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > WebUI.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
WebUI
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > WebUI.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
transport
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
web
- This is the address of the web UI to run on. The default is on all interfaces and port 80, therefore “:80”. Be careful when changing this setting.
Configuration
Configure Hardware and Software Properties
All configuration tasks can be performed via the web interface.
The default login for the web interface is: Username: admin Password: nexgentec
Open a browser and enter the device’s network address in the address bar, then press Enter.
Use the top menu bar to navigate to the option you want.
Subsections of Configuration
Network
This guide applies to all units running ngtOS >= version 1.0.13 (beta-rc3)
Status
The status of the network connections can be viewed on the status page System > Network > Status
General
Points to consider:
- Never assign a gateway to more than one connection.
- Never place more than one connection in the same IP address range.
- Use DNS servers that are reachable.
- Avoid leaving two interfaces connected to the network on DHCP.
- The unit requires internet access. This is necessary in case service personnel need to access the unit using the built-in support tool.
If things go wrong:
- Try to locate the device using your DHCP server. Attempt this on all available Ethernet interfaces.
- The display on the unit shows the full configuration for each interface, including the path to access the IP address.
Basic Functionality
In general, the physical network interfaces and the internal endpoints should be understood as a managed switch infrastructure. Each physical port can take untagged and tagged VLANs, each VLAN can be used to connect an “Endpoint” for Audio and/or Control. Finally, VLANs can be forwarded tagged or untagged between the physical interfaces, keeping the tagging or even untagging during forwarding.
There is no mandatory number of Endpoints. At least one must exist, and it can be a combined one for both audio and control. An arbitrary number of Endpoints for control can exist, but only one for audio.

 In this example, both physical ports are carrying VLANs 13, 15, and 22.
In this example, both physical ports are carrying VLANs 13, 15, and 22.
-
VLAN 13 is the untagged (native) VLAN on eth1 and gets tagged while flowing towards eth2, and vice versa. It’s also received by Endpoint 3, which is a management endpoint. The IP address (fixed or statically assigned) of Endpoint 3 can be reached on eth1 using no VLAN tag and on eth2 using a VLAN tag 13.
-
VLAN 15 is the tagged VLAN on eth1 and gets untagged while flowing towards eth2 (native), and vice versa. It’s also received by Endpoint 1, which is the audio endpoint. The IP address (fixed or statically assigned) of Endpoint 1 can be reached on eth1 using VLAN tag 15 and on eth2 using no VLAN tag.
-
VLAN 22 is a tagged VLAN which flows over both physical interfaces. It’s also received by Endpoint 2, which is a management endpoint. The IP address (fixed or statically assigned) of Endpoint 2 can be reached on any of the two physical interfaces using a VLAN tag 22.
On the Front Display
The front panel display shows the current network configuration, including how to access the shown IP address. If multiple endpoints exist, the line scrolls every 5 seconds to display all endpoints.
Syntax: physical[:Tagged VLAN]>Endpoint name > IP Address (CIDR notation).
Examples
Following the example above:
- eth1 > Endpoint 3 > 192.168.1.20/24 (See the description above on how to access 192.168.1.20)
- eth1:15 > Endpoint 1 > 192.168.5.20/24 (See the description above on how to access 192.168.5.20)
Configure
Select in the top menu System > Network > Settings
Continuing with the example above, this would look like:
Detailed Field Descriptions for “Switches”
Name
- Read-only: This field displays the name of the switch to be configured. “vswitch1” is the switch to be configured. Currently, only one virtual switch is allowed.
Multicast Snooping
- This setting allows the switch to observe and learn the multicast groups and associated members to limit the forwarding of multicast traffic. Use with caution. If you experience any problems with multicast streams flowing towards the unit or passing through it, turn this setting off.
Multicast Querier
- This setting allows the switch to send out network queries to determine which hosts belong to which multicast groups. It will be automatically set to false once the Endpoint for Audio is included in a tagged VLAN on any of the physical ports. Use it only when there is no managed switch in the network that could send out the query.
Detailed Field Descriptions for “Ports”
Link Address
- Read-only: This field displays the MAC address assigned to the port.
Switch Member
- This setting determines whether to include or exclude the physical port from being used by the managed switch.
VLAN Untagged
- This setting allows you to specify which VLANs should have their tags removed when traffic is sent out of this port.
VLAN Tagged
- This setting allows you to specify which VLANs should retain their tags when traffic is sent out of this port.
Detailed Field Descriptions for “Endpoints”
Name
- Read-only: This field displays the name of the endpoint.
Link Address
- This field displays the MAC address assigned to the endpoint.
Switch Member
- This setting determines in which virtual switch the endpoint should be included.
Usage
- This field indicates how the endpoint is being used in the network setup, either for Control, Audio, or both.
VLAN Untagged
- This setting allows you to specify which VLANs should be included and have their tags removed when traffic is sent out of this endpoint.
DHCP
- This setting enables or disables the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for the endpoint. If enabled, the endpoint will automatically receive an IP address from the DHCP server in the network.
Addresses
- This field displays the IP addresses assigned to the endpoint. The notation is in CIDR notation.
Routes (To)
- This field displays the routing table for the endpoint, showing where traffic will be directed. To add a default route (gateway), enter To: 0.0.0.0/0 Via: Gateway Address.
Nameservers
- This field displays the IP addresses of the DNS servers that the endpoint is configured to use.
Control APIs
Control the Amplifier over TCP and HTTP using JSON-RPC 2.0
This is a preliminary api documentation, subject to change
Subsections of Control APIs
JSON RPC 2.0 API
This section describes the communication protocol between the control system and the 4140PWRR3 using RPC calls using the JSON-RPC 2.0 protocol
Definitions
Commands must be formatted as defined in the JSON-RPC 2.0 protocol
All commands sent over TCP transport must end with <LF>
All replies are formatted as defined in the JSON-RPC 2.0 protocol
All replies over TCP transport end up with <LF>
<LF> stands for “line feed”, corresponding hex is 0x0A
Transport protocols
JSON-RPC 2.0 commands can flow over different transport protocols, they need to be enabled in the config file of the installed api service. Per default they might not be enabled.
| Transport | Config | Datatype | Example | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCP | jrpc2TCPInterface | string | eth1 | >v1.0.1 |
| TCP | jrpc2TCPPort | int | 64823 | >v1.0.1 |
| TCP | jrpc2HTTPInterface | string | eth1 | >v1.0.1 |
| TCP | jrpc2HTTPPort | int | 64880 | >v1.0.1 |
In subsequent pages all methods are described that can be used.
Concurrency
All JSON-RPC 2.0 services do support asynchronous message processing. 3rd party control Systems must keep tracking of the id’s to determine whether a request was successful or not
TCP transport
Any TCP capable application can be used to test commands. Do not forget to end up with <LF>
HTTP transport
The body of the HTTP POST request must contain the complete JSON-RPC request message, encoded with Content-Type: application/json. Either a single request object or a list of request objects is supported. If the request completes, whether or not there is an error, the HTTP response is 200 (OK) for ordinary requests or 204 (No Response) for notifications, and the response body contains the JSON-RPC response. If the HTTP request method is not “POST”, 4140PWRR3 reports 405 (Method Not Allowed). If the Content-Type is not application/json, 4140PWRR3 reports 415 (Unsupported Media Type).
Test from a linux shell:
curl -i -X POST -H ‘Content-Type: application/json’ -d ‘{“jsonrpc”:“2.0”,“id”:1,“method”:“rpc.serverInfo”}’ http://host:64880
Subsections of JSON RPC 2.0 API
amplifier
amplifier commands are generic commands for all nexgentec™ amplifier devices. These commands utilize the generic amplifier protocol, enabling seamless integration and control across amplifier devices.
amplifier.channel.set (channelSet)
Enable or disable, mute or unmute a amplifier channel
A hardware limitation only allows stereo channel pairs to be switched on the 2140pwrr3.
- Channel 1 & 2 will power on/off together
A hardware limitation only allows stereo channel pairs to be muted on the 2140pwrr3.
- Channel 1 & 2 will mute/unmute together
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| amplifier.channelSet | >v1.0.1 | |||
| channel | 1,2,3,4 | Channel selection | >v1.0.1 | |
| power | 0,1 | Power on (1) or off (0) | >v1.0.1 | |
| mute | 0,1 | Mute (1) or unmute (0) | >v1.0.1 | |
| amplifier.channel.set | >=v1.0.14 | |||
| channel | 1,2,3,4 | Channel selection | >=v1.0.14 | |
| power | 0,1 | Power on (1) or off (0) | >=v1.0.14 | |
| mute | 0,1 | Mute (1) or unmute (0) | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channelSet","params":{"channel":1,"power":1}}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channel.set","params":{"channel":1,"power":1}}{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channelSet","params":{"channel":1,"power":1}}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channel.set","params":{"channel":1,"power":1}}{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channelSet","params":{"channel":1,"mute":1}}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channel.set","params":{"channel":1,"mute":1}}{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channelSet","params":{"channel":1,"power":1,"mute":0}}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channel.set","params":{"channel":1,"power":1,"mute":0}}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}amplifier.channel.get (channelGet)
Get the status of an amplifier channel
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| amplifier.channelGet | >v1.0.1 | |||
| amplifier.channel.get | >=v1.0.14 | |||
| channel | 1,2,3,4 | Channel selection | >v1.0.1 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channelGet","params":{"channel":1}}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channel.get","params":{"channel":1}}Reply
| Result | Key | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| channel status | ||
| power | 1 if channel was powered on, 0 if channel was powered off | |
| mute | 1 if channel was muted, 0 if channel was unmuted | |
| error | null if no error on channel otherwise error message | |
| powerStatus | 1 if channel is powered, otherwise 0 | |
| clip | 1 if channel is clipping, otherwise 0 | |
| temp | Temperature in °C |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":{"channel":1,"power":1,"mute":0,"error":null,"powerStatus":1,"clip":0,"temp":42.3}}amplifier.channels.subscribe (channelsSubscribe)
Subscribe all amplifier channels status push messages
Enable push status messages
Pushed status messages having the same format as channelGet replies
Push messages over HTTP transport are not supported
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| amplifier.channelsSubscribe | >v1.0.1 | |||
| amplifier.channels.subscribe | >v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channelsSubscribe"}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channels.subscribe"}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}amplifier.channels.unsubscribe (channelsUnsubscribe)
Unsubscribe all amplifier channels status push messages
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| amplifier.channelsUnsubscribe | >v1.0.1 | |||
| amplifier.channels.unsubscribe | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channelsUnsubscribe"}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channels.unsubscribe"}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}2140pwrr3
2140pwrr3 commands are specific to 2140pwrr3 nexgentec™ devices. These commands are used to control the 2140pwrr3 service, which is a device specific service designed for 2140pwrr3 devices.
2140pwrr3.app.log.level.get
Get the log level for the 2140pwrr3 service running on the 2140pwrr3
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2140pwrr3.app.log.level.get | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"2140pwrr3.app.log.level.get"}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| x | Active log level |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":20,"result":{"level":3}}2140pwrr3.app.log.level.set
Set the log level for 2140pwrr3 service and associated processes
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2140pwrr3.app.log.level.set | level | 0-7 | Log level to set | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"2140pwrr3.app.log.level.set","params":{"level":6}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}api
api commands are generic commands for all nexgentec™ devices that have an API. These commands utilize the generic API protocol, enabling seamless integration and control across supported devices.
api.app.log.level.get
Get the log level for the api service running on the api
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| api.app.log.level.get | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"api.app.log.level.get"}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| x | Active log level |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":20,"result":{"level":3}}api.app.log.level.set
Set the log level
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| api.app.log.level.set | level | 0-7 | Log level to set | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"api.app.log.level.set","params":{"level":6}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}display
diplay commands are generic commands for all nexgentec™ devices that have a diplay. These commands utilize the generic diplay protocol, enabling seamless integration and control across supported devices.
diplay.backlight.level.get
Get the log level for the api service running on the api
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| diplay.backlight.level.get | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"diplay.backlight.level.get"}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| x | Active backlight level |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":20,"result":{"level":3}}diplay.backlight.level.set
Set the backlight level
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| diplay.backlight.level.set | level | 0-255 | Level to set | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"diplay.backlight.level.set","params":{"level":6}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}server
server commands are generic commands for all Nexgentec™ devices that support a JSON-RPC 2.0 API. These commands provide a standard JSON-RPC method to retrieve the list of supported methods available on the device.
rpc.server.info.get (serverInfo)
Get all supported RCP methods
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rpc.serverInfo | >1.0.1 | |||
| rpc.server.info.get | >=1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"rpc.serverInfo"}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"rpc.server.info.get"}Reply
| Result | Key | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| methods | All supported methods that can be used by a 3rd party control system | |
| counters | Server counters | |
| startTime | Server start time |
{
"result": {
"startTime": "2024-04-11T08:06:23.391135102Z",
"metrics": {
"bytes_written": 0,
"rpc_requests": 1,
"bytes_read": 55,
"notifications_pushed": 0,
"rpc_errors": 0,
"servers_active": 2,
"calls_pushed": 0
},
"methods": [
"2140pwrr3-cf11.app.log.level.get","2140pwrr3-cf11.app.log.level.set","2140pwrr3-cf11.app.version.get","2140pwrr3.app.log.level.get","2140pwrr3.app.log.level.set","2140pwrr3.app.version.get","2140pwrr3.appLogLevelGet","2140pwrr3.appLogLevelSet","2140pwrr3.appVersionGet","amplifier.channel.get","amplifier.channel.set","amplifier.channelGet","amplifier.channelSet","amplifier.channels.subscribe","amplifier.channels.unsubscribe","amplifier.channelsSubscribe","amplifier.channelsUnsubscribe","api.app.log.level.get","api.app.log.level.set","api.app.version.get","api.appLogLevelGet","api.appLogLevelSet","api.appVersionGet","display.backlight.level.get","display.backlight.level.set","rpc.server.info.get","rpc.serverInfo","webui.app.log.level.get","webui.app.log.level.set","webui.app.version.get"]
},
"id": 1,
"jsonrpc": "2.0"
}Specifications
| Digital Audio Input | |
| Type | 2 channels, full range |
| Format | Dante™, Aes67 |
| Audio Performance | |
| Output Power @4Ω | 280W/CH |
| Output Power @8Ω | 140W/CH |
| Bridge Mode | Yes@8Ohm |
| Distortion | 0.0014% 20hZ < f < 20kHz. Pout = 1W |
| Output Noise | 40 µV |
| Power Bandwidth | 20Hz - 35kHz |
| Freuquency Response | 10Hz - 48kHz +0/-3dB. All loads |
| Network Port eth1 | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 10/100/1000 Mbps Full Duplex |
| Network Port eth2 | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 10/100/1000 Mbps Full Duplex |
| General | |
| Mains Voltage | 230V/115V, 50–60 Hz |
| Power Consumption | @100–240VAC,47/63Hz 3.15A |
| Total Heat Dissipation | 10 BTU/h standby, 70 BTU/h operation |
| Operating temp | 5°C – 30°C |
| Dimensions | L: 250mm, W: 209mm, H:45mm 1/2 rack width |
| Weight | 1.5kg |
| Compliance | CE, ROHS |
Audio Channel Assignment
| Channel | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 1 | Left Channel Amplifier Module 1 |
| 2 | Right Channel Amplifier Module 1 |
CAD step file
ngtOS
Never downgrade to an older ngtOS, as it will result in a factory return of the unit in every case.
If you have multiple units to update, try the update on one and if it’s working as expected, proceed with all others.
Update Path
- All units must be updated to 1.0.14 (beta-rc4) before upgrading to any higher version of ngtOS.
- Future update paths will be published when available.
Update Notes
Version 1.0.14 (beta-rc4)
- Beginning with version 1.0.13, a new method to configure the network of the unit was introduced. Existing configurations will be converted as accurately as possible. If the update fails, a default configuration is applied which sets eth1 to DHCP. Therefore, having a DHCP server present in the network is mandatory.
Update from 1.0.13 or lower to 1.0.14 (beta-rc4)
You may need help when updating units with ngtOS below version 1.0.13. Ensure that you are inside the office opening hours of Nexgentec Audio AG Switzerland. (8am till 4pm CET +1)
Your unit(s) probably need some special treatment before the update. Please contact Nexgentec Audio AG Switzerland at info@genesis-technologies.ch before you attempt to update.
Plan the Update
- Ensure that the unit you plan to update is connected to a network with unfiltered internet access. This is necessary in case service personnel need to access the unit using the built-in support tool.
- Make sure that you are within the office hours of Nexgentec Audio AG Switzerland (8am to 4pm CET +1).
- Ensure that no one else is working on the network during the time of the update.
Run the Update
- Open a browser and enter the IP address of the unit into the address bar.
- Log into the web interface using the username ‘admin’ and the chosen password (default is ’nexgentec’).
- In the top menu bar, select ‘Help’ > ‘Update’.


- Follow the instructions shown.
- Wait for the unit to reboot
Change Log
Version 1.0.13 (beta-rc3)
- Updated DEP to support AES67
- Enabled display
- Network ports can now be configured as a manageable switch, including IGMP settings
- Enabled cluster support
- Various improvements and bug fixes across all running services
Version 1.0.14 (beta-rc4)
- WebUI: Returns to login after timeout
- Network: Endpoints maintain the same MAC address
- Display: Some graphical artifacts have been fixed
Known Issues
Version 1.0.5
- The display is not working, it only shows the NGT logo
Version 1.0.14 (beta-rc4)
- WebUI: Clustering configuration is missing
- WebUI: Mandatory password change feature is missing
- SNMP: Missing
Upcoming Features
Features Awaiting Implementation:
- User configuration support for clustering
- SNMP support
4140PWRR3
The NGTC-4140PWRR3 is a Dante™ enabled network power amplifier for the nexgentec™ audio distribution solution
Key Features
- 4 x 140 Watt @ 4 Ohm – 1 x 200 Watt @ 4 Ohm bridged
- LAN control protocol
- only 1RU high
- Dante™ audio interface
- Stereo digital power amplifier
- Manageable integrated 2 port switch
- nexgentec ngtOS, operating system for control api, configuration and monitoring
Subsections of 4140PWRR3
Apps
Configure Installed Apps of the Unit
Each installed app can be configured to a certain level via the web interface.
The default login for the web interface is: Username: admin Password: nexgentec
Open a browser and enter the device’s network address in the address bar, then press Enter.
Use the top menu bar to navigate to Apps and select the app to be configured.
Subsections of Apps
Amplifier
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > Amplifier.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
transport
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
Control
Control > Channels
Status
- These icons show the status of the amplifier channel. Also, the temperature is displayed.
Action
- Use these buttons to turn the amplifier channel on and off. The amplifier channels can also be muted and unmuted. Be aware that due to a hardware limitation, channels 1 and 2 always follow the same power and mute settings, as do channels 3 and 4.
API
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > API.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
transport
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
api
- Use the dropdown menus to select the Endpoint and the port to use for each protocol that the API can communicate with.
Broker
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > Broker.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
transport
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
Dante
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > Broker.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
network
- Select the interface to be used for Dante audio. This interface will be used for audio data transmission.
Display
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > Display.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
transport
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
time
- Select the time format to be shown on the display, 24h or AM/PM.
temperature
- Select the temperature format to be shown on the display in Celsius or Fahrenheit.
backlight
- Select the brightness level. Possible values range from 0 to 255. At 0, the display on the front is completely dark and appears to be turned off.
Netd
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > WebUI.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
WebUI
Using the top menu bar, navigate to Apps > WebUI.
Files
Files > Log
Selecting “Files” will open the file browser where you can download and view the log files from the app.
Options
Options > General
logLevel
- Select the log level for the app.
transport
- Read-only: This field shows the internally used transport address.
web
- This is the address of the web UI to run on. The default is on all interfaces and port 80, therefore “:80”. Be careful when changing this setting.
Configuration
Configure Hardware and Software Properties
All configuration tasks can be performed via the web interface.
The default login for the web interface is: Username: admin Password: nexgentec
Open a browser and enter the device’s network address in the address bar, then press Enter.
Use the top menu bar to navigate to the option you want.
Subsections of Configuration
Network
This guide applies to all units running ngtOS >= version 1.0.13 (beta-rc3)
Status
The status of the network connections can be viewed on the status page System > Network > Status
General
Points to consider:
- Never assign a gateway to more than one connection.
- Never place more than one connection in the same IP address range.
- Use DNS servers that are reachable.
- Avoid leaving two interfaces connected to the network on DHCP.
- The unit requires internet access. This is necessary in case service personnel need to access the unit using the built-in support tool.
If things go wrong:
- Try to locate the device using your DHCP server. Attempt this on all available Ethernet interfaces.
- The display on the unit shows the full configuration for each interface, including the path to access the IP address.
Basic Functionality
In general, the physical network interfaces and the internal endpoints should be understood as a managed switch infrastructure. Each physical port can take untagged and tagged VLANs, each VLAN can be used to connect an “Endpoint” for Audio and/or Control. Finally, VLANs can be forwarded tagged or untagged between the physical interfaces, keeping the tagging or even untagging during forwarding.

 In this example, both physical ports are carrying VLANs 13, 15, and 22.
In this example, both physical ports are carrying VLANs 13, 15, and 22.
-
VLAN 13 is the untagged (native) VLAN on eth1 and gets tagged while flowing towards eth2, and vice versa. It’s also received by Endpoint 3, which is a management endpoint. The IP address (fixed or statically assigned) of Endpoint 3 can be reached on eth1 using no VLAN tag and on eth2 using a VLAN tag 13.
-
VLAN 15 is the tagged VLAN on eth1 and gets untagged while flowing towards eth2 (native), and vice versa. It’s also received by Endpoint 1, which is the audio endpoint. The IP address (fixed or statically assigned) of Endpoint 1 can be reached on eth1 using VLAN tag 15 and on eth2 using no VLAN tag.
-
VLAN 22 is a tagged VLAN which flows over both physical interfaces. It’s also received by Endpoint 2, which is a management endpoint. The IP address (fixed or statically assigned) of Endpoint 2 can be reached on any of the two physical interfaces using a VLAN tag 22.
On the Front Display
The front panel display shows the current network configuration, including how to access the shown IP address. If multiple endpoints exist, the line scrolls every 5 seconds to display all endpoints.
Syntax: physical[:Tagged VLAN]>Endpoint name > IP Address (CIDR notation).
Examples
Following the example above:
- eth1 > Endpoint 3 > 192.168.1.20/24 (See the description above on how to access 192.168.1.20)
- eth1:15 > Endpoint 1 > 192.168.5.20/24 (See the description above on how to access 192.168.5.20)
Configure
Select in the top menu System > Network > Settings
Continuing with the example above, this would look like:
Detailed Field Descriptions for “Switches”
Name
- Read-only: This field displays the name of the switch to be configured. “vswitch1” is the switch to be configured. Currently, only one virtual switch is allowed.
Multicast Snooping
- This setting allows the switch to observe and learn the multicast groups and associated members to limit the forwarding of multicast traffic. Use with caution. If you experience any problems with multicast streams flowing towards the unit or passing through it, turn this setting off.
Multicast Querier
- This setting allows the switch to send out network queries to determine which hosts belong to which multicast groups. It will be automatically set to false once the Endpoint for Audio is included in a tagged VLAN on any of the physical ports. Use it only when there is no managed switch in the network that could send out the query.
Detailed Field Descriptions for “Ports”
Link Address
- Read-only: This field displays the MAC address assigned to the port.
Switch Member
- This setting determines whether to include or exclude the physical port from being used by the managed switch.
VLAN Untagged
- This setting allows you to specify which VLANs should have their tags removed when traffic is sent out of this port.
VLAN Tagged
- This setting allows you to specify which VLANs should retain their tags when traffic is sent out of this port.
Detailed Field Descriptions for “Endpoints”
Name
- Read-only: This field displays the name of the endpoint.
Link Address
- This field displays the MAC address assigned to the endpoint.
Switch Member
- This setting determines in which virtual switch the endpoint should be included.
Usage
- This field indicates how the endpoint is being used in the network setup, either for Control, Audio, or both.
VLAN Untagged
- This setting allows you to specify which VLANs should be included and have their tags removed when traffic is sent out of this endpoint.
DHCP
- This setting enables or disables the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for the endpoint. If enabled, the endpoint will automatically receive an IP address from the DHCP server in the network.
Addresses
- This field displays the IP addresses assigned to the endpoint. The notation is in CIDR notation.
Routes (To)
- This field displays the routing table for the endpoint, showing where traffic will be directed. To add a default route (gateway), enter To: 0.0.0.0/0 Via: Gateway Address.
Nameservers
- This field displays the IP addresses of the DNS servers that the endpoint is configured to use.
Time
Status
You can view the status of the time on the status page by navigating to System > Time > Status.


Configuration
Select in the top menu System > Network > Settings


Detailed Field Description
NTP Server
- Enter a reachable NTP server that is geographically close to you.
Fallback NTP Server
- Enter another reachable NTP server that is geographically close to you. This server will be queried if the first server becomes unreachable.
Time Zone
- Select the time zone that you are in.
Control APIs
Control the Amplifier over TCP and HTTP using JSON-RPC 2.0
This is a preliminary api documentation, subject to change
Subsections of Control APIs
JSON RPC 2.0 API
This section describes the communication protocol between the control system and the 4140PWRR3 using RPC calls using the JSON-RPC 2.0 protocol
Definitions
Commands must be formatted as defined in the JSON-RPC 2.0 protocol
All commands sent over TCP transport must end with <LF>
All replies are formatted as defined in the JSON-RPC 2.0 protocol
All replies over TCP transport end up with <LF>
<LF> stands for “line feed”, corresponding hex is 0x0A
Transport protocols
JSON-RPC 2.0 commands can flow over different transport protocols, they need to be enabled in the config file of the installed api service. Per default they might not be enabled.
| Transport | Config | Datatype | Example | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCP | jrpc2TCPInterface | string | eth1 | >v1.0.1 |
| TCP | jrpc2TCPPort | int | 64823 | >v1.0.1 |
| TCP | jrpc2HTTPInterface | string | eth1 | >v1.0.1 |
| TCP | jrpc2HTTPPort | int | 64880 | >v1.0.1 |
In subsequent pages all methods are described that can be used.
Concurrency
All JSON-RPC 2.0 services do support asynchronous message processing. 3rd party control Systems must keep tracking of the id’s to determine whether a request was successful or not
TCP transport
Any TCP capable application can be used to test commands. Do not forget to end up with <LF>
HTTP transport
The body of the HTTP POST request must contain the complete JSON-RPC request message, encoded with Content-Type: application/json. Either a single request object or a list of request objects is supported. If the request completes, whether or not there is an error, the HTTP response is 200 (OK) for ordinary requests or 204 (No Response) for notifications, and the response body contains the JSON-RPC response. If the HTTP request method is not “POST”, 4140PWRR3 reports 405 (Method Not Allowed). If the Content-Type is not application/json, 4140PWRR3 reports 415 (Unsupported Media Type).
Test from a linux shell:
curl -i -X POST -H ‘Content-Type: application/json’ -d ‘{“jsonrpc”:“2.0”,“id”:1,“method”:“rpc.serverInfo”}’ http://host:64880
Subsections of JSON RPC 2.0 API
amplifier
amplifier commands are generic commands for all nexgentec™ amplifier devices. These commands utilize the generic amplifier protocol, enabling seamless integration and control across amplifier devices.
amplifier.channel.set (channelSet)
Enable or disable, mute or unmute a amplifier channel
A hardware limitation only allows stereo channel pairs to be switched on the 4140PWRR3.
- Channel 1 & 2 will power on/off together
- Channel 3 & 4 will power on/off together
A hardware limitation only allows stereo channel pairs to be muted on the 4140PWRR3.
- Channel 1 & 2 will mute/unmute together
- Channel 3 & 4 will mute/unmute together
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| amplifier.channelSet | >v1.0.1 | |||
| channel | 1,2,3,4 | Channel selection | >v1.0.1 | |
| power | 0,1 | Power on (1) or off (0) | >v1.0.1 | |
| mute | 0,1 | Mute (1) or unmute (0) | >v1.0.1 | |
| amplifier.channel.set | >=v1.0.14 | |||
| channel | 1,2,3,4 | Channel selection | >=v1.0.14 | |
| power | 0,1 | Power on (1) or off (0) | >=v1.0.14 | |
| mute | 0,1 | Mute (1) or unmute (0) | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channelSet","params":{"channel":1,"power":1}}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channel.set","params":{"channel":1,"power":1}}{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channelSet","params":{"channel":1,"power":1}}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channel.set","params":{"channel":1,"power":1}}{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channelSet","params":{"channel":1,"mute":1}}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channel.set","params":{"channel":1,"mute":1}}{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channelSet","params":{"channel":1,"power":1,"mute":0}}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channel.set","params":{"channel":1,"power":1,"mute":0}}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}amplifier.channel.get (channelGet)
Get the status of an amplifier channel
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| amplifier.channelGet | >v1.0.1 | |||
| amplifier.channel.get | >=v1.0.14 | |||
| channel | 1,2,3,4 | Channel selection | >v1.0.1 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channelGet","params":{"channel":1}}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channel.get","params":{"channel":1}}Reply
| Result | Key | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| channel status | ||
| power | 1 if channel was powered on, 0 if channel was powered off | |
| mute | 1 if channel was muted, 0 if channel was unmuted | |
| error | null if no error on channel otherwise error message | |
| powerStatus | 1 if channel is powered, otherwise 0 | |
| clip | 1 if channel is clipping, otherwise 0 | |
| temp | Temperature in °C |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":{"channel":1,"power":1,"mute":0,"error":null,"powerStatus":1,"clip":0,"temp":42.3}}amplifier.channels.subscribe (channelsSubscribe)
Subscribe all amplifier channels status push messages
Enable push status messages
Pushed status messages having the same format as channelGet replies
Push messages over HTTP transport are not supported
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| amplifier.channelsSubscribe | >v1.0.1 | |||
| amplifier.channels.subscribe | >v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channelsSubscribe"}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channels.subscribe"}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}amplifier.channels.unsubscribe (channelsUnsubscribe)
Unsubscribe all amplifier channels status push messages
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| amplifier.channelsUnsubscribe | >v1.0.1 | |||
| amplifier.channels.unsubscribe | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channelsUnsubscribe"}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"amplifier.channels.unsubscribe"}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}4140pwrr3
4140pwrr3 commands are specific to 4140pwrr3 nexgentec™ devices. These commands are used to control the 4140pwrr3 service, which is a device specific service designed for 4140pwrr3 devices.
4140pwrr3.app.log.level.get
Get the log level for the 4140pwrr3 service running on the 4140pwrr3
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4140pwrr3.app.log.level.get | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"4140pwrr3.app.log.level.get"}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| x | Active log level |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":20,"result":{"level":3}}4140pwrr3.app.log.level.set
Set the log level for 4140pwrr3 service and associated processes
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4140pwrr3.app.log.level.set | level | 0-7 | Log level to set | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"4140pwrr3.app.log.level.set","params":{"level":6}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}api
api commands are generic commands for all nexgentec™ devices that have an API. These commands utilize the generic API protocol, enabling seamless integration and control across supported devices.
api.app.log.level.get
Get the log level for the api service running on the api
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| api.app.log.level.get | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"api.app.log.level.get"}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| x | Active log level |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":20,"result":{"level":3}}api.app.log.level.set
Set the log level
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| api.app.log.level.set | level | 0-7 | Log level to set | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"api.app.log.level.set","params":{"level":6}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}display
diplay commands are generic commands for all nexgentec™ devices that have a diplay. These commands utilize the generic diplay protocol, enabling seamless integration and control across supported devices.
diplay.backlight.level.get
Get the log level for the api service running on the api
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| diplay.backlight.level.get | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"diplay.backlight.level.get"}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| x | Active backlight level |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":20,"result":{"level":3}}diplay.backlight.level.set
Set the backlight level
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| diplay.backlight.level.set | level | 0-255 | Level to set | >=v1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"diplay.backlight.level.set","params":{"level":6}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}server
server commands are generic commands for all Nexgentec™ devices that support a JSON-RPC 2.0 API. These commands provide a standard JSON-RPC method to retrieve the list of supported methods available on the device.
rpc.server.info.get (serverInfo)
Get all supported RCP methods
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rpc.serverInfo | >1.0.1 | |||
| rpc.server.info.get | >=1.0.14 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"rpc.serverInfo"}
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"rpc.server.info.get"}Reply
| Result | Key | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| methods | All supported methods that can be used by a 3rd party control system | |
| counters | Server counters | |
| startTime | Server start time |
{
"result": {
"startTime": "2024-04-11T08:06:23.391135102Z",
"metrics": {
"bytes_written": 0,
"rpc_requests": 1,
"bytes_read": 55,
"notifications_pushed": 0,
"rpc_errors": 0,
"servers_active": 2,
"calls_pushed": 0
},
"methods": [
"4140pwrr3-cf11.app.log.level.get","4140pwrr3-cf11.app.log.level.set","4140pwrr3-cf11.app.version.get","4140pwrr3.app.log.level.get","4140pwrr3.app.log.level.set","4140pwrr3.app.version.get","4140pwrr3.appLogLevelGet","4140pwrr3.appLogLevelSet","4140pwrr3.appVersionGet","amplifier.channel.get","amplifier.channel.set","amplifier.channelGet","amplifier.channelSet","amplifier.channels.subscribe","amplifier.channels.unsubscribe","amplifier.channelsSubscribe","amplifier.channelsUnsubscribe","api.app.log.level.get","api.app.log.level.set","api.app.version.get","api.appLogLevelGet","api.appLogLevelSet","api.appVersionGet","display.backlight.level.get","display.backlight.level.set","rpc.server.info.get","rpc.serverInfo","webui.app.log.level.get","webui.app.log.level.set","webui.app.version.get"]
},
"id": 1,
"jsonrpc": "2.0"
}Specifications
| Digital Audio Input | |
| Type | 4 channels, full range |
| Format | Dante™, Aes67 |
| Audio Performance | |
| Output Power @4Ω | 280W/CH |
| Output Power @8Ω | 140W/CH |
| Bridge Mode | Yes@8Ohm |
| Distortion | 0.0014% 20hZ < f < 20kHz. Pout = 1W |
| Output Noise | 40 µV |
| Power Bandwidth | 20Hz - 35kHz |
| Freuquency Response | 10Hz - 48kHz +0/-3dB. All loads |
| Network Port eth1 | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 10/100/1000 Mbps Full Duplex |
| Network Port eth2 | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 10/100/1000 Mbps Full Duplex |
| General | |
| Mains Voltage | 230V/115V, 50–60 Hz |
| Power Consumption | @100–240VAC,47/63Hz 6.4A |
| Total Heat Dissipation | 10 BTU/h standby, 139 BTU/h operation |
| Operating temp | 5°C – 30°C |
| Dimensions | L: 250mm, W: 209mm, H:45mm 1/2 rack width |
| Weight | 1.9kg |
| Compliance | CE, ROHS |
Audio Channel Assignment
| Channel | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 1 | Left Channel Amplifier Module 1 |
| 2 | Right Channel Amplifier Module 1 |
| 3 | Left Channel Amplifier Module 2 |
| 4 | Right Channel Amplifier Module 2 |
CAD step file
ngtOS
Never downgrade to an older ngtOS, as it will result in a factory return of the unit in every case.
If you have multiple units to update, try the update on one and if it’s working as expected, proceed with all others.
Update Path
- All units must be updated to 1.0.14 (beta-rc4) before upgrading to any higher version of ngtOS.
- Future update paths will be published when available.
Update Notes
Version 1.0.14 (beta-rc4)
- Beginning with version 1.0.13, a new method to configure the network of the unit was introduced. Existing configurations will be converted as accurately as possible. If the update fails, a default configuration is applied which sets eth1 to DHCP. Therefore, having a DHCP server present in the network is mandatory.
Update from 1.0.13 or lower to 1.0.14 (beta-rc4)
You may need help when updating units with ngtOS below version 1.0.13. Ensure that you are inside the office opening hours of Nexgentec Audio AG Switzerland. (8am till 4pm CET +1)
Your unit(s) probably need some special treatment before the update. Please contact Nexgentec Audio AG Switzerland at info@genesis-technologies.ch before you attempt to update.
Plan the Update
- Ensure that the unit you plan to update is connected to a network with unfiltered internet access. This is necessary in case service personnel need to access the unit using the built-in support tool.
- Make sure that you are within the office hours of Nexgentec Audio AG Switzerland (8am to 4pm CET +1).
- Ensure that no one else is working on the network during the time of the update.
Run the Update
- Open a browser and enter the IP address of the unit into the address bar.
- Log into the web interface using the username ‘admin’ and the chosen password (default is ’nexgentec’).
- In the top menu bar, select ‘Help’ > ‘Update’.


- Follow the instructions shown.
- Wait for the unit to reboot
Change Log
Version 1.0.13 (beta-rc3)
- Updated DEP to support AES67
- Enabled display
- Network ports can now be configured as a manageable switch, including IGMP settings
- Enabled cluster support
- Various improvements and bug fixes across all running services
Version 1.0.14 (beta-rc4)
- WebUI: Returns to login after timeout
- Network: Endpoints maintain the same MAC address
- Display: Some graphical artifacts have been fixed
Known Issues
Version 1.0.5
- The display is not working, it only shows the NGT logo
Version 1.0.14 (beta-rc4)
- WebUI: Clustering configuration is missing
- WebUI: Mandatory password change feature is missing
- SNMP: Missing
Upcoming Features
Features Awaiting Implementation:
- User configuration support for clustering
- SNMP support
16/24/32140PWR2
The NGTC-16/24/32140PWR2 are DanteTM enabled network power amplifiers for the nexgentec™ audio distribution solution
Key Features
- 16/24/32 x 140 Watt @ 8 Ohm / 280 Watt @ 4 Ohm
- LAN control protocol
- only 2RU high
- 2 kW wide range power supply
- 44.1 kHz / 48 kHz
- Web UI for monitoring and configuration
- SNMP
Subsections of 16/24/32140PWR2
Control API
This section describes the communication protocol between the control system and the 32140PWR
| Connection | TCP/HTTP (NGTC-32140PWR is HTTP server), Port 80 |
| Command Format | IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=action¶m=value |
Multiple parameters and values must be sent like: …?action=21&channel=1&name=MySpeaker
All commands must be sent as standard HTTP requests including headers, the server responds with a reply header and a JSON data table
Server will close the connection once replied, to keep the connection open set the keep-alive flag in the request header
Use any browser to test the communication"
Example
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 0 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=0 |
|||
| Reply | {“version”: “1.0.0”, “api-version”: “N3”,“fpga-version”: “2.2.0-d51c0cc4-#1040”, | ||
| “serial”: “240818000117”,“type”: 1,“type-string”: “32140PWR”,“channel”: 32} |
Subsections of Control API
General
Get device info
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 0 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=0 |
|||
| Reply | {“version”: “1.0.0”, “api-version”: “N3”,“fpga-version”: “2.2.0-d51c0cc4-#1040”, | ||
| “serial”: “240818000117”,“type”: 1,“type-string”: “32140PWR”,“channel”: 32} |
Get host name
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 1 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“hostname”: “My Amp”} |
Set host name
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 2 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=2&hostname=“MyAmp” |
|||
| Reply | {“hostname”: “MyAmp”} |
Get IP configuration
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 3 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=3 |
|||
| Reply | {“type”: “dhcp”,“ip”: “10.77.178.237”,“subnet”: “255.255.0.0”,“gateway”: “10.77.178.1”} |
Set IP configuration
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 4 | ||
| type=static/dhcp/auto | |||
| ip=x.x.x.x | |||
| netmask=x.x.x.x | |||
| gateway=x.x.x.x | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=4&type=static&ip=10.77.178.10&subnet=255.255.0.0&gateway=10.77.178.1 |
|||
| Reply | {“type”: “dhcp”,“ip”: “10.77.178.237”,“subnet”: “255.255.0.0”,“gateway”: “10.77.178.1”} |
Get mains voltage
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 5 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=5 |
|||
| Reply | {“value”: 230} |
Set mains voltage
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 6 | ||
| value=90-240V | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=6&value=110 |
|||
| Reply | {“value”: 110} |
Audio
Get master volume
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 7 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=7 |
|||
| Reply | {“volume”: 0.0} |
Set master volume
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 8 | ||
| volume=-100.0 - 24.0 | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=6&volume=0 |
|||
| Reply | {“volume”: 0.0} |
Get master mute
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 9 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=9 |
|||
| Reply | {“mute”: 1} |
Set master mute
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 10 | ||
| mute=0/1 | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=10&mute=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“mute”: 1} |
Get PSU gain reduction
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 11 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=11 |
|||
| Reply | {“reduction”: -0.0} |
Get channel name
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 20 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=20&channel=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”:1,“name”: “Ch 1”} |
Set channel name
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 21 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number | |||
| name=MAX 30 Chars | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=21&channel=1&name=MySpeaker |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”:1,“name”: “MySpeaker”} |
Get channel enable
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 22 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=22&channel=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”:1,“enable”: 1} |
Set channel enable
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 23 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number, comma seperated if multiple | |||
| enable=1/0 | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=23&channel=1,2,3,4,5&enable=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”: [1,2,3,4,5],“enable”: 0} |
Get channel volume
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 24 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=24&channel=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”:1,“volume”: 0.0} |
Set channel volume
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 25 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number | |||
| volume=-72.0 - 24.0 | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=25&channel=1&volume=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”:1,“volume”: 1.0} |
Get channel level
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 30 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=30&channel=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”:1,“peak”: -11.1,“hold”: -9.7,“clip”: 0} |
Get channel status
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 31 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=31&channel=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”:1,“status”: 0,“status_text”: “OFF”,“temp”: 38.5} |
Get all channel level
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 40 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=40 |
|||
| Reply | {“level”: [{ | ||
| “peak”: -10.0,“hold”: -9.3,“clip”: 0}, | |||
| {“peak”: -12.0,“hold”: -11.4,“clip”: 0}, | |||
| … ]} |
Get overview status data
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 41 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=41 |
|||
| Reply | {“overview”: [ | ||
| { “status”: 0,“status_text”: “OFF”,“temp”: 38.5,“enable”: 0,“volume”: 1.0,“name”: “MySpeaker”}, | |||
| { “status”: 1,“status_text”: “OK”,“temp”: 38.5,“enable”: 1,“volume”: 0.0,“name”: “Ch 2”}, | |||
| … ]} |
Syslog
Get get attached syslog server address
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 50 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=50 |
|||
| Reply | {“syslog_ip”: “192.168.1.1”,“syslog_port”: “555”} |
Set set syslog server address
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 51 | ||
| syslog_ip=x.x.x.x | |||
| syslog_port=x | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=action=51 &syslog_ip=192.168.1.1&syslog_port=555 |
|||
| Reply | {“syslog_ip”: “192.168.1.1”,“syslog_port”: “555”} |
Get number of syslog messages
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 52 | ||
| number=x | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=52&number=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“log”: [“Jan 1 01:42:37 32140PWR-000117user.info root: Amp is ok”]} |
Firmware
Updates
Firmware updates can be downloaded directly with the updater tool. If on site no internet is available do not forget to download previously
How to update
-
Download updater
-
Disable Windows Firewall on the interface which connects to the same network as the amp
-
Start update software
-
Click on the row for each device to display the firmwares available
- Hit Download to download the desired version or just download the latest one.
- Once the firmware desired is downloaded go back to Devices If the devide is not listed it can be added using +DEVICE NOT IN LIST. If the device is shown already skip the next 2 steps
- Click on the row which shows the network card of your computer that is in the same network as the device. BASE ADDRESS will be autofilled with the corresponding network address.
Now do a FULL NETWOR SCAN
Alternatively add the device by typing its IP adress into IP ADDRESS and press ADD DEVICE
- Once the device is listed selet UPDATE MANAGER
- Select which version the device should be updated to and hit UPDATE
- Wait for the update to finish. It can take several minutes.
Specification
| Digital Audio Input | |
| Type | 16/24/32 channels, full range |
| Format | Dante™, Aes67 |
| Audio Performance | |
| Output Power @4Ω | 280W/CH |
| Output Power @8Ω | 140W/CH |
| Bridge Mode | Yes@8Ohm |
| Distortion | 0.005% 20hZ < f < 20kHz. Pout = 1W |
| Output Noise | 40 µV |
| Power Bandwidth | 20Hz - 35kHz |
| Freuquency Response | 10Hz - 48kHz +0/-3dB. All loads |
| Network Port P1 | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 10/100/1000 Mbps Full Duplex |
| Configuration | Switched, Redundant, Independent (see below) |
| Network Port P2 | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 10/100/1000 Mbps Full Duplex |
| Configuration | Switched, Redundant, Independent (see below) |
| General | |
| Mains Voltage | 230V/115V, 50–60 Hz |
| Compliance | CE, ROHS |
| Power Consumption | |
| 16140PWR2 | @100–240VAC,47/63Hz 6A |
| 24140PWR2 | @100–240VAC,47/63Hz 8A |
| 32140PWR2 | @100–240VAC,47/63Hz 10A |
| Heat Dissipation | |
| 16140PWR2 | Idle 333 BTU/h, 1/8 power @4Ohm 595 BTU/h |
| 24140PWR2 | Idle 333 BTU/h, 1/8 power @4Ohm 833 BTU/h |
| 32140PWR2 | Idle 333 BTU/h, 1/8 power @4Ohm 1066 BTU/h |
| Operating temp | 5°C – 30°C |
| Dimensions | L: 482mm, W: 392mm, H:88mm (2RU) |
| Weight | |
| 16140PWR2 | 13kg |
| 24140PWR2 | 14kg |
| 32140PWR2 | 15kg |
Network Port Configurations
32140PWR
The NGTC-32140PWR is a DanteTM enabled network power amplifier for the nexgentec™ audio distribution solution
Key Features
- 32 x 140 Watt @ 8 Ohm / 280 Watt @ 4 Ohm
- LAN control protocol
- only 2RU high
Subsections of 32140PWR
Control API
This section describes the communication protocol between the control system and the 32140PWR
| Connection | TCP/HTTP (NGTC-32140PWR is HTTP server), Port 80 |
| Command Format | IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=action¶m=value |
Multiple parameters and values must be sent like: …?action=21&channel=1&name=MySpeaker
All commands must be sent as standard HTTP requests including headers, the server responds with a reply header and a JSON data table
Server will close the connection once replied, to keep the connection open set the keep-alive flag in the request header
Use any browser to test the communication"
Example
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 0 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=0 |
|||
| Reply | {“version”: “1.0.0”, “api-version”: “N3”,“fpga-version”: “2.2.0-d51c0cc4-#1040”, | ||
| “serial”: “240818000117”,“type”: 1,“type-string”: “32140PWR”,“channel”: 32} |
Subsections of Control API
General
Get device info
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 0 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=0 |
|||
| Reply | {“version”: “1.0.0”, “api-version”: “N3”,“fpga-version”: “2.2.0-d51c0cc4-#1040”, | ||
| “serial”: “240818000117”,“type”: 1,“type-string”: “32140PWR”,“channel”: 32} |
Get host name
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 1 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“hostname”: “My Amp”} |
Set host name
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 2 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=2&hostname=“MyAmp” |
|||
| Reply | {“hostname”: “MyAmp”} |
Get IP configuration
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 3 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=3 |
|||
| Reply | {“type”: “dhcp”,“ip”: “10.77.178.237”,“subnet”: “255.255.0.0”,“gateway”: “10.77.178.1”} |
Set IP configuration
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 4 | ||
| type=static/dhcp/auto | |||
| ip=x.x.x.x | |||
| netmask=x.x.x.x | |||
| gateway=x.x.x.x | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=4&type=static&ip=10.77.178.10&subnet=255.255.0.0&gateway=10.77.178.1 |
|||
| Reply | {“type”: “dhcp”,“ip”: “10.77.178.237”,“subnet”: “255.255.0.0”,“gateway”: “10.77.178.1”} |
Get mains voltage
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 5 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=5 |
|||
| Reply | {“value”: 230} |
Set mains voltage
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 6 | ||
| value=90-240V | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=6&value=110 |
|||
| Reply | {“value”: 110} |
Audio
Get master volume
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 7 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=7 |
|||
| Reply | {“volume”: 0.0} |
Set master volume
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 8 | ||
| volume=-100.0 - 24.0 | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=6&volume=0 |
|||
| Reply | {“volume”: 0.0} |
Get master mute
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 9 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=9 |
|||
| Reply | {“mute”: 1} |
Set master mute
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 10 | ||
| mute=0/1 | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=10&mute=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“mute”: 1} |
Get PSU gain reduction
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 11 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=11 |
|||
| Reply | {“reduction”: -0.0} |
Get channel name
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 20 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=20&channel=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”:1,“name”: “Ch 1”} |
Set channel name
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 21 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number | |||
| name=MAX 30 Chars | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=21&channel=1&name=MySpeaker |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”:1,“name”: “MySpeaker”} |
Get channel enable
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 22 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=22&channel=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”:1,“enable”: 1} |
Set channel enable
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 23 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number, comma seperated if multiple | |||
| enable=1/0 | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=23&channel=1,2,3,4,5&enable=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”: [1,2,3,4,5],“enable”: 0} |
Get channel volume
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 24 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=24&channel=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”:1,“volume”: 0.0} |
Set channel volume
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 25 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number | |||
| volume=-72.0 - 24.0 | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=25&channel=1&volume=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”:1,“volume”: 1.0} |
Get channel level
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 30 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=30&channel=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”:1,“peak”: -11.1,“hold”: -9.7,“clip”: 0} |
Get channel status
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 31 | ||
| channel=1-MAX Channel Number | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=31&channel=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“channel”:1,“status”: 0,“status_text”: “OFF”,“temp”: 38.5} |
Get all channel level
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 40 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=40 |
|||
| Reply | {“level”: [{ | ||
| “peak”: -10.0,“hold”: -9.3,“clip”: 0}, | |||
| {“peak”: -12.0,“hold”: -11.4,“clip”: 0}, | |||
| … ]} |
Get overview status data
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 41 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=41 |
|||
| Reply | {“overview”: [ | ||
| { “status”: 0,“status_text”: “OFF”,“temp”: 38.5,“enable”: 0,“volume”: 1.0,“name”: “MySpeaker”}, | |||
| { “status”: 1,“status_text”: “OK”,“temp”: 38.5,“enable”: 1,“volume”: 0.0,“name”: “Ch 2”}, | |||
| … ]} |
Syslog
Get get attached syslog server address
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 50 | ||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=50 |
|||
| Reply | {“syslog_ip”: “192.168.1.1”,“syslog_port”: “555”} |
Set set syslog server address
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 51 | ||
| syslog_ip=x.x.x.x | |||
| syslog_port=x | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=action=51 &syslog_ip=192.168.1.1&syslog_port=555 |
|||
| Reply | {“syslog_ip”: “192.168.1.1”,“syslog_port”: “555”} |
Get number of syslog messages
| Communication | Action | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Request | 52 | ||
| number=x | |||
IP/0CXQRB2XQ3KD7XB/nexgentec.fcgi?action=52&number=1 |
|||
| Reply | {“log”: [“Jan 1 01:42:37 32140PWR-000117user.info root: Amp is ok”]} |
Firmware
Updates
Firmware updates can be downloaded directly with the updater tool. If on site no internet is available do not forget to download previously
How to update
-
Download updater
-
Disable Windows Firewall on the interface which connects to the same network as the amp
-
Start update software
-
Click on the row for each device to display the firmwares available
- Hit Download to download the desired version or just download the latest one.
- Once the firmware desired is downloaded go back to Devices If the devide is not listed it can be added using +DEVICE NOT IN LIST. If the device is shown already skip the next 2 steps
- Click on the row which shows the network card of your computer that is in the same network as the device. BASE ADDRESS will be autofilled with the corresponding network address.
Now do a FULL NETWOR SCAN
Alternatively add the device by typing its IP adress into IP ADDRESS and press ADD DEVICE
- Once the device is listed selet UPDATE MANAGER
- Select which version the device should be updated to and hit UPDATE
- Wait for the update to finish. It can take several minutes.
Specification
| Digital Audio Input | |
| Type | 32 channels, full range |
| Format | Dante™, Aes67 |
| Audio Performance | |
| Output Power @4Ω | 280W/CH |
| Output Power @8Ω | 140W/CH |
| Bridge Mode | No |
| Distortion | 0.005% 20hZ < f < 20kHz. Pout = 1W |
| Output Noise | 40 µV |
| Power Bandwidth | 20Hz - 35kHz |
| Freuquency Response | 10Hz - 48kHz +0/-3dB. All loads |
| Network Port P1 | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 10/100/1000 Mbps Full Duplex |
| Configuration | Switched, Redundant, Independent (see below) |
| Network Port P2 | |
| Physical Level | Standard Ethernet |
| Connector | Single RJ-45 |
| Cable Quality | CAT-5/6/7 |
| Transmission Speed | 10/100/1000 Mbps Full Duplex |
| Configuration | Switched, Redundant, Independent (see below) |
| General | |
| Mains Voltage | 230V/115V, 50–60 Hz |
| Compliance | CE, ROHS |
| Power Consumption | @100–240VAC,47/63Hz 10A |
| Heat Dissipation | Idle 333 BTU/h, 1/8 power @4Ohm 1066 BTU/h |
| Operating temp | 5°C – 30°C |
| Dimensions | L: 482mm, W: 392mm, H:88mm (2RU) |
| Weight | 15kg |
Network Port Configurations
Legacy Products
NGTC-SSPR2
CRBIBOB
NGTC-CRBIBOB
SDM
SDM is a Dante™ and AES67 enabled “software defined matrix” for nexgentec™ audio distribution solution or any other solution that uses Dante™ and/or AES67
Features
- Software defined matrixing, channels are routed directly on the network using Dante™’s DAPI.
- Unlimited number of Dante™ and/or AES67 devices supported.* **
- Unlimited number of Dante™ and/or AES67 channels supported.* **
- Creates routings from Dante™ and/or AES67 transmitter channels to Dante™ receivers.
- Deletes routings from Dante™ receivers.
- Supports single or batch routing operations.
- TCP and HTTP API for 3rd party control.
- Integrates with Symetrix SymNet devices for automated matrixing.
- Preset support for channel map presets.
- Syslog support
* Depends on hardware resources.
** Depends on mDNS limitations, DAPI limitations and hardware resource availability. Audinate recommends no more than 300 devices in a system.
NGT-SDM-A32 is limited to up to 32 Dante™ devices
NGT-SDM-A64 is limited to up to 64 Dante™ devices
NGT-SDM-AUNL is intended to work with up to 2500 devices, more available on request
Product Codes and Variations
- NGT-SDM-A32BDL01 bundle contains the softwares NGT-SDM-A32, NGT-HWM and hardware NGT-SDM-APU2
- NGT-SDM-A64BDL01 bundle contains the softwares NGT-SDM-A64, NGT-HWM and hardware NGT-SDM-APU2
- NGT-SDM-AUBDL01 bundle contains the softwares NGT-SDM-AUNL, NGT-HWM and hardware NGT-SDM-APU2
- NGT-SDM-APU2U1 option contains OS update service for NGT-SDM-APU2 (Yearly subscription)
NGT-SDM-APU2
- Half rack width and one rack unit high
- Powered with included power supply, 12V DC, about 6 to 12W depending on CPU load

- Configure SDM service to use enp2s0 as primary Dante™ interface SDM service configuration
Control on Ethernet Interface, Dante™ Primary Port on VLAN
We would like to use the Ethernet interface enp1s0 for control and the VLAN 10 on Ethernet interface enp1s0 for Dante™
- Assign a static IP address to enp1s0 if DHCP is not wished
- Assign a Gateway to enp1s0 if not on DHCP
- Assign at least to enp1s0 one DNS server if not on DHCP
- Add a new VLAN using the + symbol. In the popup window enter the name Dante, the VLAN id 10 and as option select enp1s0. Press Add :-)
- Assign a static IP address to VLAN Dante (mandatory)
Configuration Options
Network configuration be done on the settings page Host > Network > Settings
This is not an end consumer product. It requires qualified personnel to be installed If you screw up the settings the hardware have to be sent back to the manufacturer, there is no way back
Points you should pay attention to
- Never assign a Gateway to more than one connection
- Never place more than one connection in the same IP address range
- Use DNS servers that are reachable. SDM needs internet access for licensing purposes
- Never leave 2 interfaces connected to the network on DHCP
Oops, I did it again!
- If everything went wrong, try to find the device using your DHCP server. Try all available Ethernet interfaces
All interfaces are on DHCP if no static address is present
Network settings page uses JavaScript Please activate it in your browser and deactivate popup blockers
Ethernet
All available Ethernet connections found on the hardware are listed. Any Ethernet interface can be added to a new bridge using the bridge symbol. The new bridge will overtake all settings from the Ethernet interface
DHCP
- A click on the sentence true or false opens a popup window for the new setting
- With the setting true, all statically assigned addresses are deleted and the connection to this Ethernet interface can be interrupted. Look at the leases table on your DHCP server to find out the new address
- If the previous setting was true the popup window will let you assign a static address. This address will be immediately applied as soon as you select add
Addresses
- A click on the IP address opens a popup window to modify the existing address
- Using the trash can symbol an address can be deleted
- With the + symbol a new address can be added
Gateway
- A click on the IP address opens a popup window to modify the existing address
- Using the trash can symbol an address can be deleted
- With the + symbol a new address can be added
Nameservers
- A click on the IP address opens a popup window to modify the existing address
- Using the trash can symbol an address can be deleted
- With the + symbol a new address can be added
VLAN
VLAN interfaces can be added to all available Ethernet interfaces. Any VLAN interface can be added to a new bridge using the bridge symbol. The new bridge will overtake all settings from the VLAN interface
If you don’t know what a VLAN is keep away from these settings
- A VLAN can be removed using the trash can symbol on the same horizontal line as the VLAN name
ID
- A click on the VLAN id opens a popup window to modify the existing VLAN id
Link
- A click on the interface name opens a popup window to modify the interface on which the VLAN resides
DHCP
- A click on the sentence true or false opens a popup window for the new setting
- With the setting true, all statically assigned addresses are deleted and the connection to this Ethernet interface can be interrupted. Look at the leases table on your DHCP server to find out the new address
- If the previous setting was true the popup window will let you assign a static address. This address will be immediately applied as soon as you select add
Addresses
- A click on the IP address opens a popup window to modify the existing address
- Using the trash can symbol an address can be deleted
- With the + symbol a new address can be added
Gateway
- A click on the IP address opens a popup window to modify the existing address
- Using the trash can symbol an address can be deleted
- With the + symbol a new address can be added
Nameservers
- A click on the IP address opens a popup window to modify the existing address
- Using the trash can symbol an address can be deleted
- With the + symbol a new address can be added
Bridge
A bridge contains one or multiple Ethernet and/or VLAN interfaces.
If you don’t know what a network bridge is keep away from these settings
- A brige can be removed using the trash can symbol on the same horizontal line as the brige name
Interfaces
- List of the included interfaces in this bridge
- A new interface can be added with the + symbol
- An interface can be excluded with the trash can symbol
DHCP
- A click on the sentence true or false opens a popup window for the new setting
- With the setting true, all statically assigned addresses are deleted and the connection to this Ethernet interface can be interrupted. Look at the leases table on your DHCP server to find out the new address
- If the previous setting was true the popup window will let you assign a static address. This address will be immediately applied as soon as you select add
Addresses
- A click on the IP address opens a popup window to modify the existing address
- Using the trash can symbol an address can be deleted
- With the + symbol a new address can be added
Gateway
- A click on the IP address opens a popup window to modify the existing address
- Using the trash can symbol an address can be deleted
- With the + symbol a new address can be added
Nameservers
- A click on the IP address opens a popup window to modify the existing address
- Using the trash can symbol an address can be deleted
- With the + symbol a new address can be added
Time
SDM needs a valid time to work correctly. Without time source the service is not guaranteed to work
Status
The status of the time service can be viewed on the status page Host > Time > Status
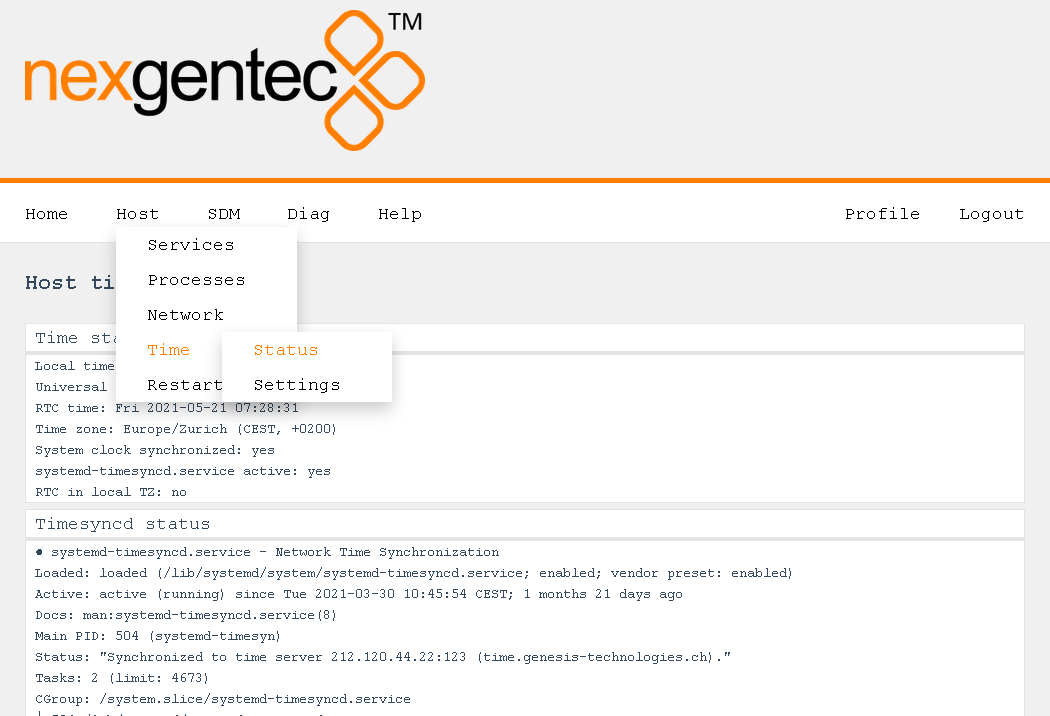

Configuration
NTP Server
- Insert a reachable NTP server near you
Fallback NTP Server
- Insert another reachable NTP server near you which will be queried once the first server is unreachable
Time Zone
- Select the time zone you are in
SDM Service
SDM service features and functionality are defined in different configuration files
Editing a SDM service configuration file
Edid a config file using the web interface, for example sdm.conf
Do not edid a config file unless you are very sure what you do
Web interface default login
admin / nexgentec
-
Open a browser and enter the devices network address in the address bar, press enter
-
Download the sdm.conf file
-
Make your changes to the sdm.conf file and save as unix format text file. configuration options
-
Upload the sdm.conf file, it will overwrite the existing one
-
Restart SDM process, Host -> Services -> Software Defined Matrix Service (this step is not needed for .toml files)

Subsections of SDM Service
sdm.conf
This section describes the various configuration options sdm.conf file can contain.
Use UNIX file fomatting when editing the file
File entries must be formatted as follows:
[Section]
key=value
For example to activate syslog:
[syslog]
address=“server.example.com”
port=53
level=6
tag=“sdm”
uuid
Do not delete the uuid, it identifies the sdm software. All licenses are bound to the uuid which is individual to every instance of sdm, it is like a product key for an OS
| Section | Key | Value | Example | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| uuid | key | 408aca84-a2b0-11eb-bcbc-0242ac130002 | key=408aca84-a2b0-11eb-bcbc-0242ac130002 | >v0.0.1 |
logLevel
| Section | Key | Value | Example | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| logLevel | level | 1-7 | level=1 | >v0.0.1 |
syslog
| Section | Key | Value | Example | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| syslog | level | 1-7 | level=6 | >v0.0.1 |
| address | your servers address | address=“server.example.com” | >v0.0.1 | |
| port | 53 or custom | port=53 | >v0.0.1 | |
| tag | sdm | tag=“sdm” | >v0.0.1 |
logAuth
logAuth is for only internal usage
| Section | Key | Value | Example | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| logAuth | key | key="" | >v0.0.1 |
api
| Section | Key | Value | Example | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| api | jrpc2TCPInterface | Any network interface | jrpc2TCPInterface=“enp1s0” | >v1.8.50 |
| jrpc2TCPPort | Default: 64823 | jrpc2TCPPort=64823 | >v1.8.50 | |
| jrpc2HTTPInterface | Any network interface | jrpc2HTTPInterface=“enp1s0” | >v1.8.50 | |
| jrpc2HTTPPort | Default: 64880 | jrpc2HTTPPort=64880 | >v1.8.50 | |
| jrpc2Console | on/off | jrpc2Console=on | >v1.8.50 |
dante
| Section | Key | Value | Example | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dante | primary | Any network interface | primary=“enp1s0” | >v1.8.50 |
| secondary | Any network interface | secondary=“enp2s0” | >v1.8.50 |
preset
| Section | Key | Value | Example | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| preset | recallPresetIDOnStart | Any preset as defined in presets_config.toml | recallOnStart=1 | >v1.8.50 |
| preset | recallPresetNameOnStart | Any preset as defined in presets_config.toml | recallOnStart=mypreset | >v1.8.50 |
| recallOnStartDelay | x (seconds) | recallOnStartDelay=10 | >v1.8.50 |
ifConfig (deprecated)
ifConfig is deprecated
Use api section to define interface/port for 3rd party communication and dante section to define the interfaces used for Dante™
| Section | Key | Value | Example | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dante | primary | Any network interface | primary=“enp1s0” | <v1.8.50 |
| secondary | Any network interface | secondary=“enp2s0” | <v1.8.50 | |
| cmdServer | Any network interface | cmdServer=“enp2s0” | <v1.8.50 |
cmdServer (deprecated)
cmdServer is deprecated
Use api section to define the port for 3rd party communication
| Section | Key | Value | Example | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cmdServer | port | port=48648 | <v1.8.50 |
presets_config.toml
Presets can be recalled on start up and using the Control API
Use UNIX file fomatting when editing the file
Generate yourself an example Generate example
See the fully commented definition below
- The file must be in TOML format
- Check the correct syntax online toml-lint
- Mandatory means that it will not work without.
[[preset]]
# ID (s) of the preset object, mandatory
preset_id = [56, 59, 33, 38]
# Name of the preset object, can be omitted
preset_name = "MyPreset_1"
# Destination object
[preset.destination]
[[preset.destination.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMS0000011"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 1
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_1"
[[preset.destination.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMS0000012"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 2
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_1"
[[preset.destination.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMS0000013"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 3
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_1"
[[preset.destination.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMS0000014"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 4
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_1"
# Source object
[preset.source]
[[preset.source.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMS0000011"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 1
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_1"
[[preset.source.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMS0000012"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 2
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_1"
[[preset.source.channel]]
# AES Flow name, mandatory for AES devices
aes_flow_name = "239.69.x.x@MyAesDevice_1"
# AES flow slot ID for this channel (1-x), mandatory for AES devices
aes_flow_slot_id = 1
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 3
[[preset.source.channel]]
# AES Flow name, mandatory for AES devices
aes_flow_name = "239.69.x.x@MyAesDevice_1"
# AES flow slot ID for this channel (1-x), mandatory for AES devices
aes_flow_slot_id = 2
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 4
[[preset]]
preset_id = [26, 9, 3, 63]
preset_name = "MyPreset_2"
[preset.destination]
[[preset.destination.channel]]
channel_name = "SDMS0000021"
index = 1
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_2"
[[preset.destination.channel]]
channel_name = "SDMS0000022"
index = 2
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_2"
[[preset.destination.channel]]
channel_name = "SDMS0000023"
index = 3
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_2"
[[preset.destination.channel]]
channel_name = "SDMS0000024"
index = 4
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_2"
[preset.source]
[[preset.source.channel]]
channel_name = "SDMS0000021"
index = 1
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_2"
[[preset.source.channel]]
channel_name = "SDMS0000022"
index = 2
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_2"
[[preset.source.channel]]
aes_flow_name = "239.69.x.x@MyAesDevice_2"
aes_flow_slot_id = 1
index = 3
[[preset.source.channel]]
aes_flow_name = "239.69.x.x@MyAesDevice_2"
aes_flow_slot_id = 2
index = 4symnet_config_sources.toml
The source config file describe the sources which are selected by a Symetrix Symnet control number value. If there is no Symetrix device present or SDM should not listen to Symetrix this file can be omitted
Use UNIX file fomatting when editing the file
Generate yourself an example" Generate example
See the fully commented definition below
- The file must be in TOML format
- Check the correct syntax online toml-lint
- Mandatory means that it will not work without.
# Defaults can be omitted if all values are defined source specific.
# Source object defined values are taking precedence
[default]
# Default delay settings for all objects that are not carrying its own settings for delay
# Object defined values are taking precedence , can be omitted
[default.delay]
# Delay value (ms) on switch over, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
switch = 500
[[source]]
# Name of the source or destination object, can be omitted
name = "MyDanteSource_1"
[[source.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMS0000011"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 1
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_1"
[[source.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMS0000012"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 2
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_1"
# Object defined delay settings, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
[source.delay]
# Delay value (ms) on switch over, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
switch = 800
# Object defined Symetrix settings, mandatory
[source.symnet]
# Symetrix Control Number Value for this source object, mandatory
control_value = 1
[[source]]
# Name of the source or destination object, can be omitted
name = "MyDanteSource_2"
[[source.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMS0000021"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 1
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_2"
[[source.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMS0000022"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 2
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_2"
# Object defined delay settings, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
[source.delay]
# Delay value (ms) on switch over, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
switch = 800
# Object defined Symetrix settings, mandatory
[source.symnet]
# Symetrix Control Number Value for this source object, mandatory
control_value = 2
[[source]]
# Name of the source or destination object, can be omitted
name = "MyDanteSource_3"
[[source.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMS0000031"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 1
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_3"
[[source.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMS0000032"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 2
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_3"
# Object defined delay settings, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
[source.delay]
# Delay value (ms) on switch over, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
switch = 800
# Object defined Symetrix settings, mandatory
[source.symnet]
# Symetrix Control Number Value for this source object, mandatory
control_value = 3symnet_config_destinations.toml
The destination config file describe the destinations which are identified by a Symetrix Symnet control number. If there is no Symetrix device present or SDM should not listen to Symetrix this file can be omitted
Use UNIX file fomatting when editing the file
Generate yourself an example Generate example
See the fully commented definition below
- The file must be in TOML format
- Check the correct syntax online toml-lint
- Mandatory means that it will not work without.
# Defaults can be omitted if all values are defined destination specific.
# Destination object defined values are taking precedence
[default]
# Default delay settings for all objects that are not carrying its own settings for delay
# Object defined values are taking precedence , can be omitted
[default.delay]
# Delay value (ms) on disconnect, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
disconnect = 2000
# Default Symetrix settings for all objects that are not carrying its own settings for delay
# Object defined values are taking precedence, can be omitted
[default.symnet]
# Symetrix Site ID, defined in project settings, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
site_id = 2
# Symetrix DSP IP Address (v4), if omitted on object basis default settings apply
unit_ip = "127.0.0.1"
[[destination]]
# Name of the source or destination object, can be omitted
name = "MyDanteDestination_1"
[[destination.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMD0000011"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 1
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_1"
[[destination.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMD0000012"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 2
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_1"
# Object defined delay settings, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
[destination.delay]
# Delay value (ms) on disconnect, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
disconnect = 800
# Object defined Symetrix settings, mandatory
[destination.symnet]
# Symetrix Control Number for this destination object, mandatory
control_id = 5001
# Symetrix Control Number that is feed back to Symetrix once the destination has changed, can be omitted
feedback_id = 6001
# Symetrix Site ID, defined in project settings, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
site_id = 3
# Symetrix DSP IP Address (v4), if omitted on object basis default settings apply
unit_ip = "127.0.0.2"
[[destination]]
# Name of the source or destination object, can be omitted
name = "MyDanteDestination_2"
[[destination.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMD0000021"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 1
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_2"
[[destination.channel]]
# Dante channel name, mandatory for Dante devices
channel_name = "SDMD0000022"
# Channel index, if omitted the order of the channels below the object determines the index
index = 2
# Dante device name, can be omitted but should not.
node_name = "MyDanteDevice_2"
# Object defined delay settings, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
[destination.delay]
# Delay value (ms) on disconnect, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
disconnect = 800
# Object defined Symetrix settings, mandatory
[destination.symnet]
# Symetrix Control Number for this destination object, mandatory
control_id = 5002
# Symetrix Control Number that is feed back to Symetrix once the destination has changed, can be omitted
feedback_id = 6002
# Symetrix Site ID, defined in project settings, if omitted on object basis default settings apply
site_id = 3
# Symetrix DSP IP Address (v4), if omitted on object basis default settings apply
unit_ip = "127.0.0.2"Control APIs
Control sdm over TCP and HTTP using JSON-RPC 2.0
Subsections of Control APIs
JSON RPC 2.0 API
This section describes the communication protocol between the control system and SDM using RPC calls using the JSON-RPC 2.0 protocol
Definitions
Commands must be formatted as defined in the JSON-RPC 2.0 protocol
All commands sent over TCP transport must end with <LF>
All replies are formatted as defined in the JSON-RPC 2.0 protocol
All replies over TCP transport end up with <LF>
<LF> stands for “line feed”, corresponding hex is 0x0A
Transport protocols
JSON-RPC 2.0 commands can flow over different transport protocols, once enabled in the api section of the config files. Per default they might not be enabled. Edid the config file to suite your needs and restart sdm service
| Transport | Config | Datatype | Example | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCP | jrpc2TCPInterface | string | enp1s0 | >v1.8.50 |
| TCP | jrpc2TCPPort | int | 64823 | >v1.8.50 |
| TCP | jrpc2HTTPInterface | string | enp1s0 | >v1.8.50 |
| TCP | jrpc2HTTPPort | int | 64880 | >v1.8.50 |
In subsequent pages all methods are described that can be used.
Concurrency
All JSON-RPC 2.0 services do support asynchronous message processing. 3rd party control Systems must keep tracking of the id’s to determine whether a request was successful or not
TCP transport
Any TCP capable application can be used to test commands. Do not forget to end up with <LF>
HTTP transport
The body of the HTTP POST request must contain the complete JSON-RPC request message, encoded with Content-Type: application/json. Either a single request object or a list of request objects is supported. If the request completes, whether or not there is an error, the HTTP response is 200 (OK) for ordinary requests or 204 (No Response) for notifications, and the response body contains the JSON-RPC response. If the HTTP request method is not “POST”, SDM reports 405 (Method Not Allowed). If the Content-Type is not application/json, SDM reports 415 (Unsupported Media Type).
Test from a linux shell:
curl –header “Content-Type: application/json” –request POST –data ‘{“jsonrpc”:“2.0”,“id”:1,“method”:“sdm.Get”,“params”:{“property”:“version”}}’ http://host:64880
Subsections of JSON RPC 2.0 API
SDM
sdm.Get version
Get the running software version
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sdm.Get | property | version | Property name to get | >v1.8.50 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"sdm.Get","params":{"property":"version"}}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| x.x.x | Version of sdm installed |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":"1.8.64"}sdm.Get activation
Get the activation status
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sdm.Get | property | activation | Property name to get | >v1.8.50 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"sdm.Get","params":{"property":"activation"}}Reply
| Result | Key | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trial | Deprecated >v1.8.70 | <v1.8.70 | |
| IsTrial | Is trial license is active? (deprecated >v1.8.70) | <v1.8.70 | |
| License | |||
| Channels | Allowed channels (unused)(deprecated >v1.8.70) | ||
| Devices | Allowed devices | ||
| Gracetime | Gracetime sdm runs with this license without online check | ||
| Exceed | Time exceed since last online license check | ||
| Valid | License if true, invalid if false | ||
| Expiration | Timestamp for fixed expiration licenses (defaults to 2000-01-01T00:00:00Z -> ignored) | >v1.8.72 | |
| Validation | Timestamp of last online validation | >v1.8.72 | |
| Refreshed | License online refreshed since last start. If false license infomation may be invalid |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": {
"Trial": {
"IsTrial": false
},
"License": {
"Channels": 500,
"Devices": 500,
"Gracetime": 168,
"Exceed": 0.002686415741388889,
"Valid": true
"Expiration":"2000-01-01T00:00:00Z"
"Validation":"2021-09-10T16:47:08.452207569+02:00"
},
"Refreshed": true
}
}System
system.Get
log.level
Get the log level for sdm and associated processes
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| system.Get | property | log.level | Property name to get | >v1.8.50 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"system.Get","params":{"property":"log.level"}}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| x | Active log level |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":6}system.Set
log.level
Set the log level for sdm and associated processes
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| system.Set | property | log.level | Property name to set | >v1.8.50 |
| level | 0-7 | Log level to set | >v1.8.50 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"system.Set","params":{"property":"log.level","level":6}}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}Config
config.Create
preset
Have sdm to create an example preset toml in the config directory. presets_config_example.toml will be created and can be modified and renamed as presets_config.toml. presets_config.toml is recognized by the system as file with preset definitions. See file content description for more info
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| config.Create | file | presets_config_example.toml | Example file to create | >v1.8.67 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"config.Create","params":{"file":"presets_config_example.toml"}}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}symnet
Have sdm to create symnet source and destination config examples in the config directory. Either symnet_config_sources_example.toml or symnet_config_destinations_example.toml will be created and can be renamed as symnet_config_sources.toml, symnet_config_destinations.toml
symnet_config_sources.toml is recognized by the system as file with source definitions. See file content description for more info symnet_config_destinations.toml is recognized by the system as file with destination definitions. See file content description for more info
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| config.Create | file | symnet_config_sources_example.toml | Example file to create | >v1.8.67 |
| symnet_config_destinations_example.toml | Example file to create | >v1.8.67 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"config.Create","params":{"file":"symnet_config_sources_example.toml"}}{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"config.Create","params":{"file":"symnet_config_destinations_example.toml"}}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}Preset
preset.Recall
Recall a preset defined in presets_config.toml. presets_config.toml is recognized by the system as file with preset definitions. See file content description for more info
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| preset.Recall | preset | 1-x | Preset to recall | >v1.8.67 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"preset.Recall","params":{"preset":1}}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}Monitor
monitor.Get
status
Request a status from monitoring, like PTP states from Dante™
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| monitor.Get | status | clocking | Status to get | >v1.8.50 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"monitor.Get", "params":{"status": "clocking"}}Reply
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": {
"SDM-DEV-DSP1-4": {
"Preferred": 0,
"Mutes": {},
"Ports": {
"1": {
"PortState": "PASSIVE",
"PathType": "MULTICAST",
"Layer": "LAYER3",
"LinkDown": 0,
"PtpVersion": 1,
"InterfaceIndex": 2
},
"2": {
"PortState": "SLAVE",
"PathType": "MULTICAST",
"Layer": "LAYER3",
"LinkDown": 0,
"PtpVersion": 2,
"InterfaceIndex": 2
},
"3": {
"PortState": "DISABLED",
"PathType": "UNICAST",
"Layer": "LAYER3",
"LinkDown": 0,
"PtpVersion": 1,
"InterfaceIndex": 2
},
"4": {
"PortState": "DISABLED",
"PathType": "UNICAST",
"Layer": "LAYER3",
"LinkDown": 0,
"PtpVersion": 2,
"InterfaceIndex": 2
}
}
},
"SDM-DEV-DSP2-1": {
"Preferred": 0,
"Mutes": {},
"Ports": {
"1": {
"PortState": "PASSIVE",
"PathType": "MULTICAST",
"Layer": "LAYER3",
"LinkDown": 0,
"PtpVersion": 1,
"InterfaceIndex": 2
},
"2": {
"PortState": "SLAVE",
"PathType": "MULTICAST",
"Layer": "LAYER3",
"LinkDown": 0,
"PtpVersion": 2,
"InterfaceIndex": 2
},
"3": {
"PortState": "DISABLED",
"PathType": "UNICAST",
"Layer": "LAYER3",
"LinkDown": 0,
"PtpVersion": 1,
"InterfaceIndex": 2
},
"4": {
"PortState": "DISABLED",
"PathType": "UNICAST",
"Layer": "LAYER3",
"LinkDown": 0,
"PtpVersion": 2,
"InterfaceIndex": 2
}
}
}
}
}Discovery
discovery.Get
media
Get all discovered Dante™ devices
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| discovery.Get | type | media | Type for Dante™ is “media” | >v1.8.50 |
| domain | ADHOC | Dante domain, may be used in future versions |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"discovery.Get","params":{"domain":"ADHOC","type":"media"}}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| Map of all Dante devices discovered |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":["SDM-DEV-XIN1-3","SDM-DEV-DSP2-1","SDM-DEV-DSP1-4"]}sdp
Get all discovered sdp sending devices, mostly these are AES67 compatible devices
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| discovery.Get | type | sdp | Type for AES67 is “sdp” | >v1.8.50 |
| domain | ADHOC | Dante domain, may be used in future versions |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"discovery.Get","params":{"domain":"ADHOC","type":"sdp"}}Reply
| Result | Comment | |
|---|---|---|
| Map of all Dante AES67 flows announced |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":["239.69.40.217@SDM-Test","239.69.40.179@SDM-Foo"]}Server
This section describes the communication protocol between the control system and SDM
rpc.serverInfo
Get all supported RCP methods
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rpc.serverInfo | >v1.8.50 |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"rpc.serverInfo"}Reply
| Result | Key | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| methods | All supported methods that can be used by a 3rd party control system | |
| counters | Server counters | |
| startTime | Server start time |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": {
"methods": ["config.Create", "discovery.Get", "monitor.Get", "preset.Recall", "routing.Create", "routing.Delete", "routing.Get", "routing.Subscribe", "sdm.Get", "system.Get", "system.Set"],
"usesContext": false,
"counters": {
"rpc.bytesRead": 50,
"rpc.requests": 1
},
"maxValue": {
"rpc.bytesRead": 50
},
"startTime": "2021-04-22T06:19:41.709283225Z"
}
}Routing
routing.Get
rxchannels
Get all received channels from a Dante™ device
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| routing.Get | name | string | Name of the device | >v1.8.50 |
| component | rxchannels | >v1.8.50 | ||
| domain | ADHOC | Dante domain, may be used in future versions |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":2,"method":"routing.Get","params":{"name":"SDM-DEV-DSP1-4","domain":"ADHOC","component":"rxchannels"}}Reply
| Result | Key | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| channels (map) | Receiving channels 1-x | |
| canonicalName | Channel canonical name | |
| label | Channel label name | |
| subscriptedLabel | Channel label from channel that is received | |
| subscriptedDevice | Device name from which the channel is received | |
| Name | Device name |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"result": {
"channels": {
"1": {
"canonicalName": "Zone_Channels-Ch1",
"label": "Zone_Channels-Ch1",
"subscriptedLabel": "NONE",
"subscriptedDevice": "NONE"
},
"21": {
"canonicalName": "Zone_Channels-Ch21",
"label": "Zone_Channels-Ch21",
"subscriptedLabel": "Source_Channels-Ch45",
"subscriptedDevice": "SDM-DEV-DSP1-4"
}
},
"Name": "SDM-DEV-DSP1-4"
}
}routing.Get
txchannels
Get all sent channels from a Dante™ device
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| routing.Get | name | string | Name of the device | >v1.8.50 |
| component | txchannels | >v1.8.50 | ||
| domain | ADHOC | Dante domain, may be used in future versions |
{"jsonrpc": "2.0","id":2,"method": "routing.Get","params":{"name":"SDM-DEV-DSP1-4","domain":"ADHOC","component":"txchannels"}}Reply
| Result | Key | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| channels (map) | Transmitting channels 1-x | |
| canonicalName | Channel canonical name | |
| labels | Channel labels (map) | |
| Name | Device name |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"result": {
"channels": {
"1": {
"canonicalName": "01",
"labels": {
"0": "Source_Channels-Ch1"
}
},
"10": {
"canonicalName": "10",
"labels": {
"0": "Source_Channels-Ch10"
}
}
},
"Name": "SDM-DEV-DSP1-4"
}
}txflows
Get all sent flows from a Dante™ device
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| routing.Get | name | string | Name of the device | >v1.8.50 |
| component | txflows | >v1.8.50 | ||
| domain | ADHOC | Dante domain, may be used in future versions |
{"jsonrpc": "2.0","id":2,"method": "routing.Get","params":{"name":"SDM-DEV-DSP1-4","domain":"ADHOC","component":"txflows"}}Reply
| Result | Key | Sub | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| flows (map) | Transmitting flows 1-x | ||
| name | Flow name | ||
| Slots | Flow slots (map) | ||
| ChannelName | Name of the channel | ||
| ChannelID | Channel ID | ||
| ID | Flow ID | ||
| Interfaces | How many interfaces are used for this flow | ||
| Addresses | Flow Addresses (map) | ||
| Addr | Multicast IP Address | ||
| Port | Port | ||
| FlowClass | 1=Dante&trade, 2,3=AES67, 4=RTP | ||
| Aes67OrigAddress | AES67 original address if AES67 | ||
| Transport | AES67 or Dante | ||
| DestDevice | Destination device the flow flows to if unicast | ||
| Flow ID | Destination flow name on the device the flow flows to if unicast | ||
| Name | Device name |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"result": {
"flows": {
"0": {
"name": "Source_Channels",
"indexes": null,
"Slots": {
"0": {
"ChannelName": "Source_Channels-Ch1",
"ChannelID": 1
},
"1": {
"ChannelName": "Source_Channels-Ch2",
"ChannelID": 2
}
},
"ID": 1,
"Interfaces": 1,
"Addresses": {
"0": {
"Addr": "239.255.105.118",
"Port": 4321
}
},
"FlowClass": 1,
"Aes67OrigAddress": "",
"Transport": "DANTE",
"DestDevice": "",
"DestFlow": ""
}
},
"Name": "SDM-DEV-DSP1-4"
}
}rxflows
Get all received flows from a Dante™ device
Request
| Method | Param | Value | Comment | Supported Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| routing.Get | name | string | Name of the device | >v1.8.50 |
| component | rxflows | >v1.8.50 | ||
| domain | ADHOC | Dante domain, may be used in future versions |
{"jsonrpc": "2.0","id": 2,"method": "routing.Get","params":{"name":"SDM-DEV-DSP1-4","domain": "ADHOC","component":"rxflows"}}Reply
| Result | Key | Sub | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| flows (map) | Transmitting flows 1-x | ||
| name | Flow name | ||
| Slots | Flow slots (map) | ||
| Channels (map) | Map of the channels received in this flow slot | ||
| ID | Flow ID | ||
| Interfaces | How many interfaces are used for this flow | ||
| Addresses | Flow Addresses (map) | ||
| Addr | Multicast IP Address | ||
| Port | Port | ||
| FlowClass | 1=Dante&trade, 2,3=AES67, 4=RTP | ||
| Aes67OrigAddress | AES67 original address if AES67 | ||
| Transport | AES67 or Dante | ||
| Name | Device name |
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"result": {
"flows": {
"0": {
"name": "",
"Slots": {
"0": {
"Channels": {
"0": "Zone_Channels-Ch51"
}
},
"1": {
"Channels": {
"0": "Zone_Channels-Ch52"
}
}
},
"ID": 1,
"Interfaces": 1,
"Addresses": {
"0": {
"Addr": "239.69.40.217",
"Port": 5004
}
},
"FlowClass": 1,
"Aes67OrigAddress": "",
"Transport": "Dante"
},
"2": {
"name": "",
"Slots": {
"0": {
"Channels": {
"0": "Zone_Channels-Ch1"
}
},
"1": {
"Channels": {
"0": "Zone_Channels-Ch2"
}
}
},
"ID": 3,
"Interfaces": 1,
"Addresses": {
"0": {
"Addr": "239.69.2.156",
"Port": 5004
}
},
"FlowClass": 2,
"Aes67OrigAddress": "239.69.2.156",
"Transport": "AES67"
}
},
"Name": "SDM-DEV-DSP1-4"
}
}routing.Create
Create a new routing from a Dante™ or AES67 device to a a Dante™ device
Request
| Method | Param | Sub-table key | Comment | Supported Versions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| routing.Create | tx | channelName | Source channel label/name/canonical name | >v1.8.50 | |
| nodeName | Source node name | >v1.8.50 | |||
| aesFlowName | Source flow name | >v1.8.67 | |||
| aesFlowSlotID | Slot ID of flow | >v1.8.67 | |||
| rx | destination | Destination channel label/name/canonical name | >v1.8.50 | ||
| nodeName | Destination node name | >v1.8.50 |
Include node name to create a new routing
Even if it is allowed to create a new routing only based on the channel name, it is better to include the device name. The changeover is done more quickly
{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id":1,
"method":"routing.Create",
"params":[
{
"rx":{
"channelName":"Zone_Channels-Ch10"
},
"tx":{
"channelName":"Source_Channels-Ch10"
}
}
]
}{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id":1,
"method":"routing.Create",
"params":[
{
"rx":{
"nodeName":"SDM-DEV-DSP1-4",
"channelName":"Zone_Channels-Ch10"
},
"tx":{
"nodeName":"SDM-DEV-DSP1-4",
"channelName":"Source_Channels-Ch10"
}
}
]
}{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id":1,
"method":"routing.Create",
"params":[
{
"tx":{
"nodeName":"",
"channelName":"Zone_Channels-Ch10"
},
"tx":{
"aesFlowName":"239.69.40.217@Test-BTI",
"aesFlowSlotID":1
}
},
{
"rx":{
"nodeName":"",
"channelName":"Zone_Channels-Ch11"
},
"rx":{
"aesFlowName":"239.69.40.217@Test-BTI",
"aesFlowSlotID":2
}
}
]
}Reply
| Result | ||
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":null}routing.Delete
Delete a routing from a Dante™ or AES67 device to a a Dante™ device
Request
| Method | Param | Sub-table key | Comment | Supported Versions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| routing.Delete | rx | Destination | Destination channel label/name/canonical name | >v1.8.50 | |
| nodeName | Destination node name | >v1.8.50 |
Include node name to delete routing
Even if it is allowed to delete a routing only based on the channel name, it is better to include the device name. The disconnect is done more quickly
{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id":1,
"method":"routing.Delete",
"params":[
{
"RX":{
"ChannelName":"Zone_Channels-Ch11"
}
}
]
}{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id":1,
"method":"routing.Delete",
"params":[
{
"RX":{
"NodeName":"SDM-DEV-DSP1-4",
"ChannelName":"Zone_Channels-Ch11"
}
}
]
}Reply
| Result | ||
|---|---|---|
| null | null means acknowledged, no error |
{"jsonrpc": "2.0","id": 1,"result": null}Diagnose
SDM can help you diagnose several shortcomings in the network
IGMP Querier
Dante™ networks do need a correctly set IGMP Querier
- A switch need to broadcast a IGMP Querier every 30 seconds
- The sending switch must be not on the periphere, ideally it’s the one switch which is in the destination path of most of the multicasts. Usually a core switch
- IGMP Querier version must be V3 if only Dante™ devices are used, V2 if Dante™ and AES67 devices are used
The status of a IGMP Querier can be sniffed on the page Diag > IGMP QUerier
Once you selected the Interface capture begins
What to check?
- Is there something printed at all?
- Is there something printed after 70 seconds?
- Compare timestamps, is the querier appearing every 30 seconds?
- Is the IP address really the designated switch?
Dante™ Clocking
Dante™ networks use PTP for time synchronization.
- A correctly set IGMP Querier is needed (see above)
- Switches need eventually a configuration on how to deal with PTP
- In larger networks QOS need to be setup
The clocking status of all dante devices can be sniffed on the page Diag > Dante Clocking
What to check?
- One Master (Leader) clock
- After a while all Dante™ devices must be listed
Licensing
Every SDM needs a valid license to work. SDM confirms validity online at least every 7 days
Status
The status of the license can be viewed on the status page SDM > license
A detailed explanation of the reported fields can be here
Software
Update
Updates can be uploaded and activated under Help > Update
Online Update
Once online updates are activated SDM checks for updates for SDM and associated services, as well as for operating system updates
- There is no quarantee that an update is executed immediately. It may take up to 24 hours.
- Online updates do need an Internet connection!
- Updates might be large, ensure that the Internet connection is fast and not metered
- If an update should be executed in a maintenance window please contact nexgentec and make sure your software subscription NGT-SDM-APU2 is active
Offline Update
- For SDM and associated services we may publish software updates that can be uploaded directly. Once uploaded they are processed in backgrouns. Stay patience.
Downloads
Nothing to see here yet
Specifications
Specifications
Welcome to the Firmware section!
If you are not redirected automatically, click here.
Subsections of Specifications
General
Connections
| Connector | |
|---|---|
| Ethernet | |
| Net 1 | Gigabit Ethernet (Intel i210AT) |
| Net 2 | Gigabit Ethernet (Intel i210AT) |
| Net 3 | Gigabit Ethernet (Intel i210AT) |
| Serial | |
| DB9 serial | Deactivated |
| Power | |
| Jack (2.5 mm) center positive | 12V DC, about 6 to 12W |
Environmental
| Power | 12V, 12W max |
| Heat Dissipation | Max 42 BTU / HR |
| Operating temp | 0°C – 60°C |
| Dimensions | L: 238mm, W: 208mm, H:44mm |
| Compliance | CE, ROHS |
| Weight | 900g |
CAD step file
Network
Network
None of the specified protocols or ports, nor the communication can be changed. (except port configurable in sdm.config )
Its wise to review the lists and allow SDM to communicate with all ports and protocols defined.
SDM will not work without any of the ports and protocols defined.
SDM need frequent internet access Details
Ports used by Dante™
Depending on the configuration physical ports, VLAN or bridges used for Dante™ may use these ports for communication.
| Address | Port | Usage | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 239.255.0.0/16 | 4321 | ATP Multicast Audio | Multicast |
| 239.69.0.0/16 | 5004 | AES67 Multicast Audio (RTP / AVP port) | Multicast |
| 224.0.1.129-132 | 319, 320 | PTP | Multicast & Unicast when using DDM |
| 224.0.0.251 | 5353 | mDNS | Multicast |
| 224.0.0.230 – 233 | 8700 – 8708 | Multicast Control and Monitoring | Multicast |
| 239.254.1.1 | 9998 | Logging | Multicast |
| 239.254.3.3 | 9998 | PTP Logging (if enabled) | Multicast |
| 239.254.44.44 | 9998 | Logging | Multicast |
| 239.255.255.255 | 9875 | SAP (AES67 discovery) | Multicast |
| UDP | 28800, 28700-28708 | Via control & monitoring | Unicast |
| UDP | 38800, 38700-38708 | DVS control & monitoring | Unicast |
| UDP | 14336 -14591 | Unicast Audio [Excluding Via] | Unicast |
| UDP | 34336-34600 | Unicast Audio [Via Only] | Unicast |
| UDP | 4440, 4444, 4455 | Audio Control [Excluding Via] | Unicast |
| UDP | 24440, 24441,24444,24455 | Audio Control | Unicast |
| UDP | 4777 | Via Control | Unicast |
| TCP | 4777 | Via Websocket | Unicast |
| UDP | 8850,28900, 24445 | Via control & Monitoring | Unicast |
| UDP | 8850,38900,8899 | DVS control & monitoring | Unicast |
| UDP | 8000 | Dante Domain Manager Device Port | Unicast |
| UDP | 8001 | Dante Millau Device Proxy | Unicast |
| UDP | 8002 | Dante Lock Server | Unicast |
| UDP | 8751 | Dante Controller metering port | Unicast |
| UDP | 8800 | Control & Monitoring | Unicast |
| TCP | 8753 | mDNS clients | Unicast |
| TCP | 16100-16131 | HDCP Authentication for Video Endpoints | Unicast |
| UDP | 61440-61951 | FPGA level audio flow keepalive | Unicast |
Ports used by SDM for Control
Depending on the configuration physical ports, VLAN or bridges used for control may use these ports for communication.
| Protocol | Source IP | Source Port | Destination IP | Destination Port | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HTTP | All | all | Control interface Address | Port configured in sdm.config | Control over HTTP |
| TCP | All | all | Control interface Address | Port configured in sdm.config | Control over TCP |
General ports used by OS and services (Mandatory ports)
| Protocol | Source IP | Source Port | Destination | Destination Port | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCP | All interfaces | all | l02.genesis-technologies.ch | 443 | nexgentec™ license service |
| UDP | All interfaces | all | swan.genesis-technologies.ch | 443 | nexgentec™ maintenance service |
| TCP | All interfaces | all | DNS service | 53 | DNS |
| UDP | All interfaces | all | DNS service | 53 | DNS |
| UDP | All interfaces | all | NTP service | 123 | NTP |
| TCP | All interfaces | all | www.app.qbee.io | 443 | 3rd party maintenance service |
Internet access
Why does SDM need Internet access?
- Since we live in an unpredictable world we have to protect our paying customers. Therefore we check the SDM license at least every 7 days. This avoids software piratery and allows us getting enough financial resources to further develop sdm and provide future support.
- We do monitor all relevant parameters for continuous operation. Software is always written by humans and may contain bugs like a memory leak. Without monitoring we are not able to act before you even take a notice that there is an issue.
How frequent does SDM need Internet access?
At least every 7 days a successful license check must be possible. If not SDM stops working
What if I do not agree?
Send the SDM device back to where you bought it. We have no intention to change our mind.
What if I think that this could be done better?
Sure we listen, just give us a call.
Time Server access
Why does SDM need a valid time and therefore access to a ntp time server?
- Without a valid time all license checks will fail and SDM will stop working
- Running a computer whithout correct time is in general a bad idea
How frequent does SDM need time server access?
- We do recommend that SDM has continued access to a NTP time server
- At least every 7 days a successful time sync should be possible
What if no ntp time server is accessible?
- Then the operation of SDM is not guaranteed.
User Profile
Several user settings can be made on the Profile page.
Password
To protect the access to the web interface another password can be set
Do not lose the password nexgentec customer support must be contacted to reset the password.
Settings
Time format
The time format for the web interface
Copyrights
SDM and associated software may use 3rd party code with their given copyrights. For compliance reasons we are required list them here.
creachadair/jrpc2
Copyright (c) 2017, Michael J. Fromberger
All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this
list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
3. Neither the name of the copyright holder nor the names of its contributors
may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software
without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY,
OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.eiannone/keyboard/
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (C) 2012 termbox-go authors
Copyright (c) 2015 Emanuele Iannone
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.fsnotify/fsnotify/
Copyright (c) 2012 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
Copyright (c) 2012-2019 fsnotify Authors. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
met:
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer
in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
distribution.
* Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its
contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
"AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.google/uuid/
Copyright (c) 2009,2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
met:
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer
in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
distribution.
* Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its
contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
"AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.struCoder/pidusage
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2017 David 大伟
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.golang.org/x/*
Copyright (c) 2009 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
met:
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer
in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
distribution.
* Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its
contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
"AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.gopkg.in/gcfg
Copyright (c) 2012 Péter Surányi. Portions Copyright (c) 2009 The Go
Authors. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
met:
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer
in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
distribution.
* Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its
contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
"AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.natefinch/lumberjack
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2014 Nate Finch
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.